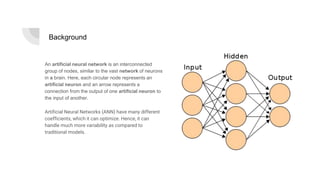
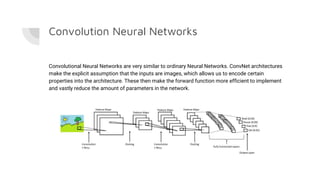
The document details a minor project by Surajit Das and Shreshth Saxena on the application of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for lung cancer prediction. It provides insights into the architecture of neural networks, the data used (2948 images), and the model development process, including hyperparameter tuning which achieved an accuracy of up to 97.51%. Significant acknowledgments are given to their professors for guidance throughout the project.










![The model was trained on different combinations of hyperparameters and the
performance in each case was recorded as below:
1.
epochs = [ 10,25]
batches = [50,100,104]
optimizers = ['SGD', 'adam']
Cross validation = 10
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 104, 'epochs': 25, 'optimizer': 'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 97.05%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-13-320.jpg)
![2.
epochs = [25,35]
batches = [50,104,150]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 10
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 150, 'epochs': 25, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 97.29%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-14-320.jpg)
![3.
epochs = [20,25,40]
batches = [200,150]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 10
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 200, 'epochs': 40, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 96.38%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-15-320.jpg)
![4.
epochs = [20,25,40]
batches = [200,150]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 3
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 200, 'epochs': 40, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 97.51%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-16-320.jpg)
![5.
epochs = [40,45]
batches = [200,250]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 3
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 250, 'epochs': 40, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 96.83%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-17-320.jpg)
![6.
epochs = [40,45]
batches = [150,250,300]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 3
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 150, 'epochs': 45, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 97.29%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-18-320.jpg)
![7.
epochs = [40,45]
batches = [150,250,300]
optimizers = ['adam']
Cross validation = 3
Best parameter combination
{'batch_size': 300, 'epochs': 45, 'optimizer':
'adam'}
Accuracy on test data: 97.51%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cnn-luna-191007184402/85/Lung-Cancer-Prediction-using-Image-Classification-19-320.jpg)