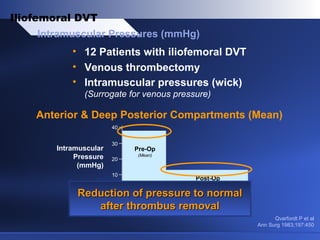
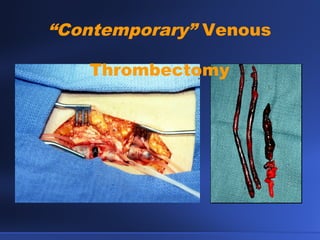
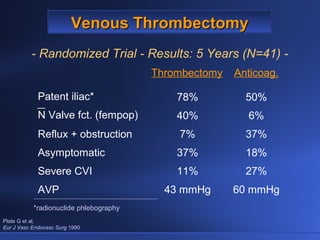
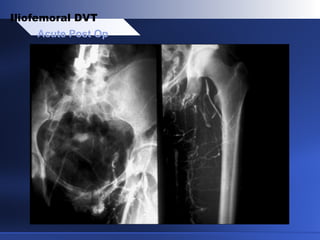
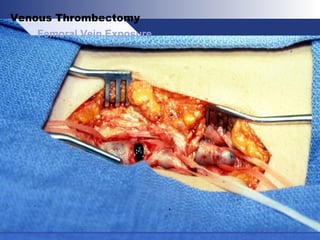
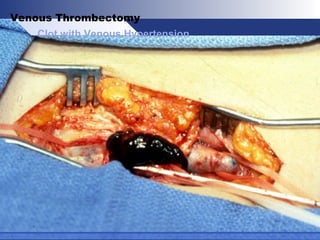
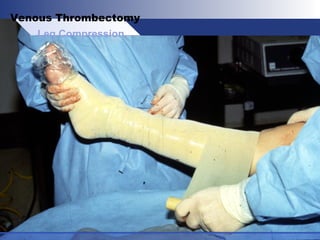
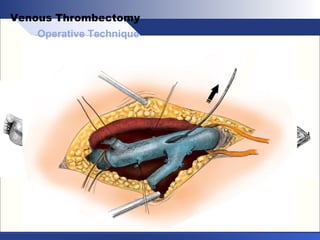
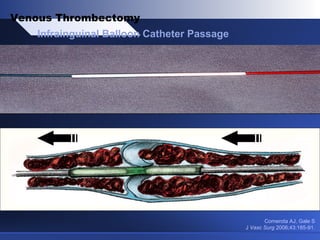
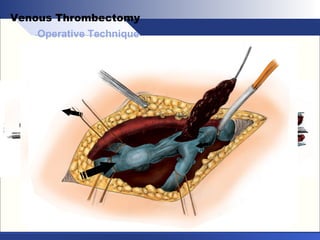
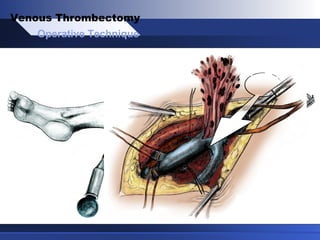
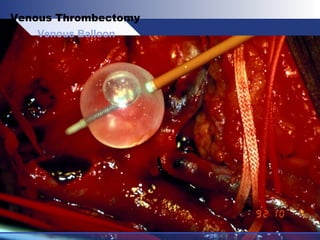
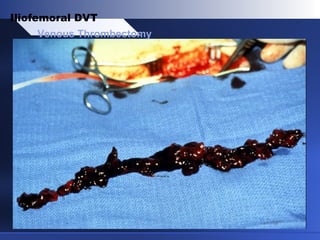
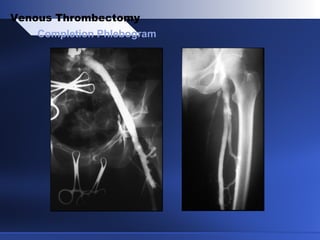
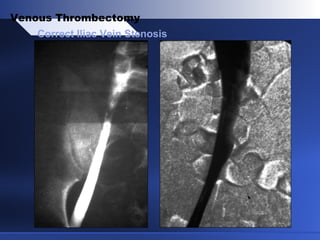
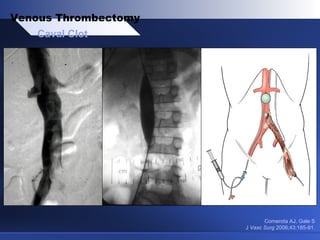
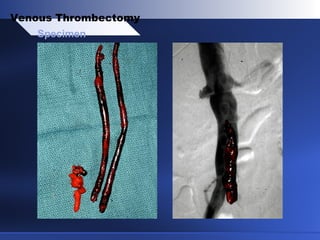
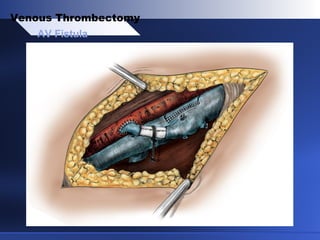
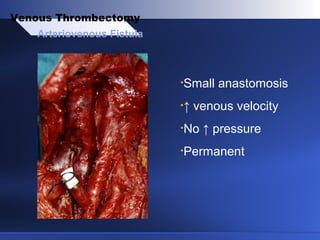
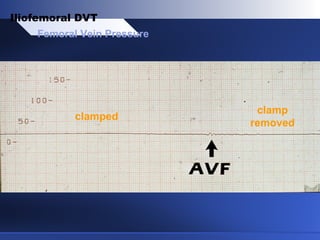
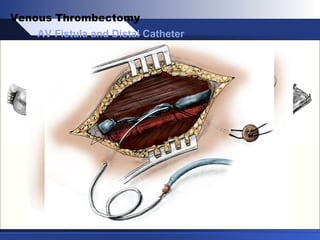
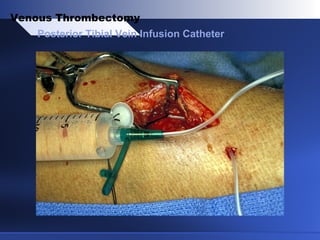
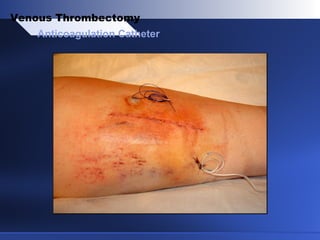
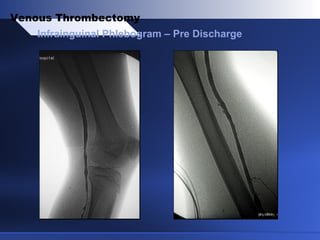
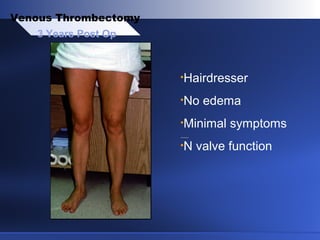
Venous thrombectomy can help treat acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and reduce long-term complications. The procedure removes the thrombus to eliminate obstruction and preserve valve function. Randomized trials found that venous thrombectomy plus anticoagulation led to better long-term outcomes than anticoagulation alone, including lower venous pressures, less venous reflux, fewer symptoms of post-thrombotic syndrome, and better patency rates. Contemporary venous thrombectomy techniques use dual catheter techniques and angiovenous fistulas to effectively clear thrombus and reduce venous hypertension in order to decrease long-term morbidity from extensive DVT.















![Acute DVT
What’s New in Venous Disease?
RecommendationsRecommendations
“In […patients] with extensive
DVT…operative venous
thrombectomy may be used to
reduce acute symptoms and post-
thrombotic morbidity…”
…GRADE 2B…
2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surgicaltreatmentacutedvt-150305074651-conversion-gate01/85/Surgical-treatment-acute-dvt-45-320.jpg)


