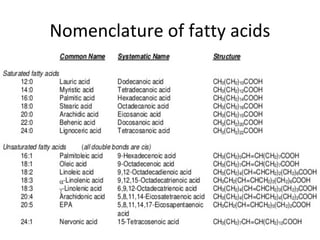
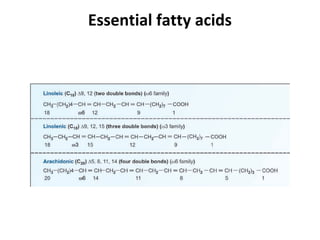
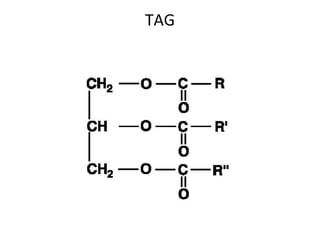
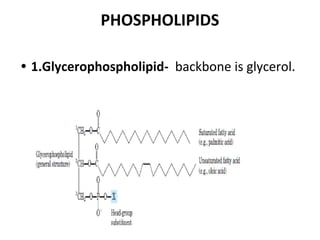
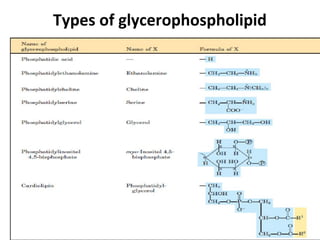
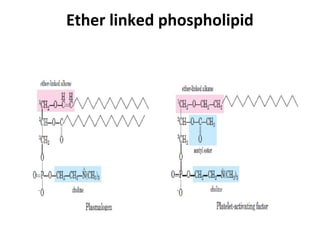
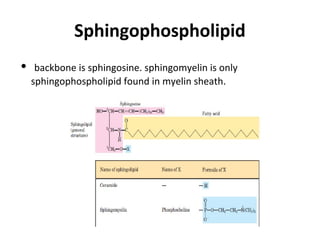
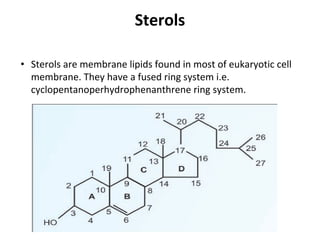
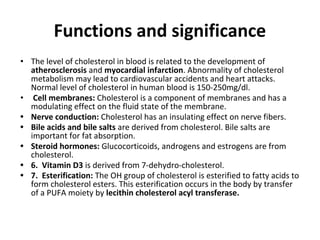
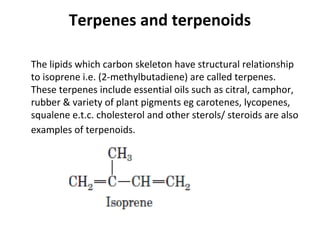
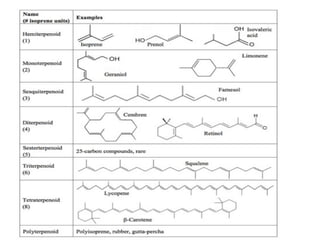
Lipids are a diverse group of compounds, including fats, oils, and steroids, characterized by their insolubility in water and solubility in nonpolar solvents. They serve various functions such as energy storage, insulation, and forming cellular components, and include classifications like simple lipids, compound lipids, and derived lipids. Fatty acids, a component of lipids, are categorized based on carbon chain length and saturation, while triglycerides (neutral fats) store fat in animals and plants and are important in metabolic processes.