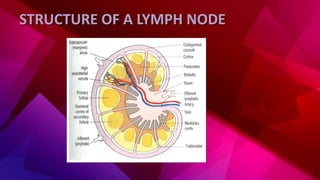
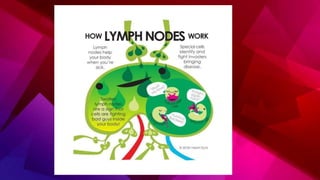
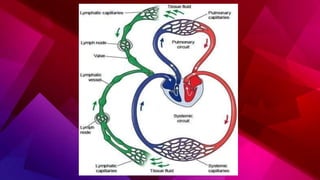
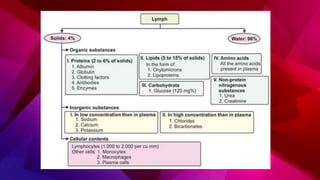
The lymphatic system transports lymph through lymph vessels and lymph nodes. Lymph nodes contain B and T lymphocytes and have three layers - cortex, paracortex, and medulla. Lymph enters through afferent vessels and exits through efferent vessels. When infected, lymph nodes swell to fight bacteria and toxins. Lymph is formed from tissue fluid, contains proteins and lipids, and returns about 120 mL to the blood per hour through the thoracic duct.