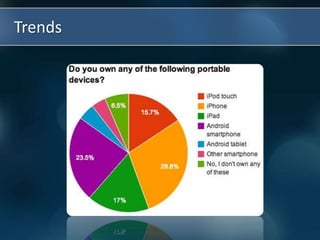
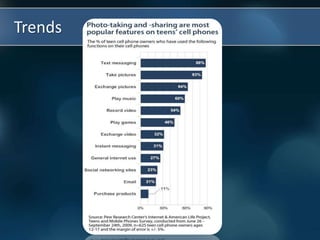
Mobile learning, or m-learning, refers to learning that takes advantage of portable technologies and can occur anywhere. With the rise of mobile devices and a new digital generation of students, m-learning allows for anytime, anywhere interaction with tutors, other learners, and educational content. While m-learning provides benefits like increased student motivation and engagement, it also presents challenges such as potential distraction and cheating as well as issues with device compatibility and teacher training. For m-learning to be effective in schools, clear guidelines, cost analysis, and continued support are needed.