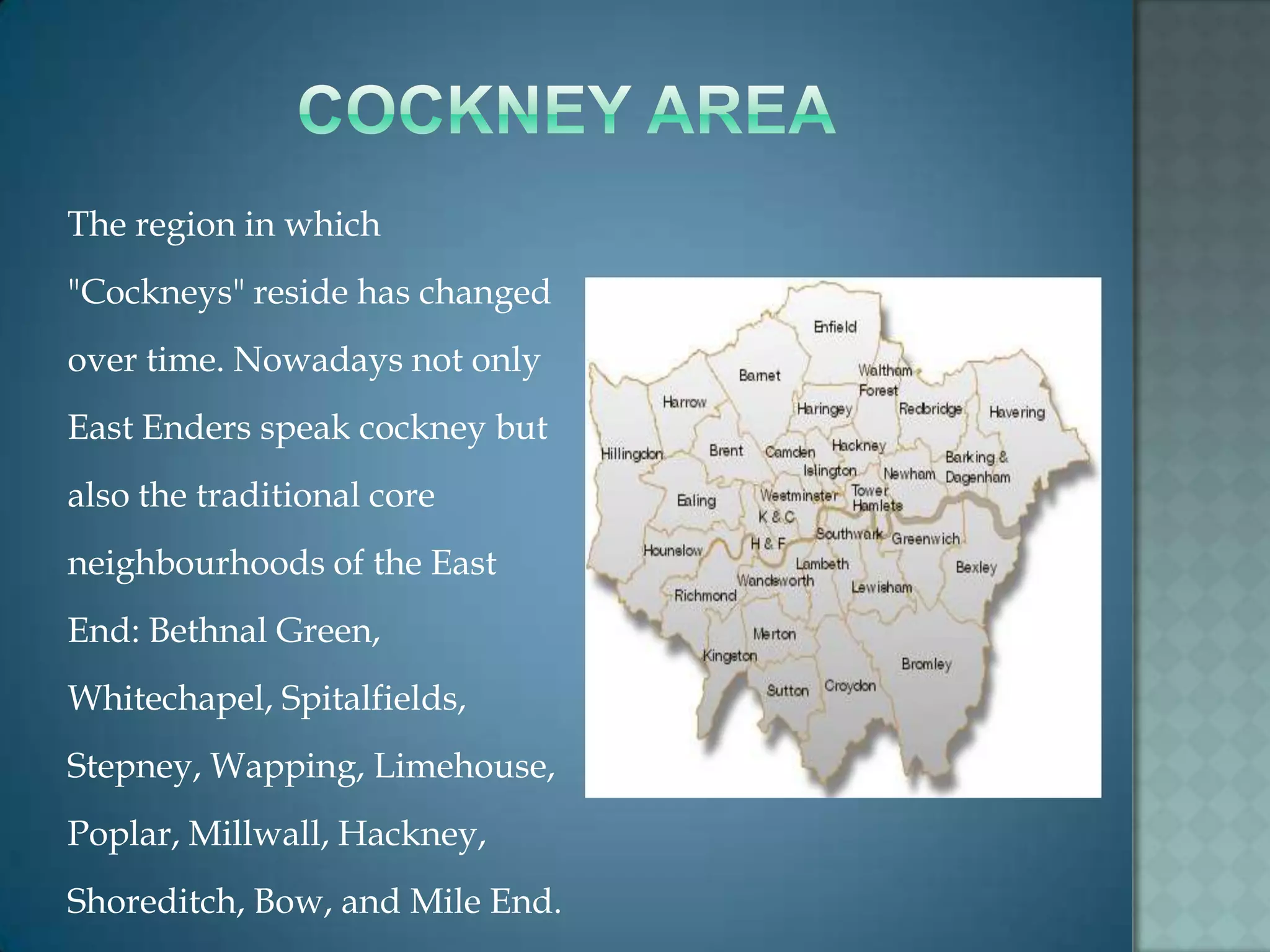
The document examines the development of the Cockney dialect spoken in London's East End. It outlines the key features of traditional Cockney speech, including h-dropping, vowel shifts, double negatives and the unique use of Cockney rhyming slang. While the Cockney dialect is still spoken today, some linguists note it is changing and blending with influences from other languages and regional slang spoken in London's diverse immigrant communities.



![PHONETICS
1. H-dropping (house – „ouse; hammer – „ammer)
2. Broad /a:/ (bath, path, demand)
3. T-glottalisation (as in bottled water)
4. Loss of dental fricatives: /ө / /f/ (maths)
/ð / /v/or /d/ ([bɒvə] "bother," [dæɪ]
"they" )
5. Diphthong alterations:
/eɪ/ → [æɪ]: [bæɪʔ] "bait"
/əʊ/ → [æʉ]: [kʰæʉʔ] "coat"
/aɪ/ → [ɑɪ]: [bɑɪʔ] "bite"
/aʊ/ may be [æə]: [tʰæən] "town"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/londonenglishdialectcockney1-121122004243-phpapp02/75/London-english-dialect-cockney1-5-2048.jpg)





