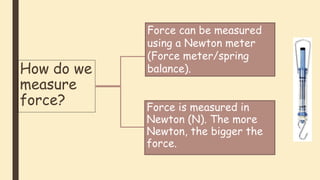
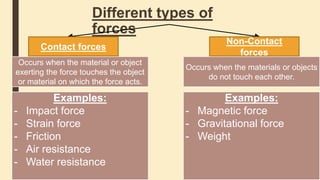
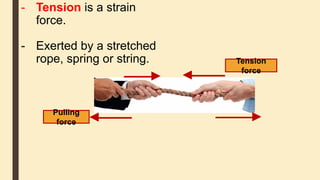
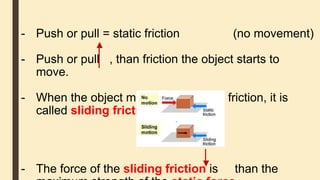
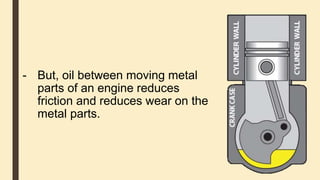
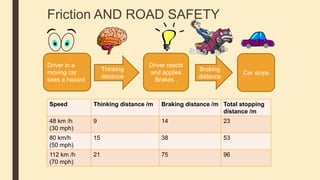
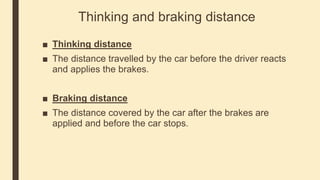
Forces can cause objects to move, stop, change speed or direction. There are two main types of forces - contact forces which act when objects touch, and non-contact forces like gravity and magnetism which act over a distance. Friction is a contact force that opposes motion between surfaces in contact. Reducing friction, through lubricants or streamlining, can reduce resistance to motion. Air and water resistance are non-contact forces caused by fluids pushing back on objects moving through them. The shape of objects can be designed to minimize resistance and maximize speed.