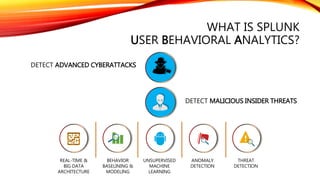
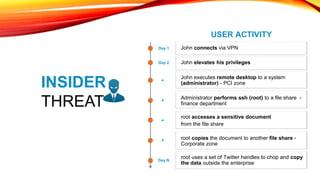
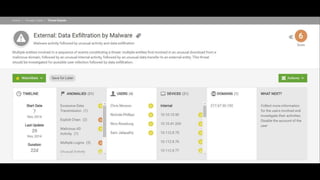
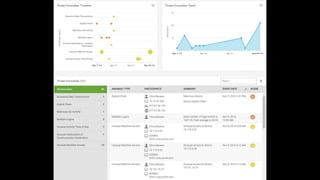
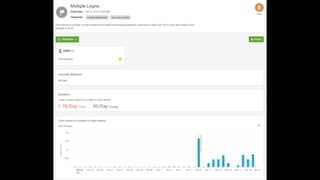
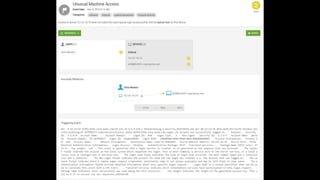
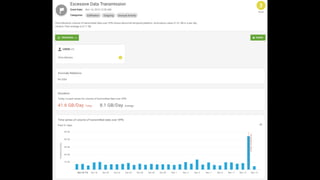
This document discusses user behavioral analytics and machine learning for threat detection. It summarizes that legacy security information and event management (SIEM) technologies are not adequate for detecting insider threats and advanced adversaries. It then describes how user behavioral analytics uses machine learning to develop multi-entity behavioral models across users, applications, hosts, and networks to detect anomalous behavior indicative of insider threats or advanced cyberattacks. Contact information is provided for the security consultant presenting on this topic.



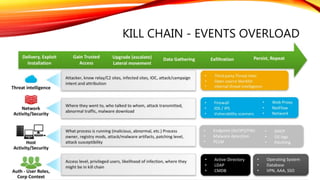
![Legacy SIEM type technologies aren’t
enough to detect insider threats and
advanced adversaries and are poorly
designed for rapid incident response.
[SIEM - Security Information & Event Management]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8splunkuba-machinelearningforthreatdetectionharrymclaren-160514174302/85/Machine-Learning-for-Threat-Detection-4-320.jpg)