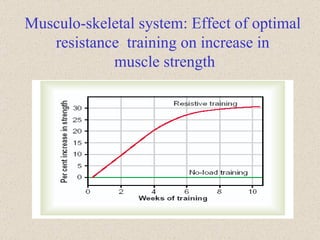
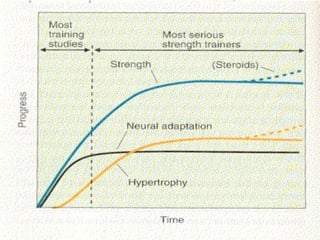
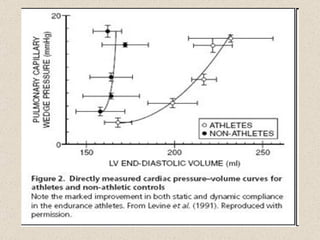
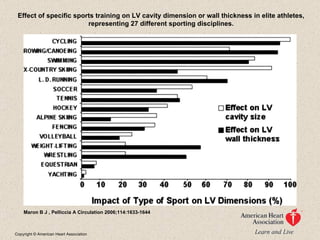
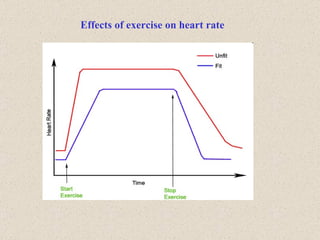
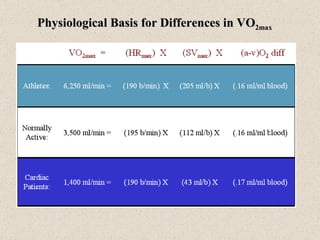
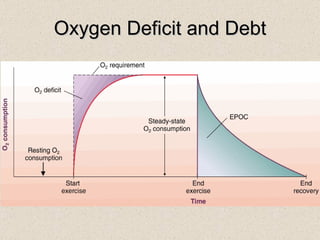
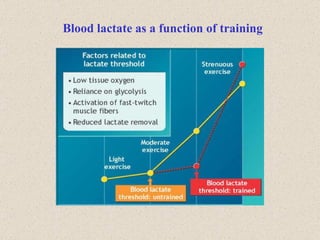
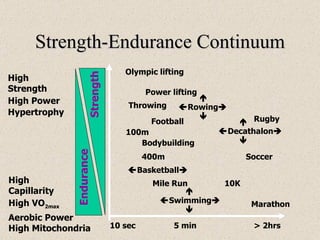
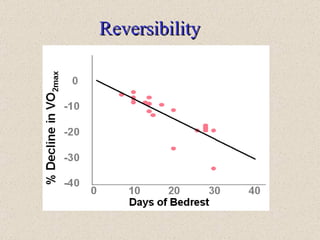
The document discusses the long-term effects of exercise, focusing on strength and endurance training and its impact on the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems. It highlights physiological changes such as increased muscle strength, improved heart efficiency, and enhanced respiratory function, alongside benefits like reduced blood pressure and enhanced bone strength. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of various training regimens for different sports and their specific adaptations in the body.