Embed presentation

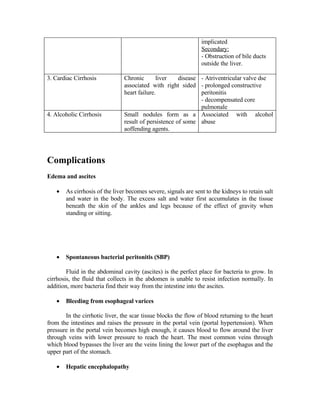










Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by the replacement of liver tissue with scar tissue. It is caused most commonly by alcoholism, hepatitis B and C, and fatty liver disease. Cirrhosis results in the progressive loss of liver function. Once cirrhosis occurs, the damage is generally irreversible and treatment focuses on preventing further progression and complications such as edema, ascites, bleeding from esophageal varices, and liver cancer.











