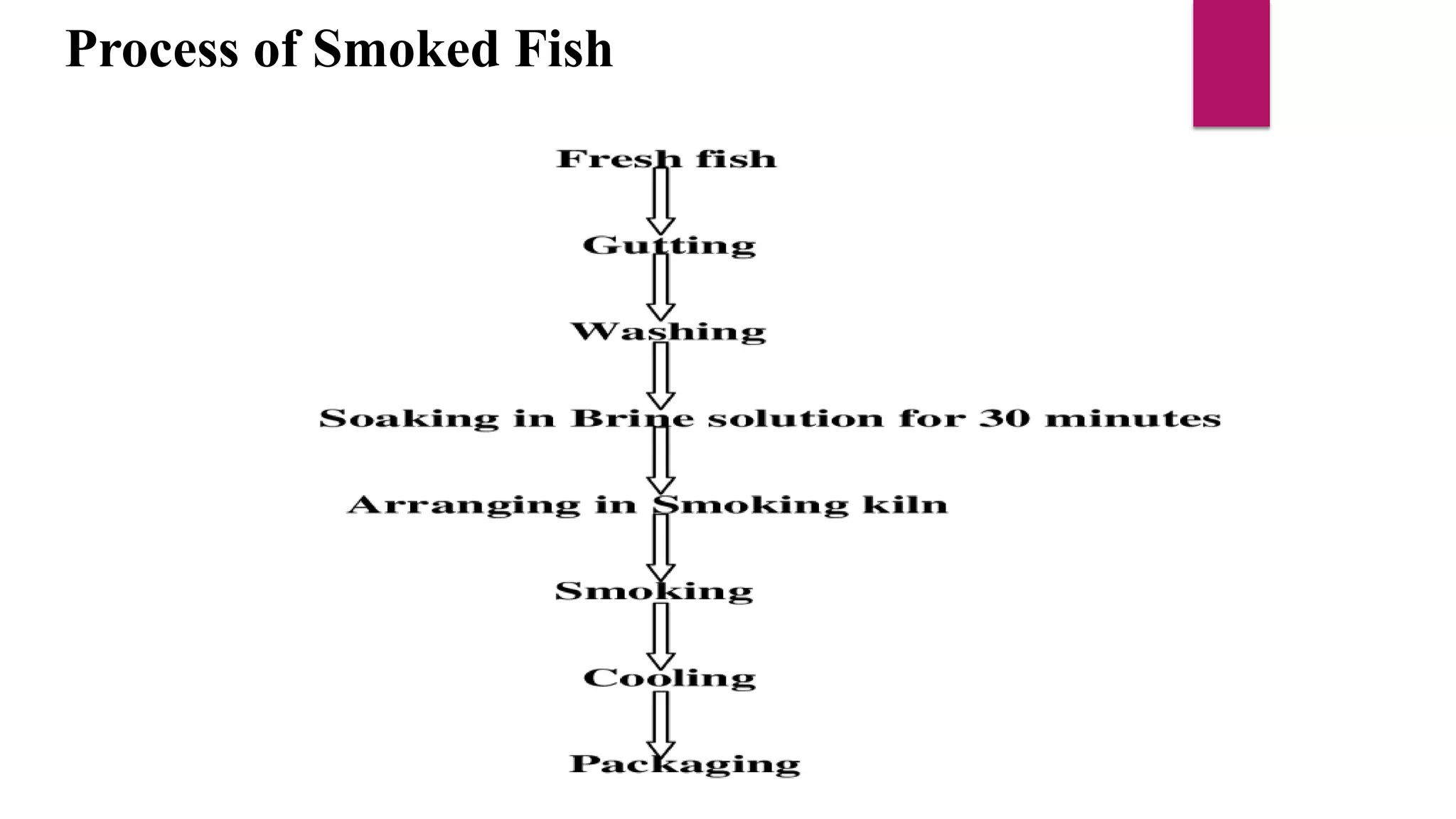
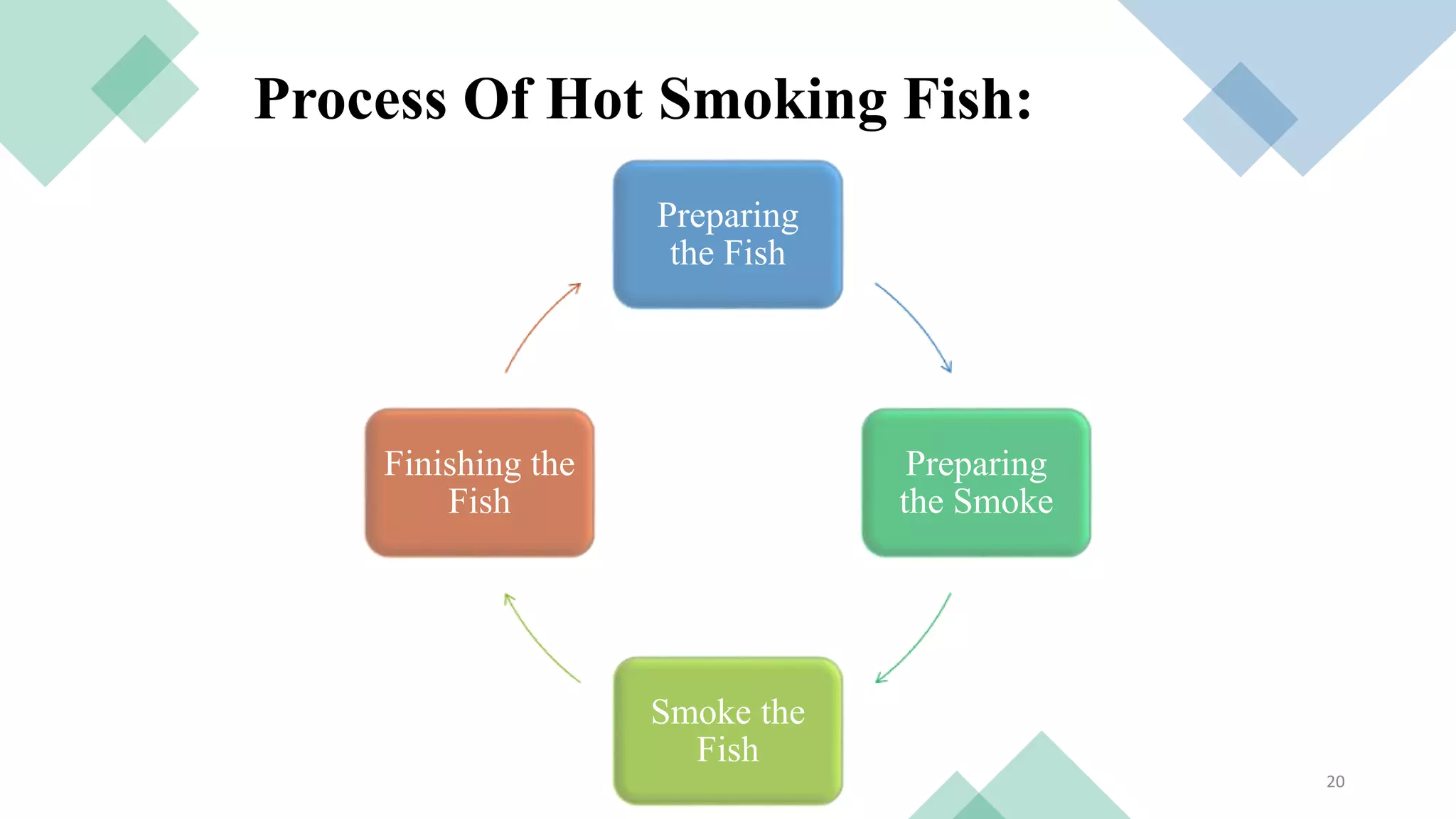
Smoking is an ancient method of food preservation that involves exposing fish to wood smoke. There are two main smoking methods - traditional hot smoking involves hanging fish over smoldering wood at temperatures over 120°F, while cold smoking is done below 90°F. Both methods preserve fish through moisture removal, addition of smoke compounds that inhibit bacteria, and imparting a smoky flavor. Hot smoking allows for longer storage times of several weeks in the refrigerator or months in the freezer. Cold smoking provides preservation without cooking but requires additional safety steps. While smoking adds flavor and nutrients, it can also produce carcinogens if consumed in large amounts.