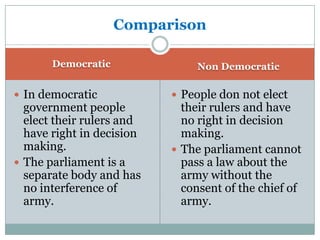
This document provides information on democracy and dictatorship. It defines democracy as a form of government where rulers are elected by the people. Key features of democracy include free and fair elections, equality of votes, and protection of citizens' rights. Dictatorships are defined as rule by one person or small group, with total control over the government. The document also discusses the merits of democracy like accountability and methods like direct democracy versus representative democracy.