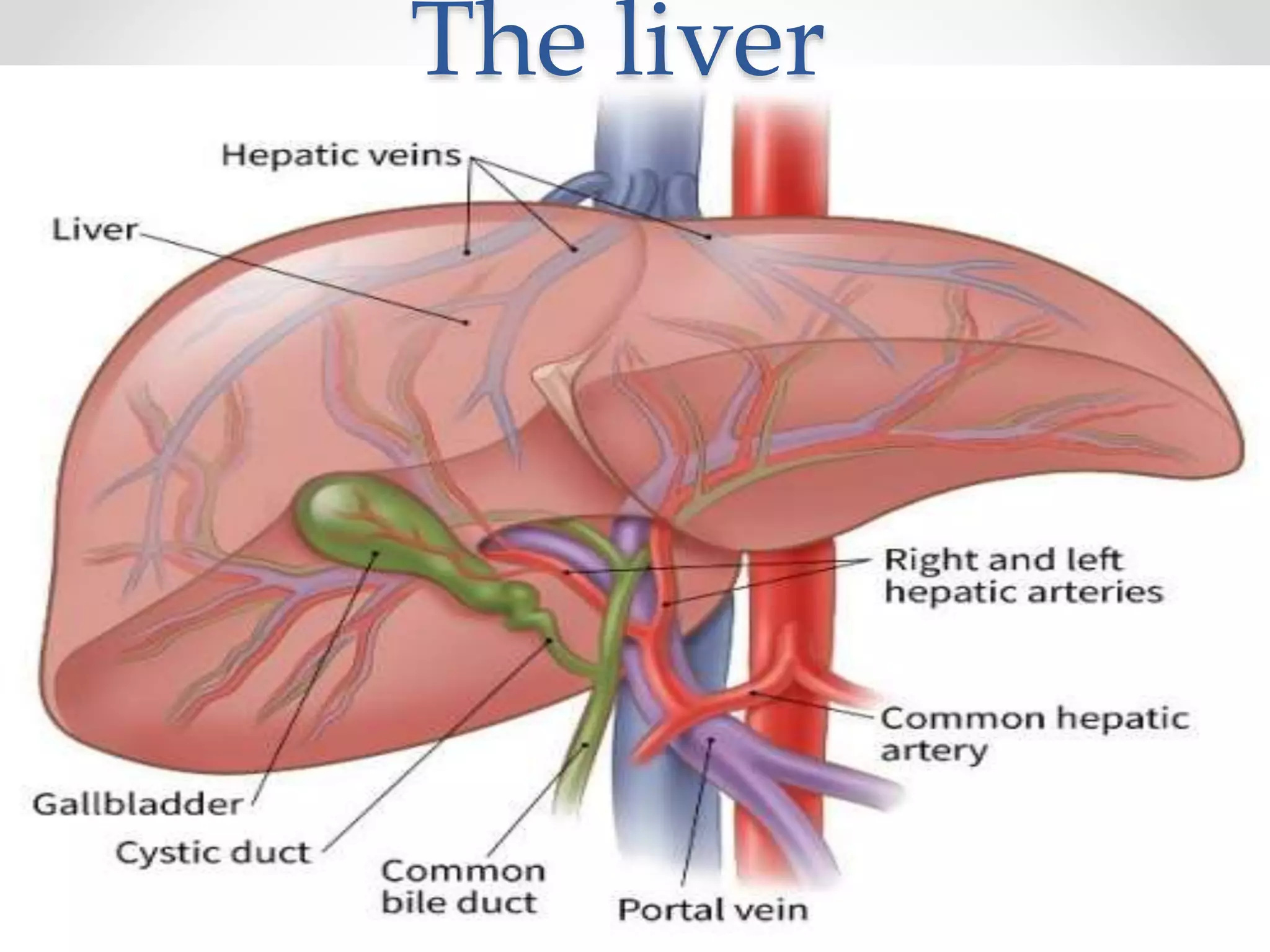
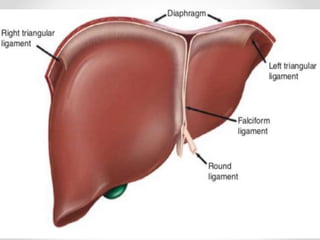
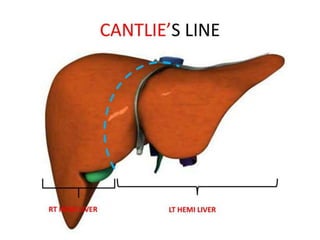
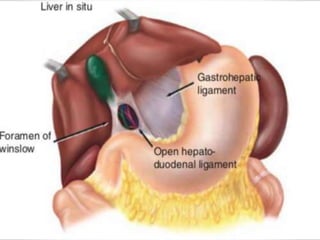
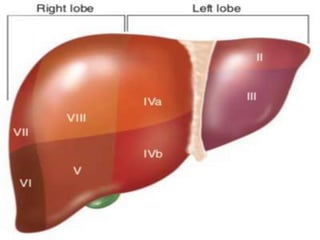
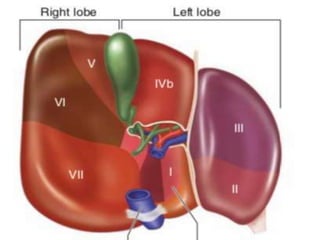
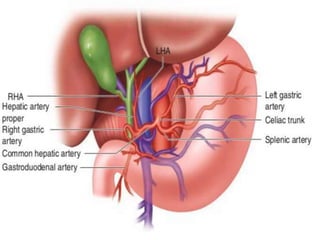
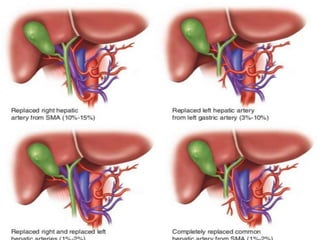
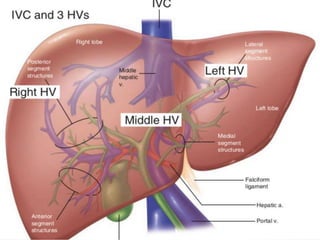
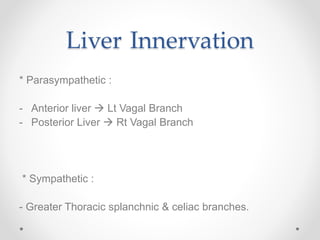
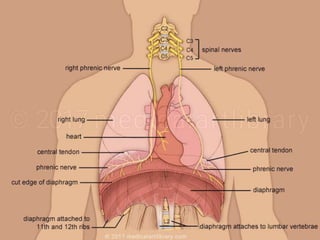
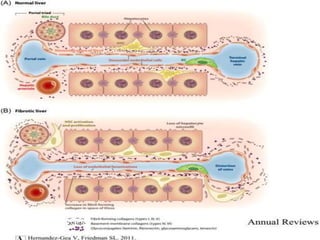
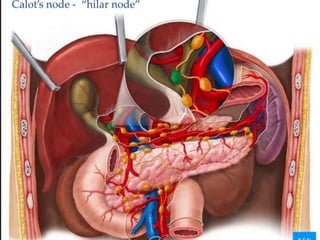
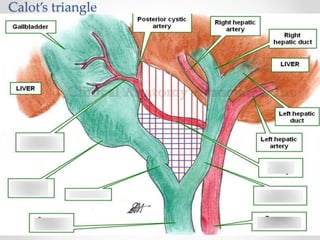
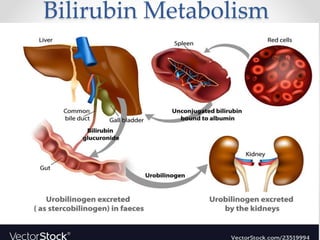
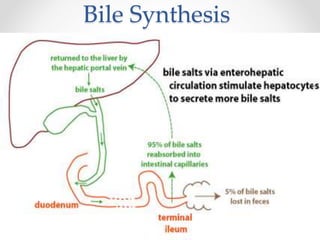
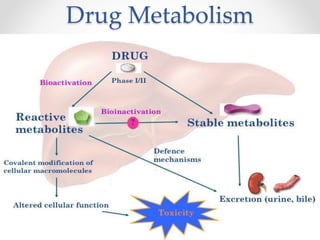
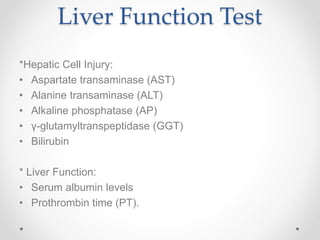
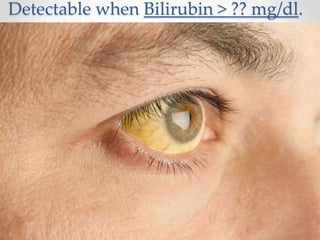
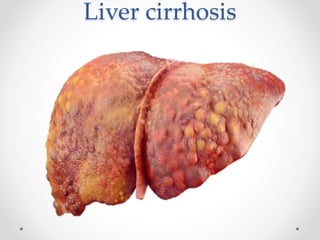
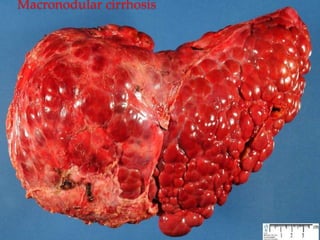
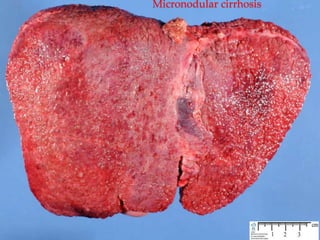
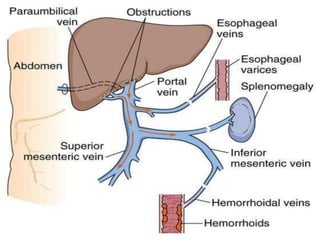
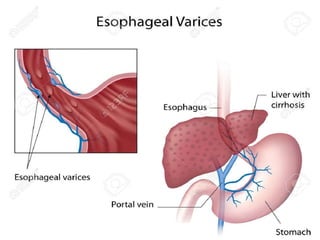
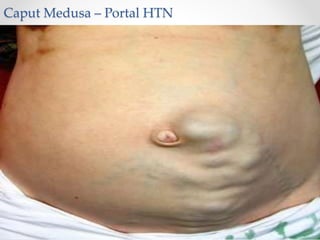
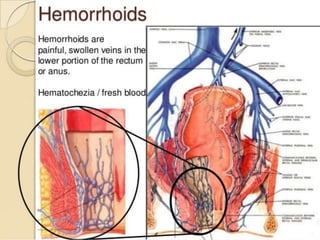
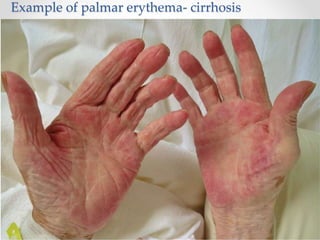
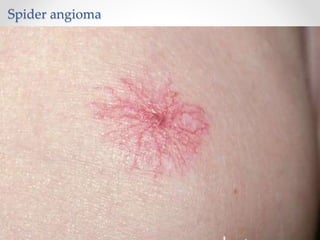
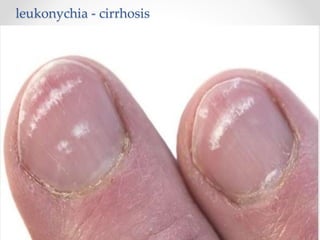
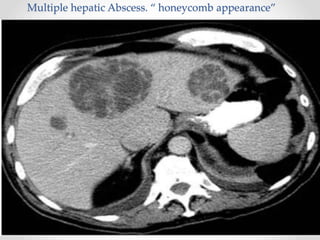
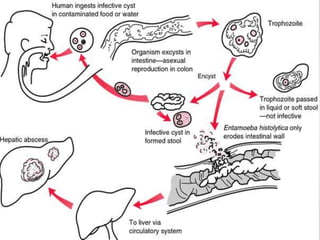
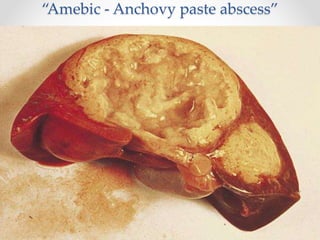
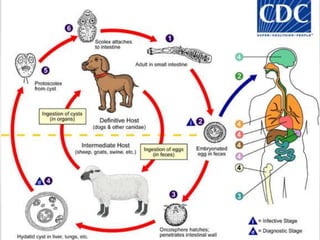
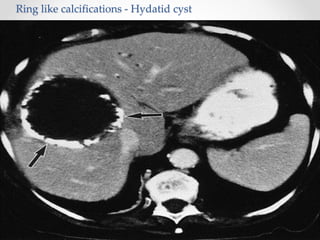
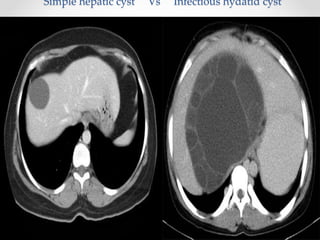
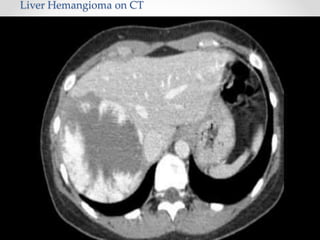
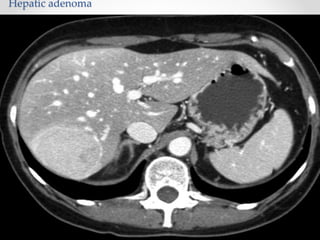
The document discusses the anatomy, physiology, and common diseases of the liver. It begins with a brief history of liver surgery and anatomy including liver innervation and lymph drainage. It then covers liver physiology including metabolism of nutrients, proteins, and drugs. Common liver diseases are summarized such as viral hepatitis, alcohol-related disease, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver cancer. Specific conditions like fatty liver disease, jaundice, acute liver failure, and infections are also reviewed. Imaging findings and treatments for various benign and malignant liver lesions are mentioned.