Embed presentation
Downloaded 41 times



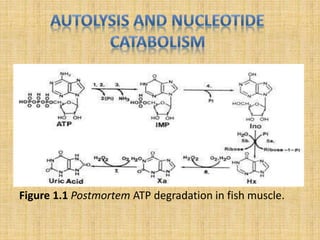

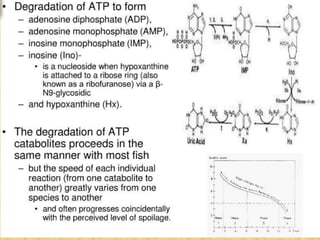

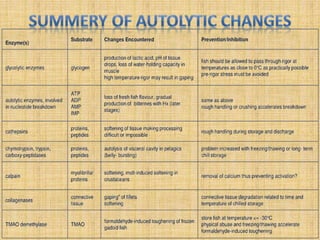


Autolysis is the self-digestion process that occurs in fish after death. There are two main types of fish spoilage - bacterial and enzymatic. In some fish species like squid and herring, enzymatic changes caused by autolysis precede and dominate over bacterial spoilage when the fish are chilled. Autolysis contributes to quality loss in fish in addition to spoilage from microbes. The K-value index provides a measurement of freshness based on autolytic changes, with higher K-values indicating lower freshness levels.









