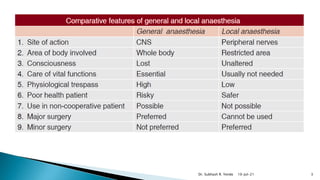
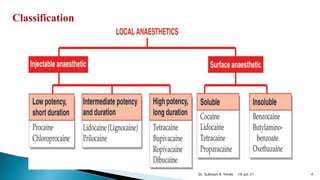
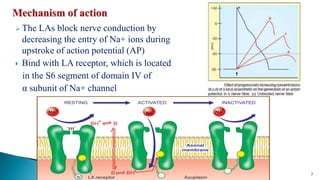
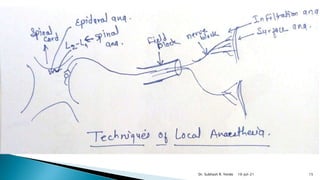
Local anesthetics are drugs that cause reversible loss of sensation, especially pain, in a restricted area of the body when applied topically or injected locally. They block nerve impulse generation and conduction by stabilizing sodium channels in the inactive state. Common examples include lidocaine, bupivacaine, and procaine. Local anesthetics are used for surface anesthesia, infiltration anesthesia, nerve blocks, spinal anesthesia, and epidural anesthesia.