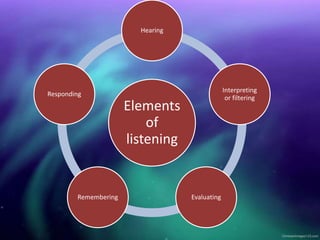
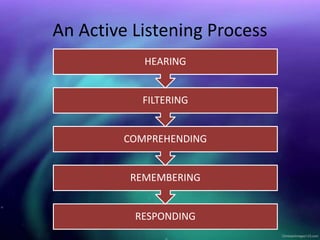
This document discusses listening skills and provides tips for being a good listener. It defines listening, distinguishes it from merely hearing, and outlines the importance of effective listening. Some key points made include: listening is an active mental process that requires conscious effort, unlike hearing which is passive; a good listener stimulates better communication and learns more; barriers to listening include distractions, biases, and cultural/linguistic differences. The document recommends making eye contact, avoiding distractions, not interrupting, and asking questions to improve listening skills.