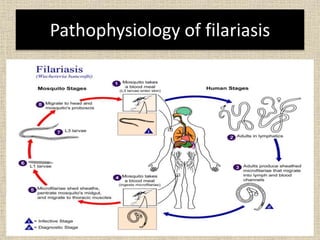
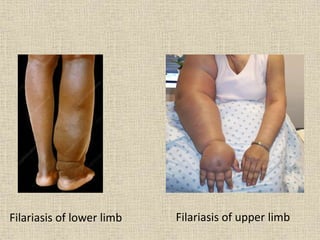
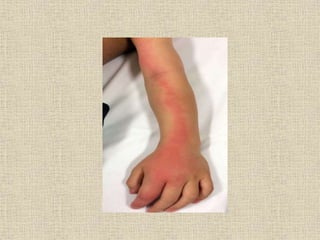
Lymphangitis is an inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, most often caused by bacterial infections like streptococci and staphylococci entering through the skin via wounds or insect bites. Filariasis, caused by parasitic worms transmitted by mosquitoes, is a common cause in certain regions. Symptoms include fever, skin redness along the path of the lymphatic vessels, and swollen lymph nodes near the infection site. Treatment involves antibiotics, pain medication, limb elevation, and physiotherapy to promote lymph drainage and prevent lymphedema.