The document is a term paper on image compression submitted by a student. It discusses various topics related to image compression including:
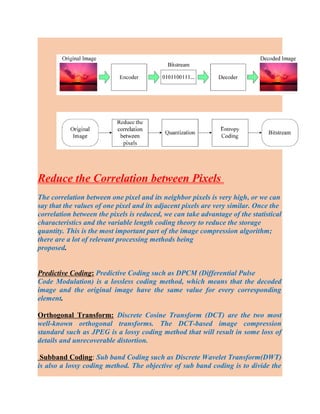
- Introduction to image compression and its goals of reducing redundancy and storing/transmitting data efficiently.
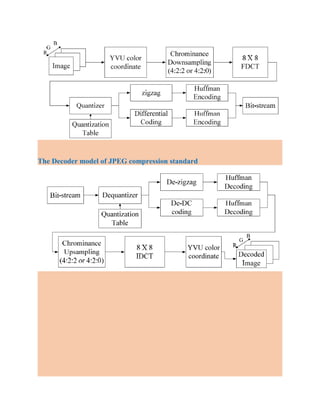
- Methods to reduce correlation between pixels like predictive coding, orthogonal transforms, and subband coding.
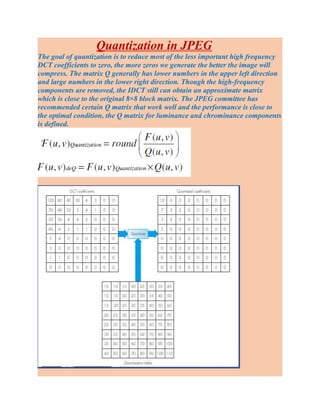
- Quantization in image compression and its role in reducing less important high frequency components.
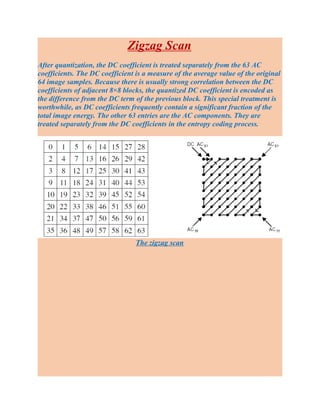
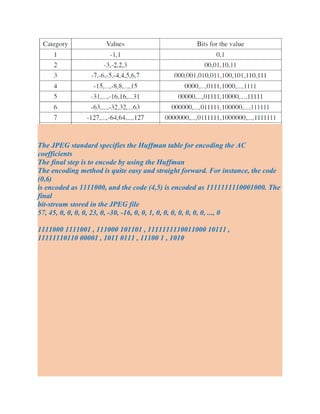
- Entropy coding techniques used in JPEG like differential coding, run-length coding, and Huffman coding to further compress the data.