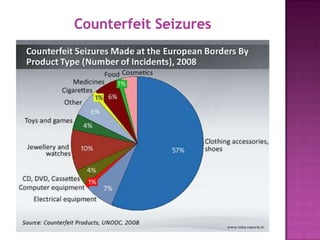
The document discusses counterfeit goods and defines a counterfeit as an unauthorized copy that is not produced by the original manufacturer and does not meet their design and quality standards. It notes that the spread of counterfeit goods, particularly fashion items, has grown significantly globally. Authorities expect counterfeiting to remain high for the next six years, with 20% of athletic merchandise estimated to be counterfeit. The counterfeit industry is clustered in certain regions of China known for illicit production.