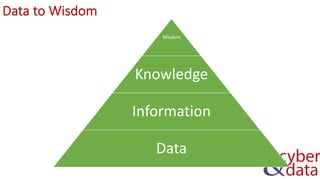
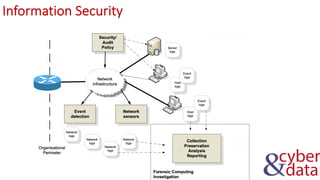
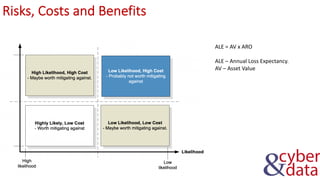
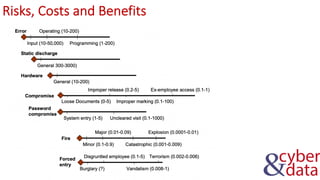
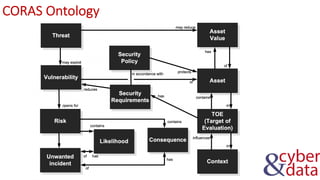
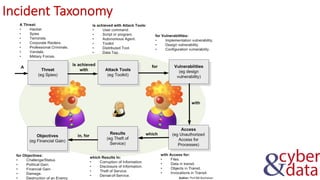
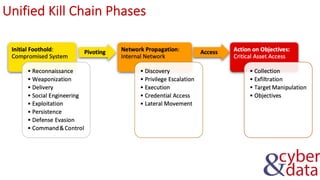
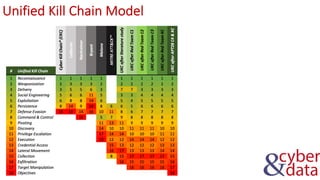
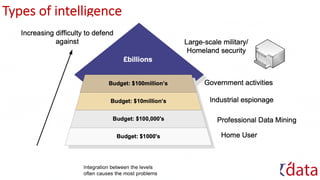
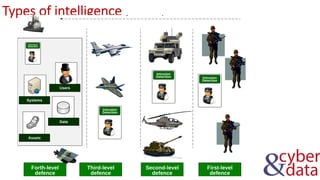
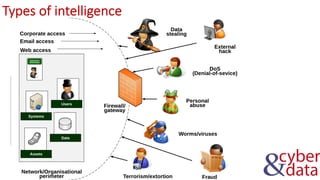
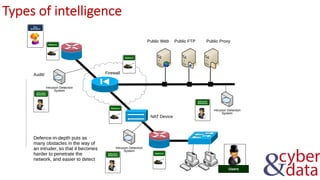
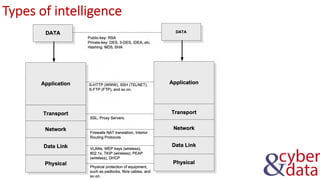
The document discusses information security, defense mechanisms, and risks. It outlines concepts like data, information, knowledge and wisdom. It describes kill chain models used to investigate security incidents and defenses that use layers like deterrence, detection, protection, reaction, recovery, and auditing. The document also covers risks, costs, benefits, and harm from physical, economic, psychological and reputational impacts.