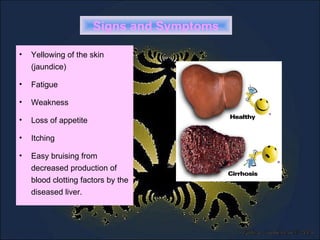
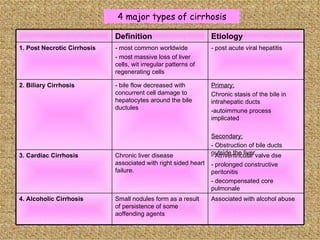
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease characterized by the replacement of liver tissue with fibrosis and the formation of regenerative nodules, leading to loss of liver function. It is commonly caused by alcoholism, viral hepatitis, and fatty liver disease. While generally irreversible, treatment focuses on preventing progression and complications like ascites, bleeding from esophageal varices, hepatic encephalopathy, and liver cancer. A diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging, and potentially a liver biopsy. Management includes medications to prevent complications and address underlying causes, with liver transplantation as a potential surgical option for end-stage disease.