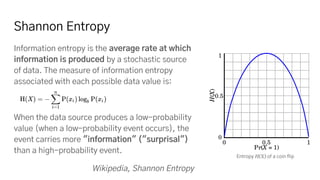
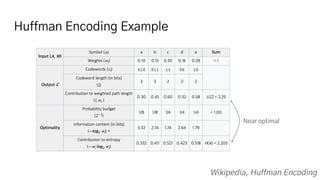
The JPEG image compression standard works by first converting the image color space to Y'CbCr and subsampling the chroma channels. It then applies the discrete cosine transform to separate the image into spatial frequencies. Quantization more heavily reduces the higher frequency components, capitalizing on human visual perception being less sensitive to color and fine details. Run-length encoding groups common values, and Huffman coding further compresses the data into an efficient binary representation for storage and transmission.