1. Lipids are greasy substances found in both plants and animals that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and sterols.
2. Lipids serve as an energy store and structural component of cell membranes. Major sources include nuts, seeds, milk, eggs, liver, and fish oils.
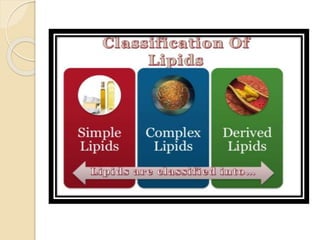
3. Lipids can be categorized as simple lipids like fats and oils, or compound lipids that contain additional components like phospholipids, glycolipids, and lipoproteins.