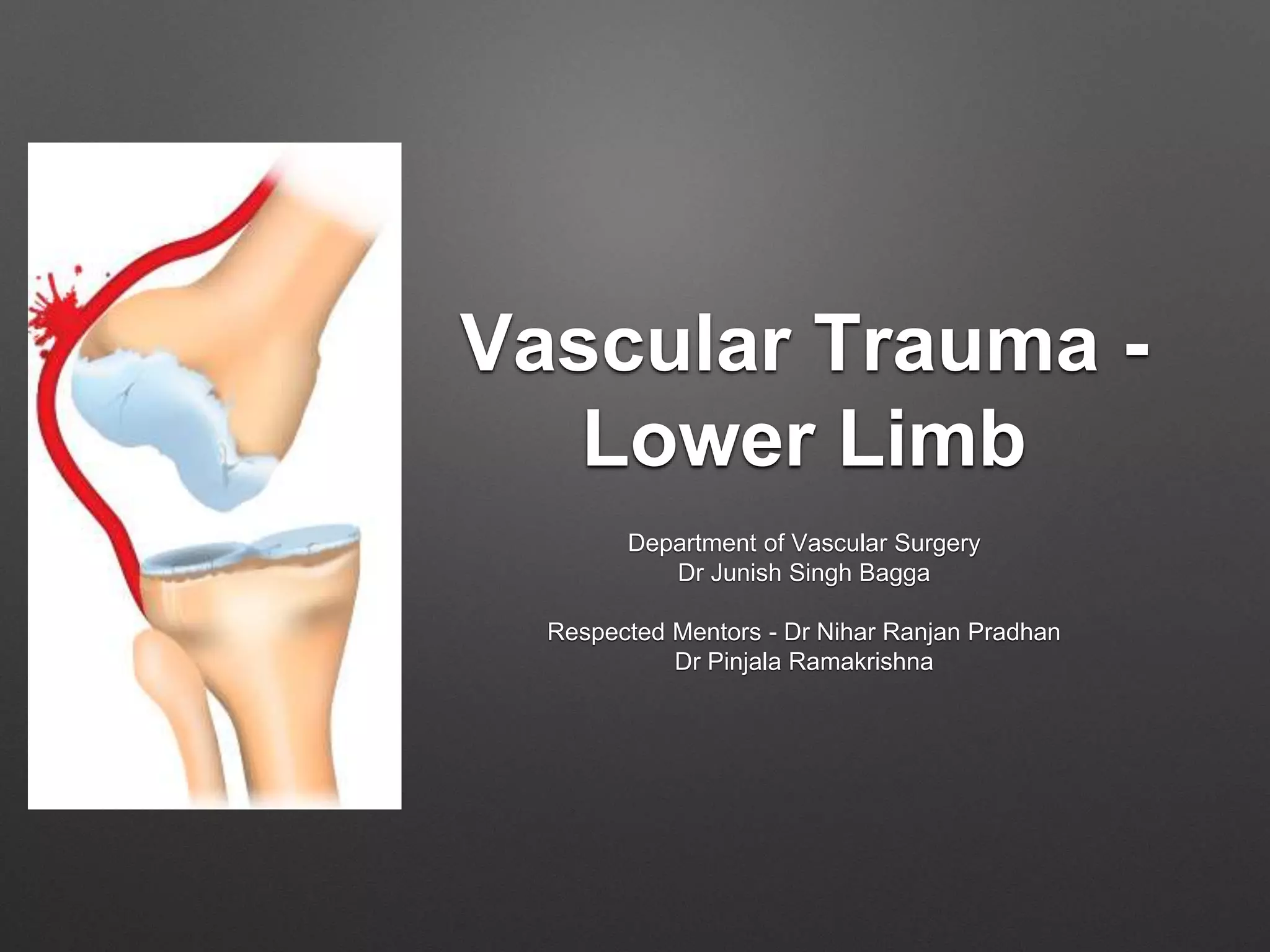
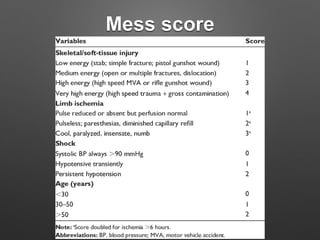
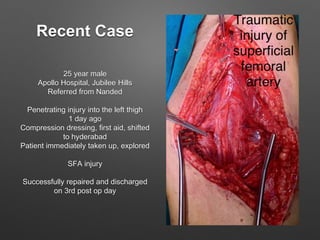
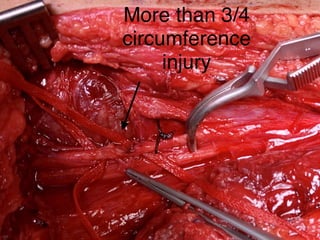
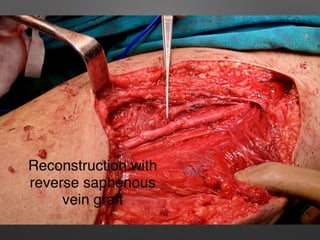
This document discusses vascular trauma to the lower limbs, specifically:
1. It provides epidemiological data on lower limb vascular injuries, noting they make up 26% of extremity injuries and are more common in males from penetrating trauma.
2. Outcomes include higher mortality rates for blunt injuries and amputation rates ranging from 7-30% for injuries below the knee. Associated bone fractures occur in 80-100% of blunt injuries.
3. Examination findings and investigations like Doppler, CT angiography are discussed for evaluating the extent of injury.
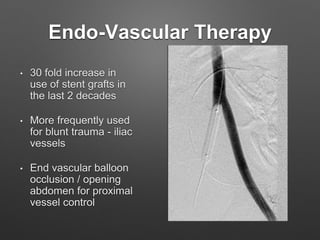
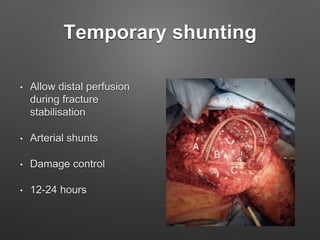
4. Treatment principles covered include non-operative management for small injuries, endovascular techniques for iliac vessels, and open surgical repair with grafts and