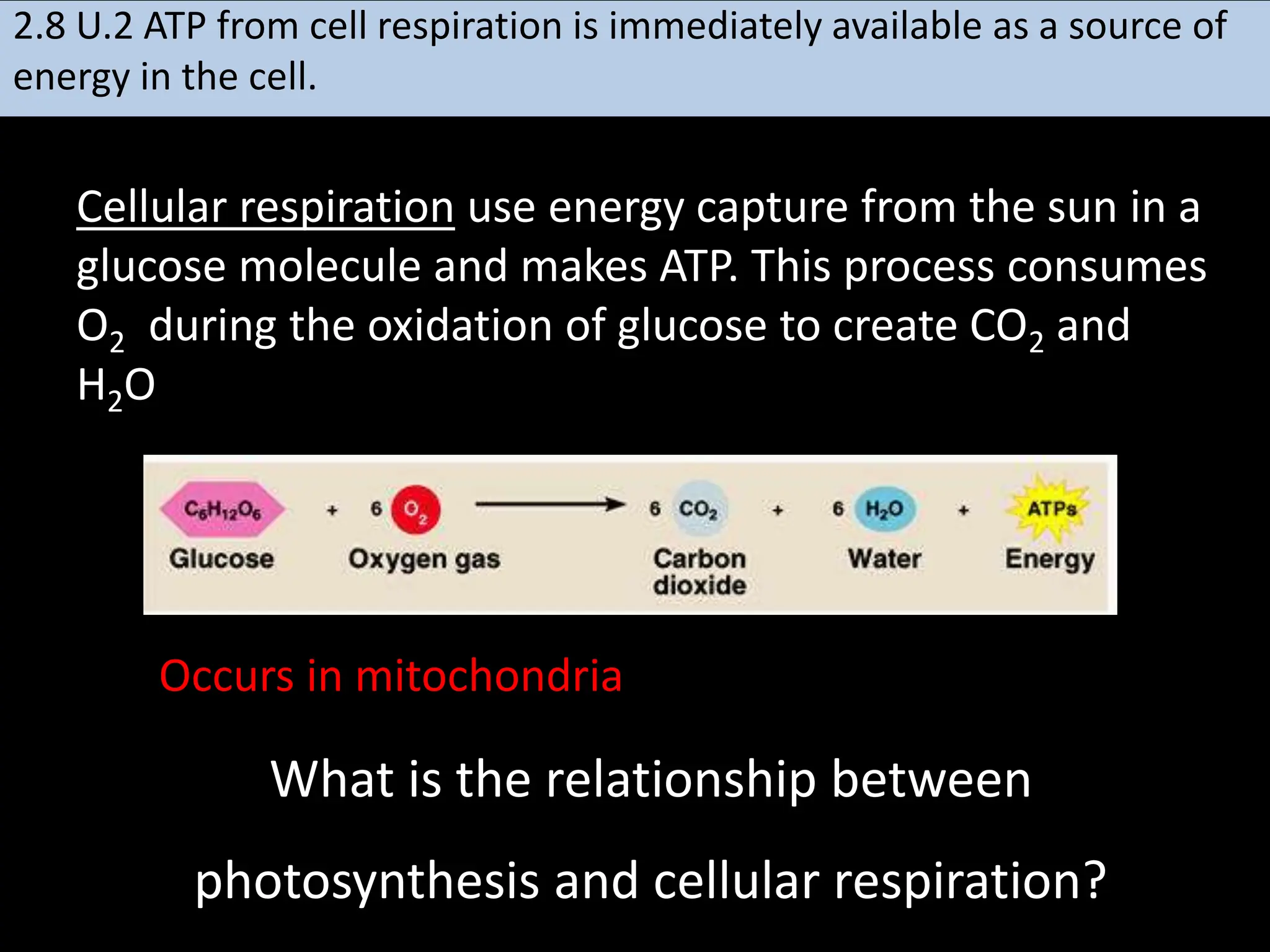
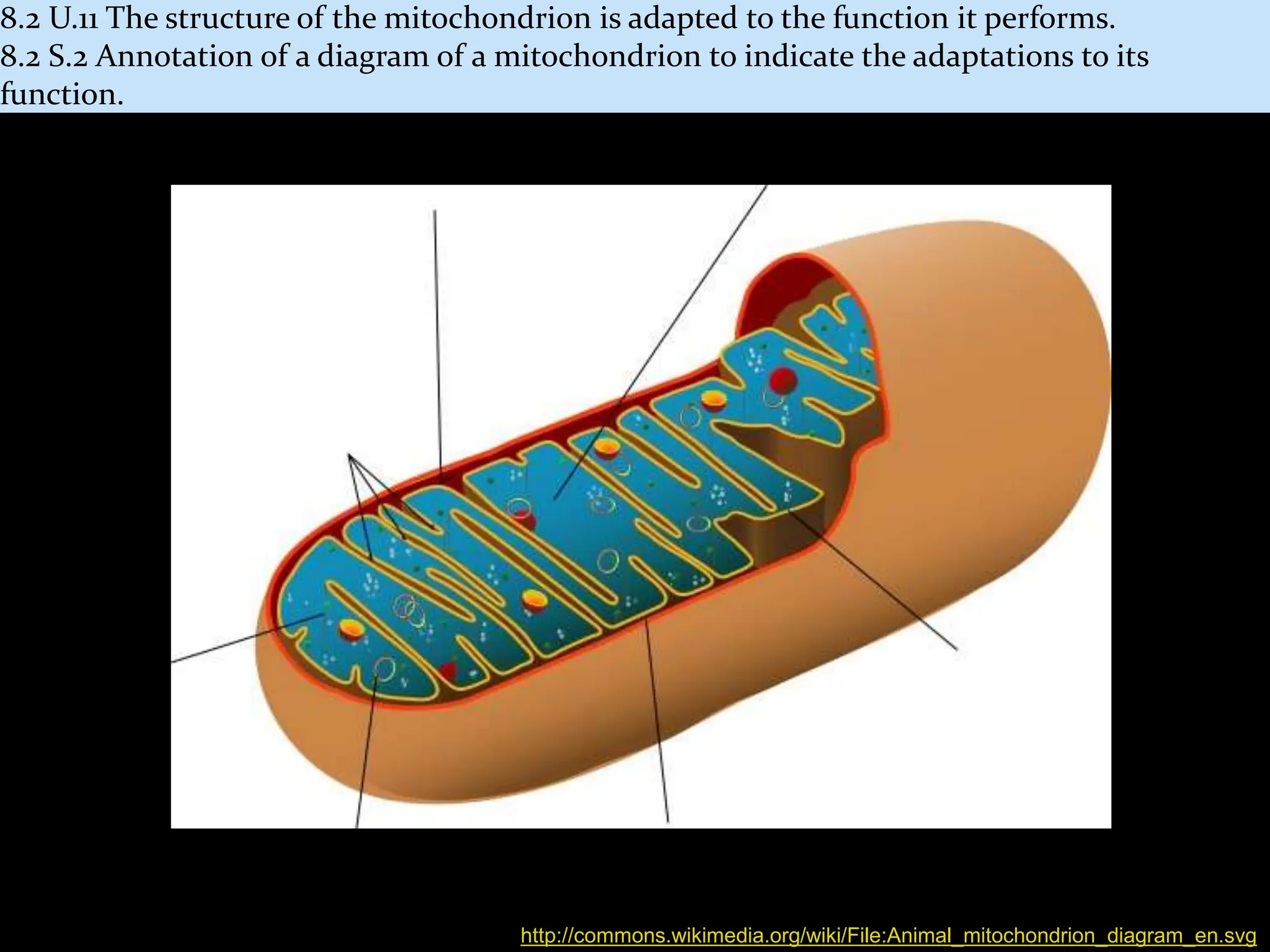
Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells and involves a series of metabolic pathways that break down glucose and harvest energy to produce ATP. There are four main phases: glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm and produces a small amount of ATP; the link reaction and Krebs cycle, which occur in the mitochondrial matrix and further oxidize pyruvate; and the electron transport chain located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, which generates the majority of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. The structure of the mitochondrion is adapted for this process, containing inner membrane folds called cristae that house the electron transport chain and facilitate ATP production.