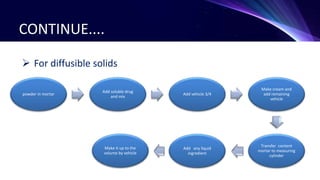
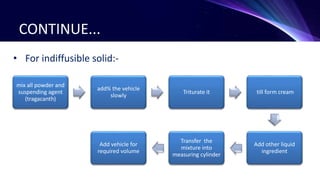
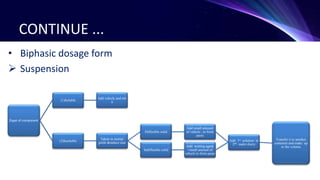
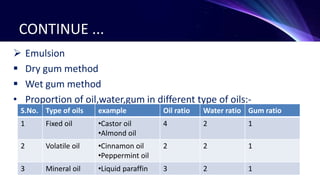
This document discusses the manufacturing of liquid dosage forms. Liquids can be monophasic, containing a single phase, or biphasic, containing two immiscible phases like suspensions and emulsions. Key components include active ingredients, vehicles, surfactants, preservatives, colors, and flavors. Manufacturing involves accurately measuring and mixing components according to their solubility and physical properties. For monophasic liquids, soluble compounds are dissolved in a vehicle while insoluble compounds require mixing to form a uniform suspension. Biphasic liquids like emulsions use wet or dry gum methods to properly combine oil and water phases into a stable final product.