The document outlines several potential mechanisms by which exercise provides benefits during cardiac rehabilitation, including cardiovascular, respiratory, muscle, and metabolic adaptations. Regular exercise leads to improvements in factors like heart size, stroke volume, blood flow, and capillary density. It also increases maximal oxygen consumption and lactate threshold through adaptations to heart function, lung function, muscle fibers, mitochondria, and metabolic pathway usage.





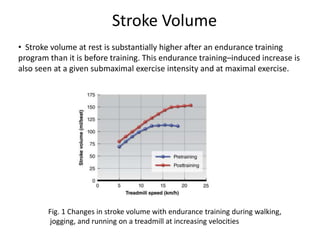

![• The thickness of the posterior and septal walls of the left ventricle also
increases slightly with endurance training. Increased ventricular muscle
mass results in increased contractile force, in turn causing a lower end-
systolic volume.
• The decrease in end-systolic volume is facilitated by the decrease in
peripheral resistance that occurs with training. Increased contractility
resulting from an increase in left ventricular thickness and greater diastolic
filling (Frank-Starling mechanism), coupled with the reduction in systemic
peripheral resistance, increases the ejection fraction [equal to (EDV – ESV)/
EDV] in the trained heart. More blood enters the left ventricle, and a greater
percentage of what enters is forced out with each contraction, resulting in
an increase in stroke volume. (Ehsani et al., 1991)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarpresentation1-201104062916/85/Seminar-presentation-1-8-320.jpg)




















