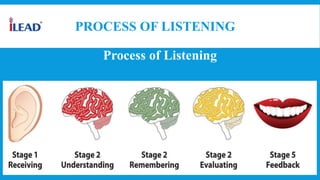
Listening is an active process that involves paying close attention to and making sense of what we hear. It is the most basic skill and the first one learned as children acquire language. True listening requires discriminating sounds, recognizing words, identifying meanings, and recalling important information. The listening process involves both top-down processing, where listeners use background knowledge, and bottom-up processing, where they focus on individual words and sounds. To listen effectively, one must stop talking, show interest, ask questions, maintain eye contact, take notes, and avoid distractions. Developing strong listening skills is important for communication, understanding, and building relationships.