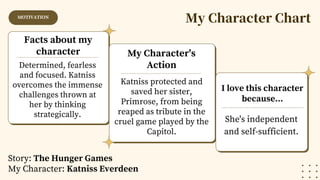
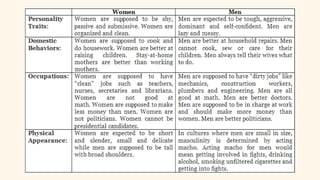
The document discusses the impact of literary characters, using Katniss Everdeen from 'The Hunger Games' as an example of a strong, determined figure. It outlines various literary criticism approaches including structuralism, formalism, moralism, Marxism, feminism, historical, and reader-response. The document also emphasizes the importance of critiquing literary works through different perspectives to gain deeper insights.