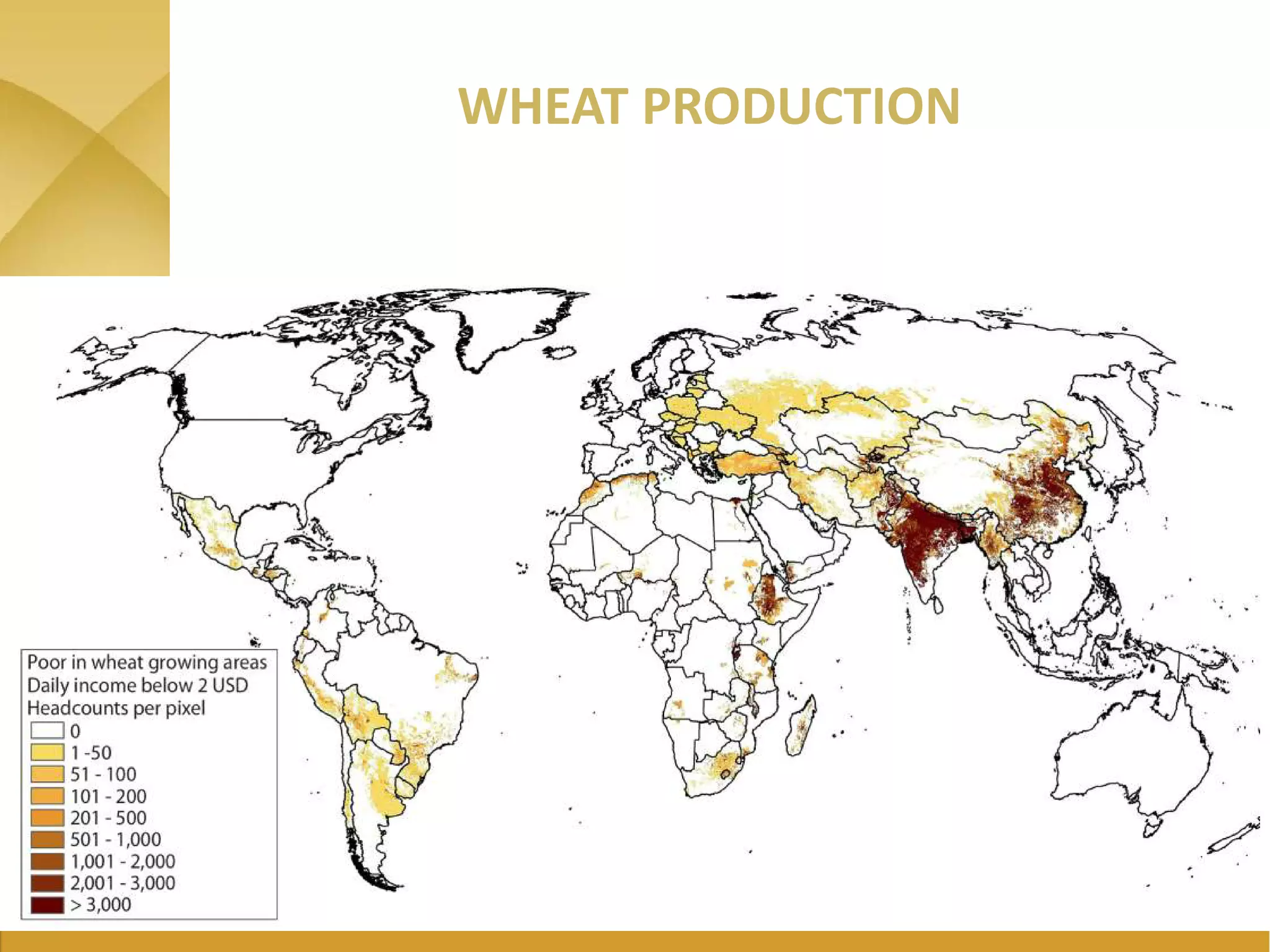
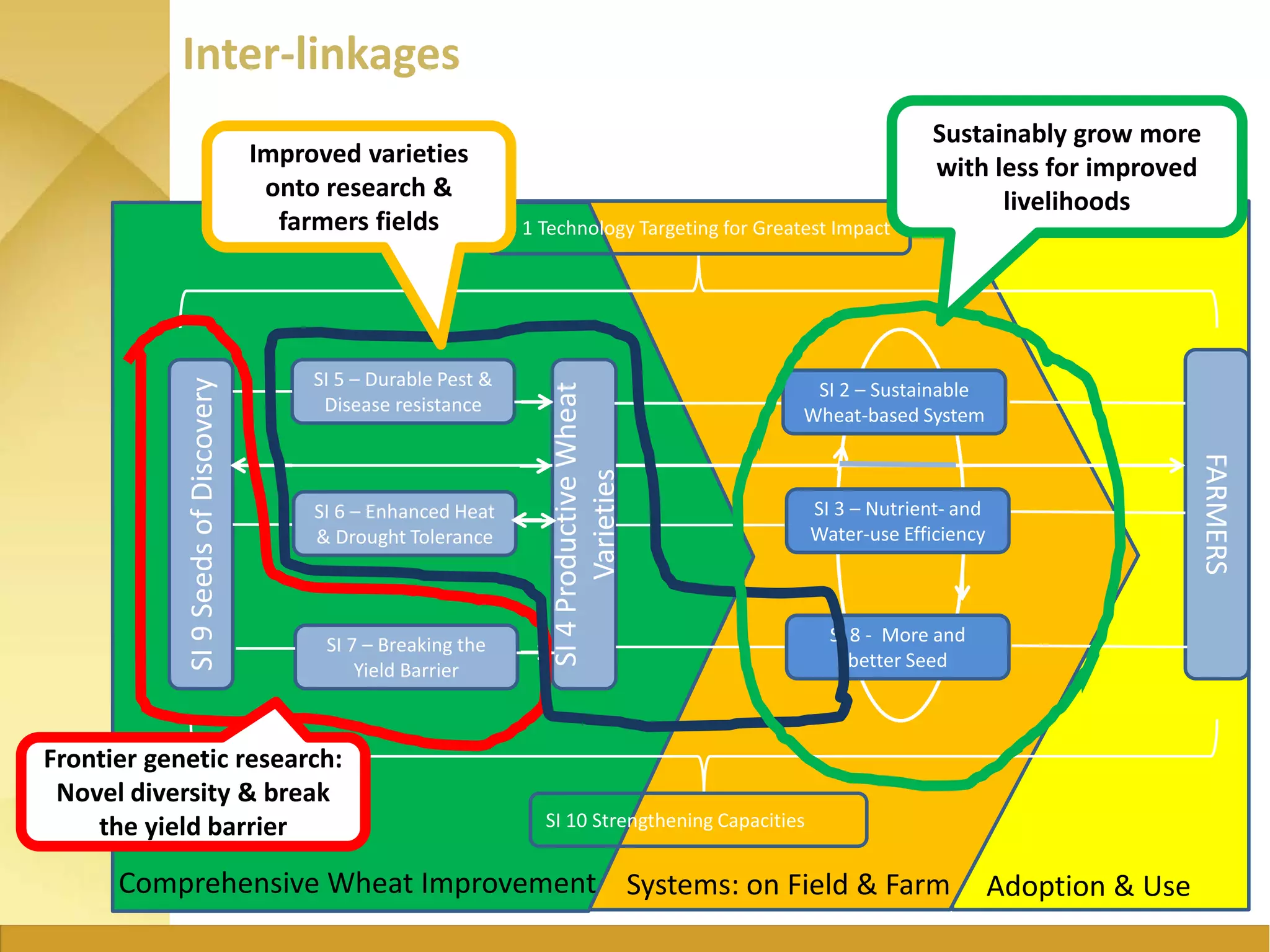
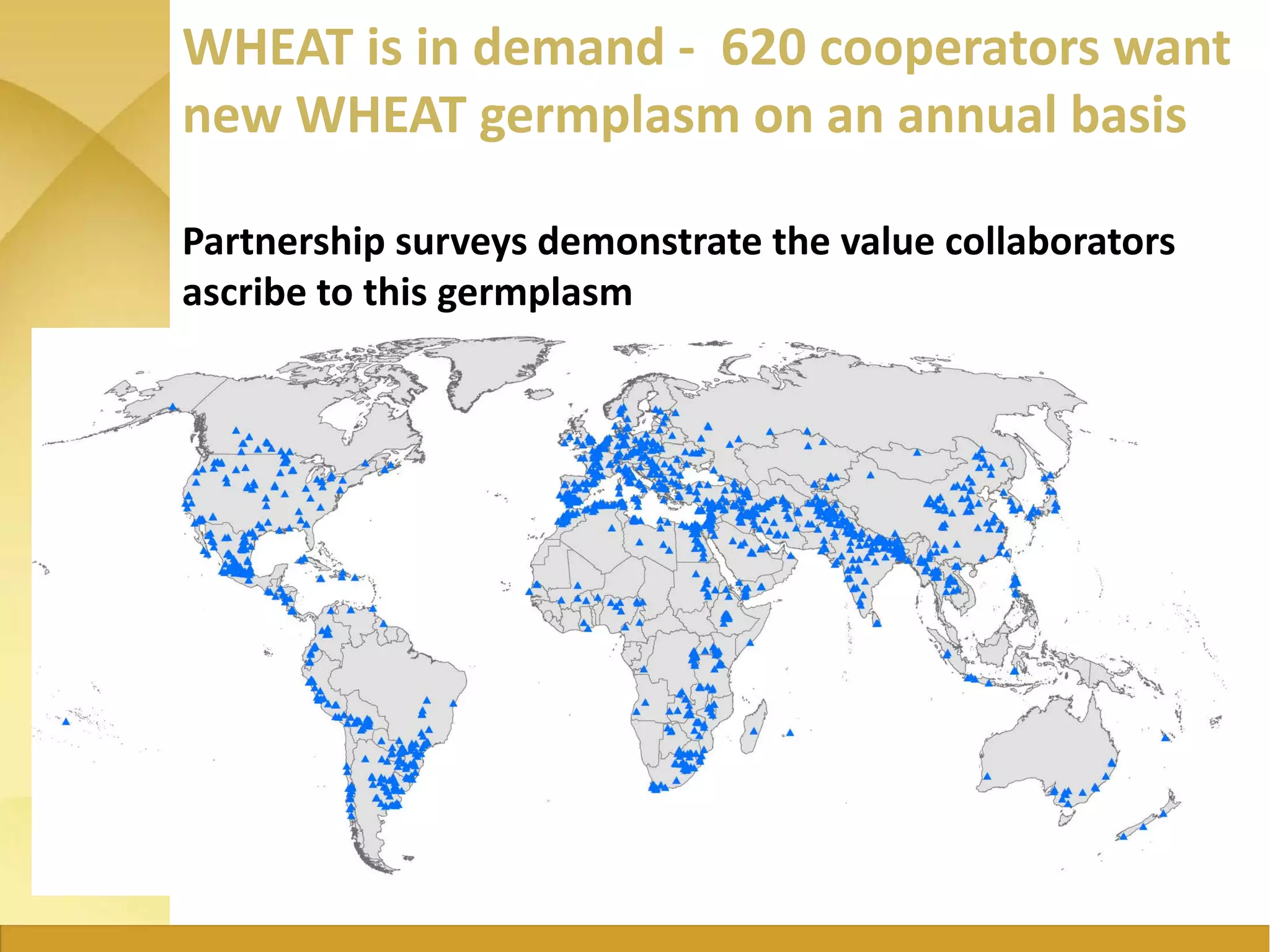
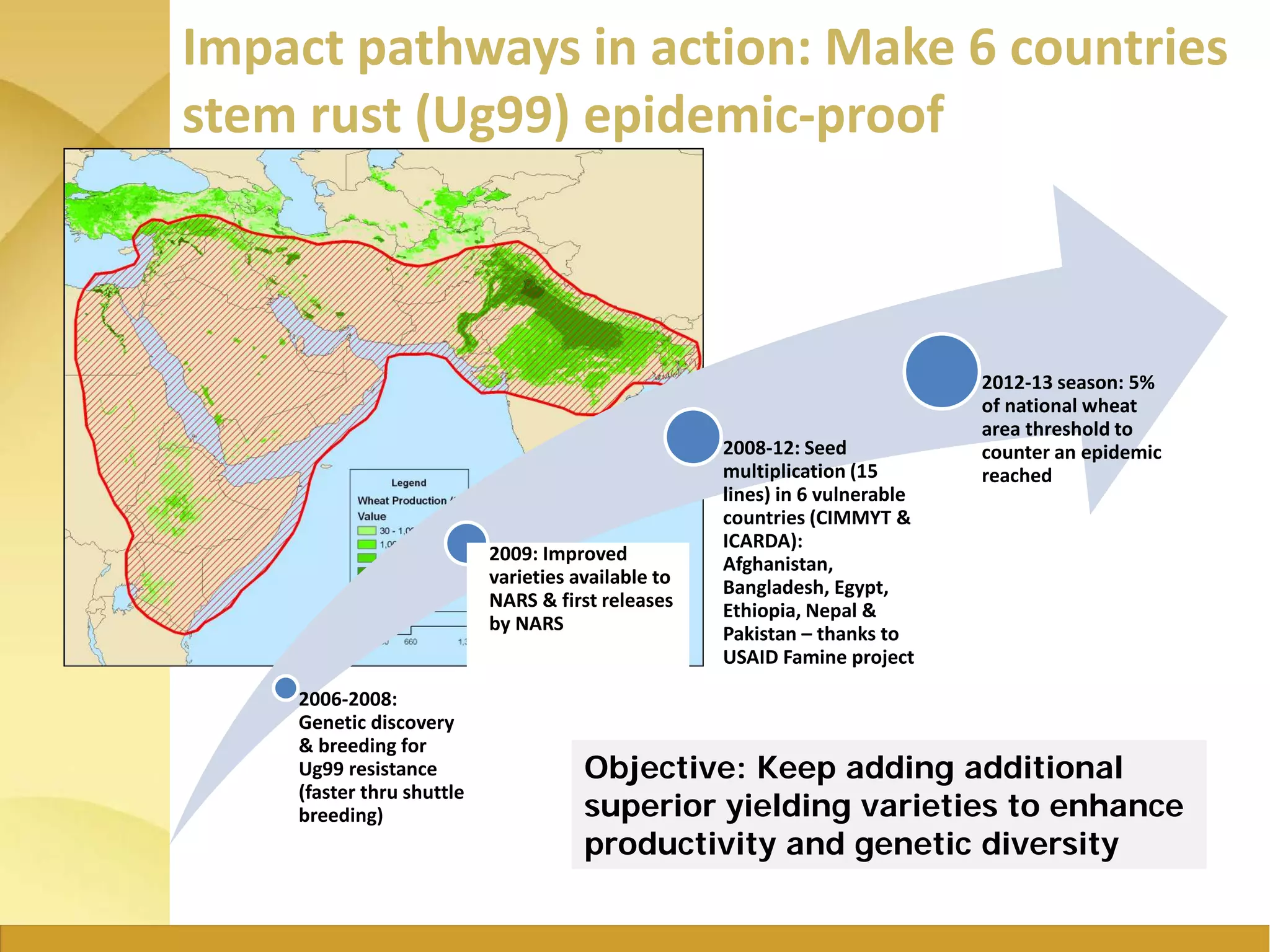
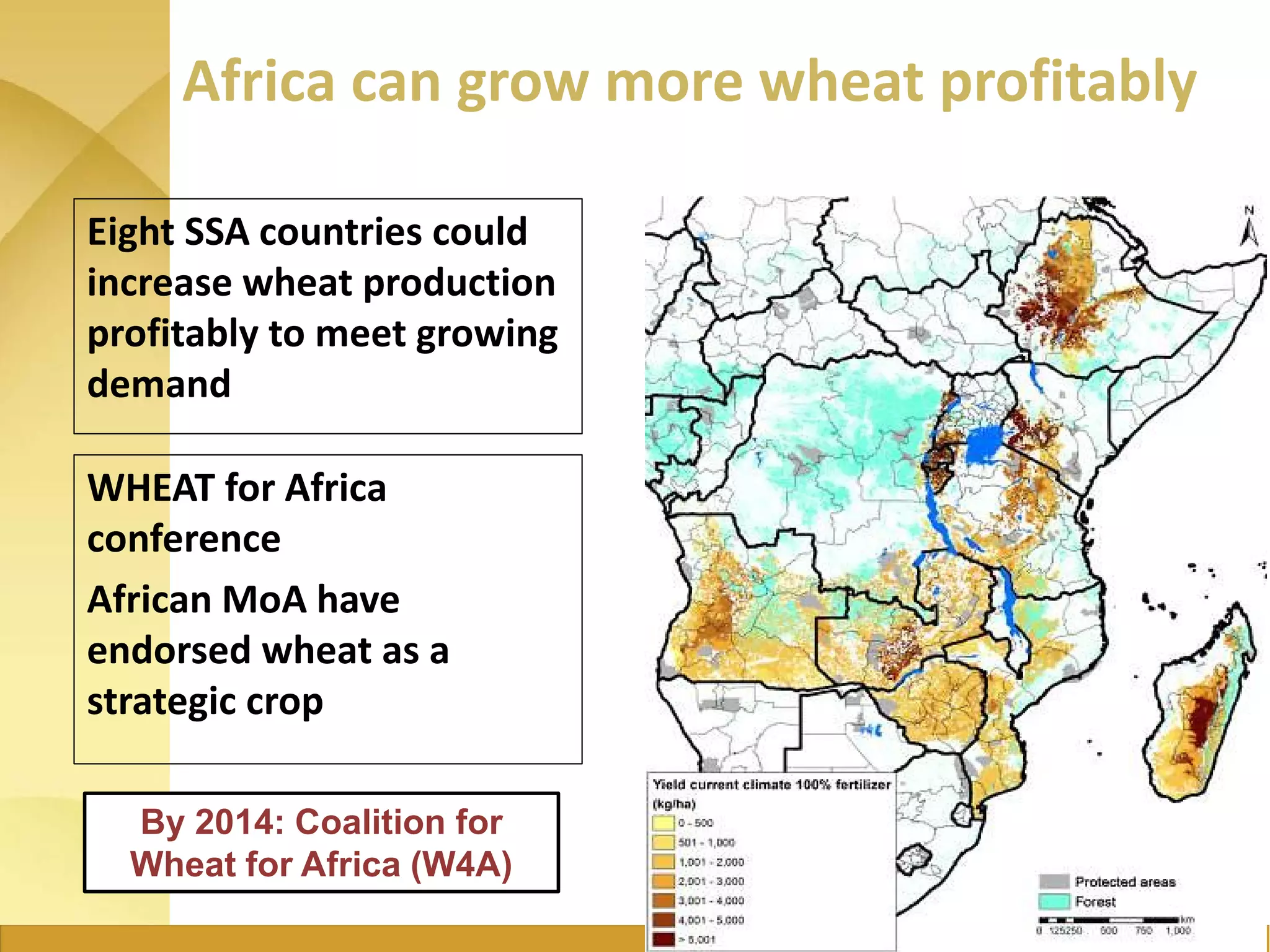
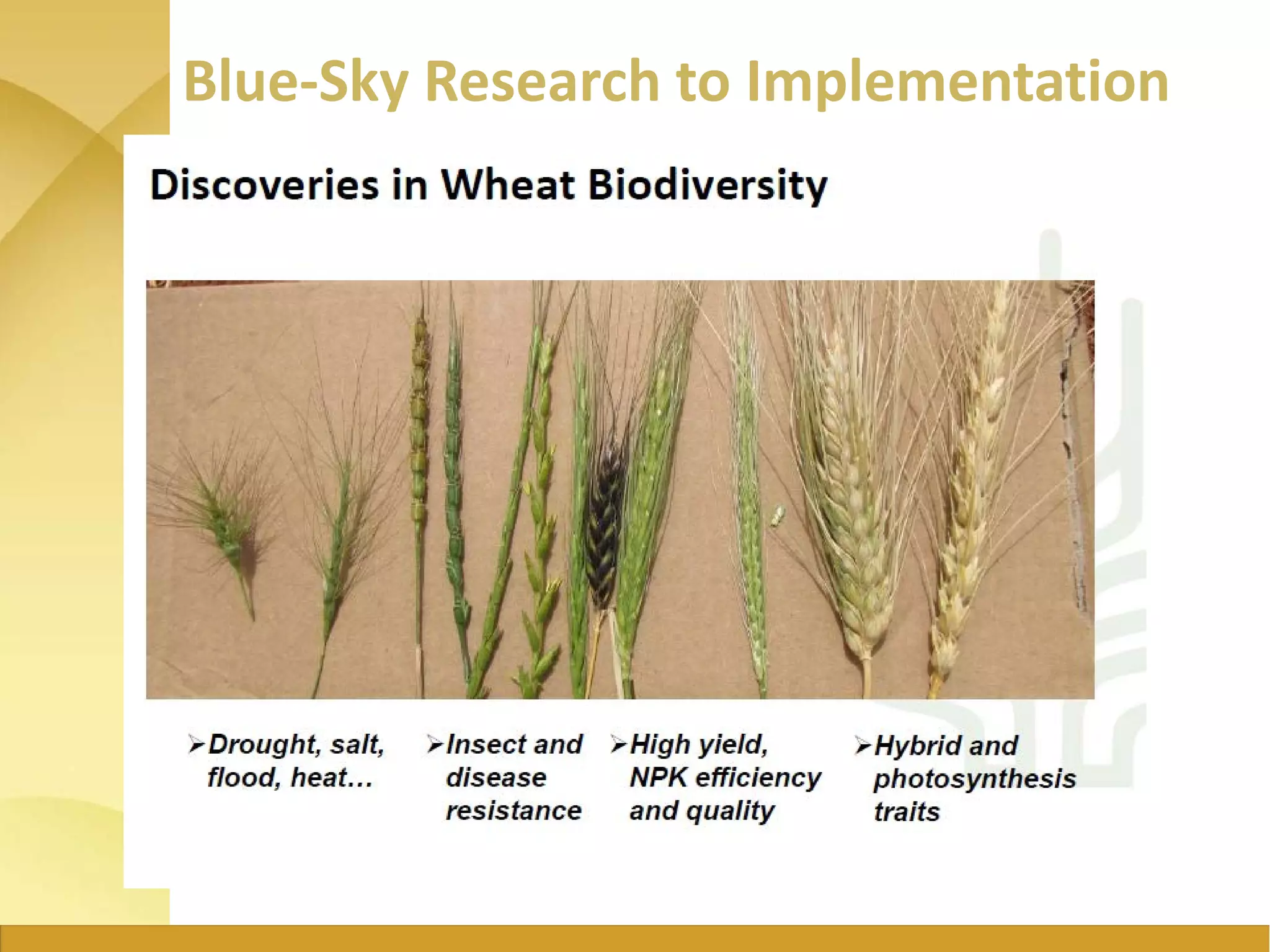
The document outlines the strategic initiatives of the Wheat CRP, which include developing wheat varieties with increased productivity, disease and pest resistance, drought tolerance, and nutrient efficiency. The goals are to increase wheat production value by $7.5 billion by 2030, feed an additional 460 million consumers, and break the wheat yield barrier by 50%. Key activities include developing improved varieties, disseminating seeds in vulnerable countries to prevent stem rust epidemics, and promoting wheat growth in Africa. The CRP measures success based on more sustainable farming systems, increased developing country productivity, reduced poverty and malnutrition, improved access to technologies, and strengthened agricultural capacity.