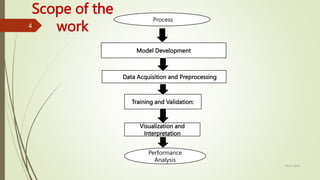
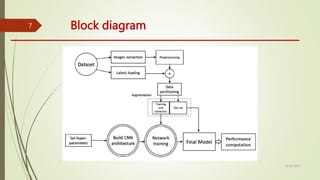
The document outlines a project focused on developing a deep learning model for accurate automatic segmentation of brain tumors in MRI images to support medical professionals in early diagnosis and treatment planning. The methodology involves data preprocessing, model training using convolutional neural networks and vision transformers, and performance evaluation with metrics like accuracy and dice coefficient. The project's goal is to enhance patient outcomes and streamline the diagnostic process while addressing ethical considerations related to data privacy and AI deployment in healthcare.









![Acknowledgement
Acknowledgements:
We would like to express our gratitude to the following individuals, organizations, and sources for their contributions and support during the
development of this project:
Kaggle: We acknowledge brain Tumor Dataset for providing the brain tumor detection dataset used in this project.
- Libraries and Tools: We extend our appreciation to the developers and contributors of TensorFlow, OpenCV, NumPy, PIL, scikit-learn, and other
libraries and tools used in this project for their invaluable contributions to the field of deep learning and image processing.
- Inspiration and References: We are thankful to the authors of [Reference Papers or Projects] for their pioneering work in medical image
segmentation and brain tumor detection, which served as inspiration and references during the development of our model.
- Classmates, Mentors, or Advisors: We would like to thank for their support, guidance, and feedback during the course of this project.
- Institution or Organization: This project was conducted as part of [Name of Institution or Organization]. We acknowledge Ramco Institute of
Technology for providing resources, facilities, and support for this research.
10-02-2024
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elysiumproject-240210063150-0e226171/85/Medical-Image-segmentation-from-dl-pptx-13-320.jpg)
