1) Lipases are water-soluble enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of ester bonds in triacylglycerols and belong to the alpha/beta hydrolase fold family. They contain a catalytic triad of Ser-His-Asp/Glu and undergo conformational changes through a flexible lid region.
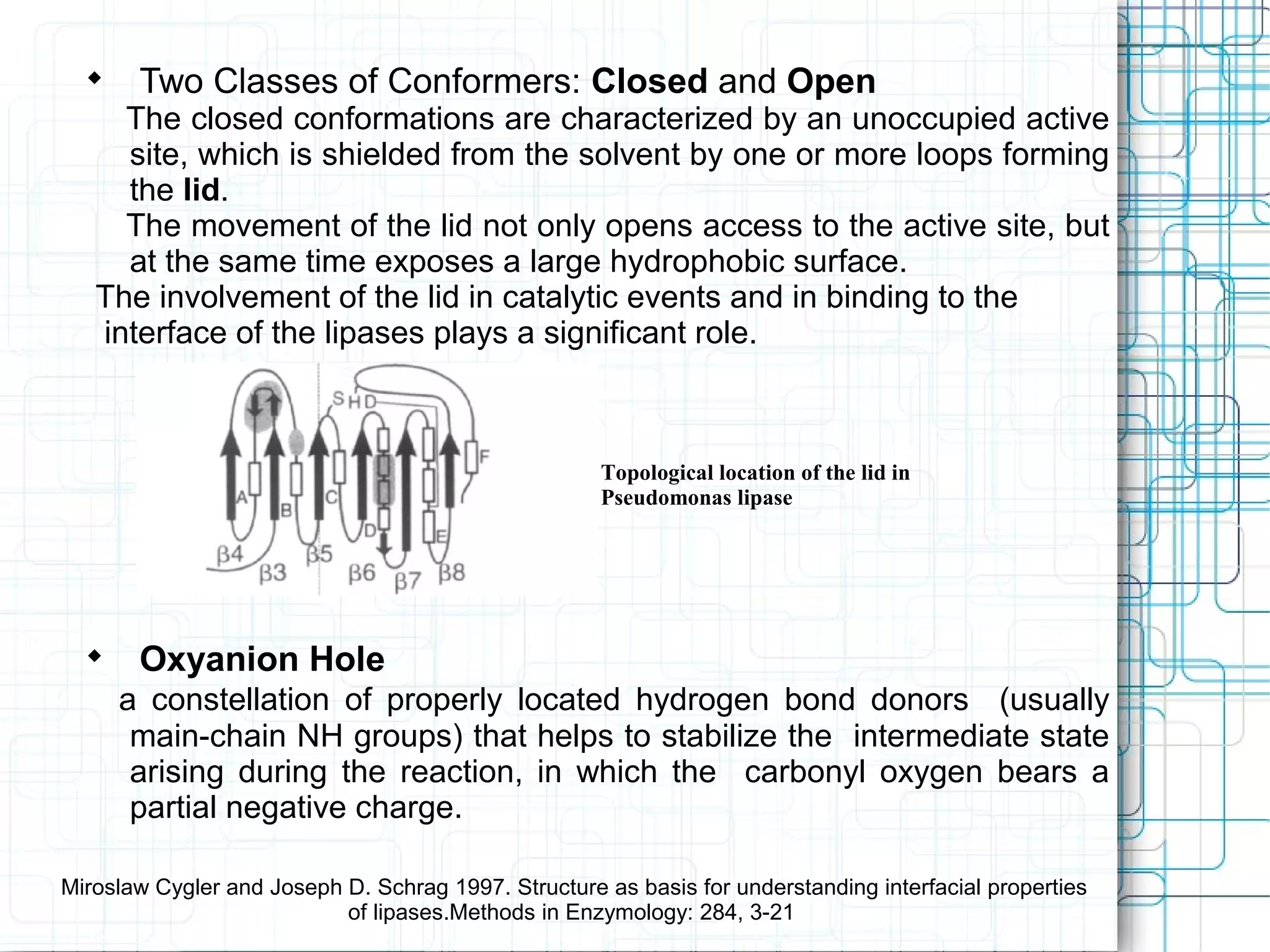
2) Lipases exist in both closed and open conformations, with the closed state shielding the active site and the open state exposing a hydrophobic surface upon lid movement. This lids movement is important for catalytic activity and binding to interfaces.
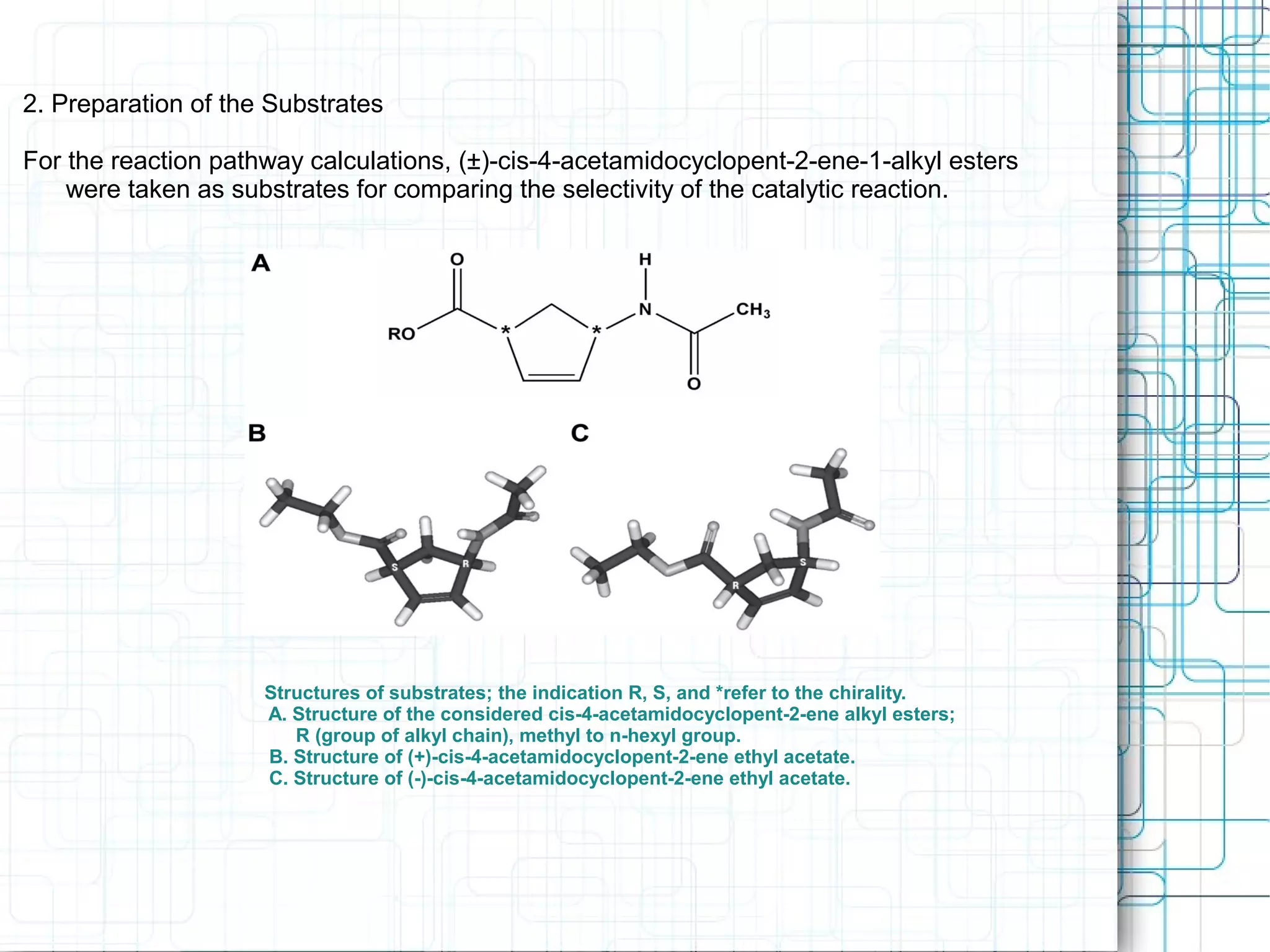
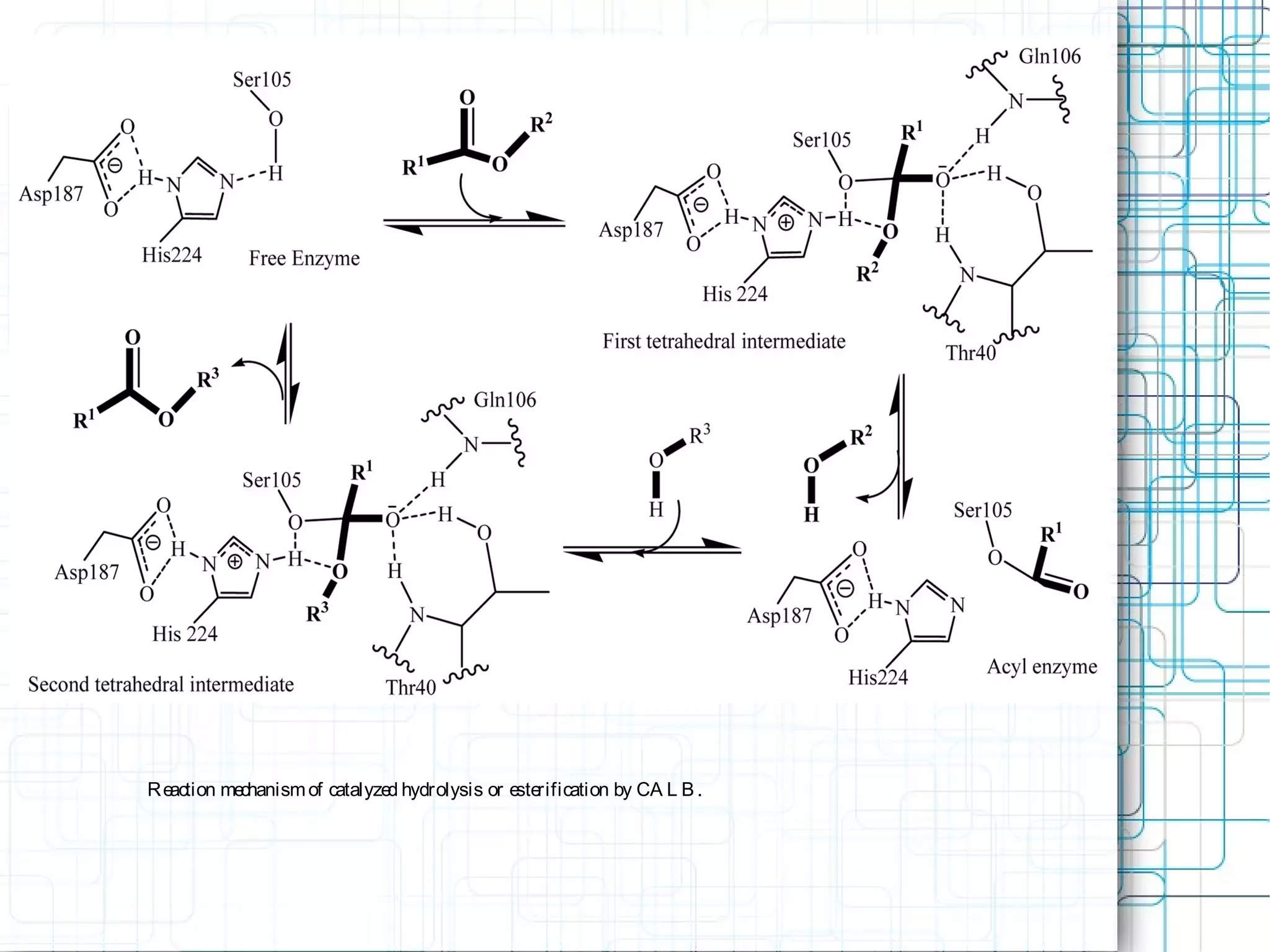
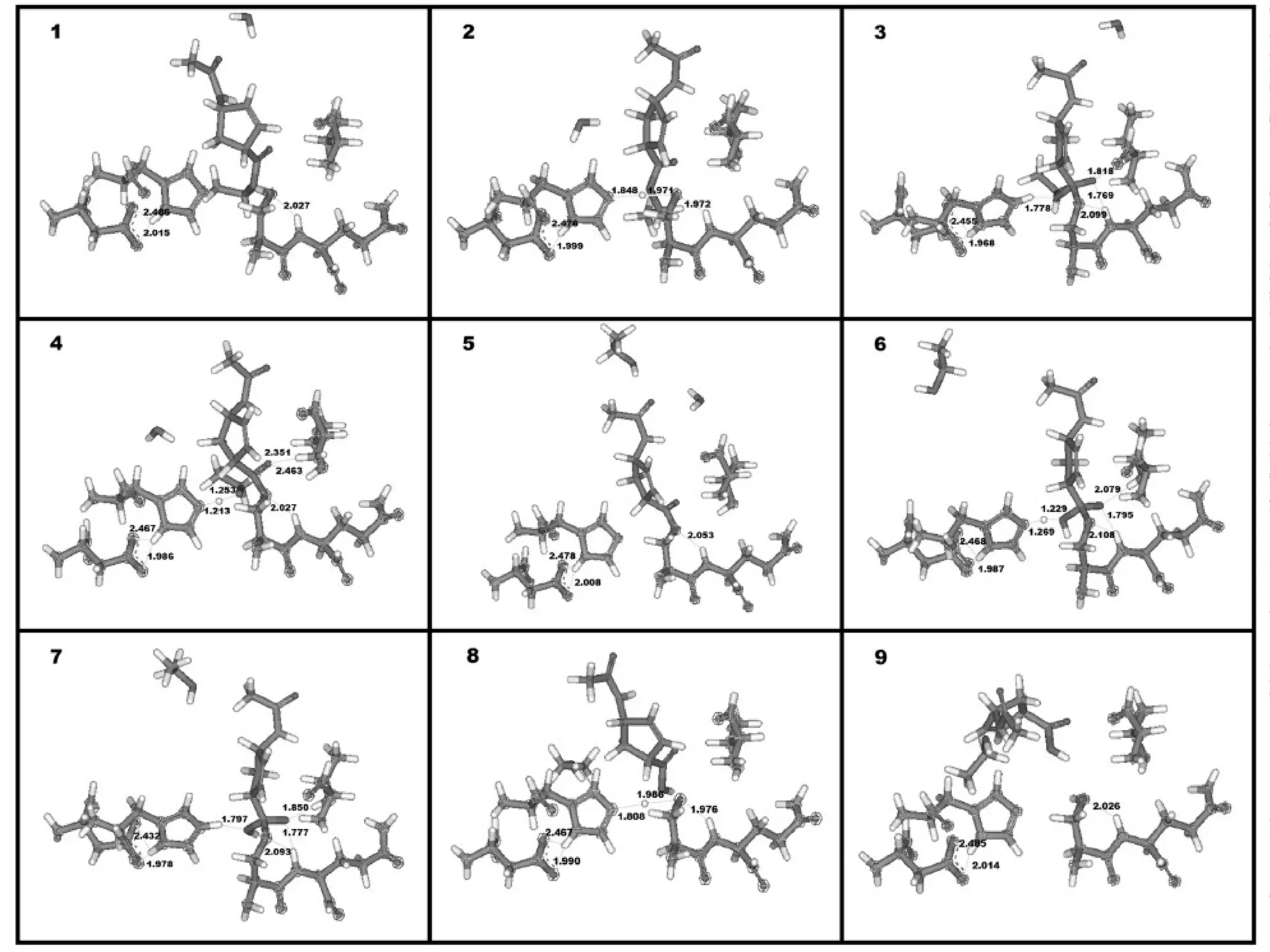
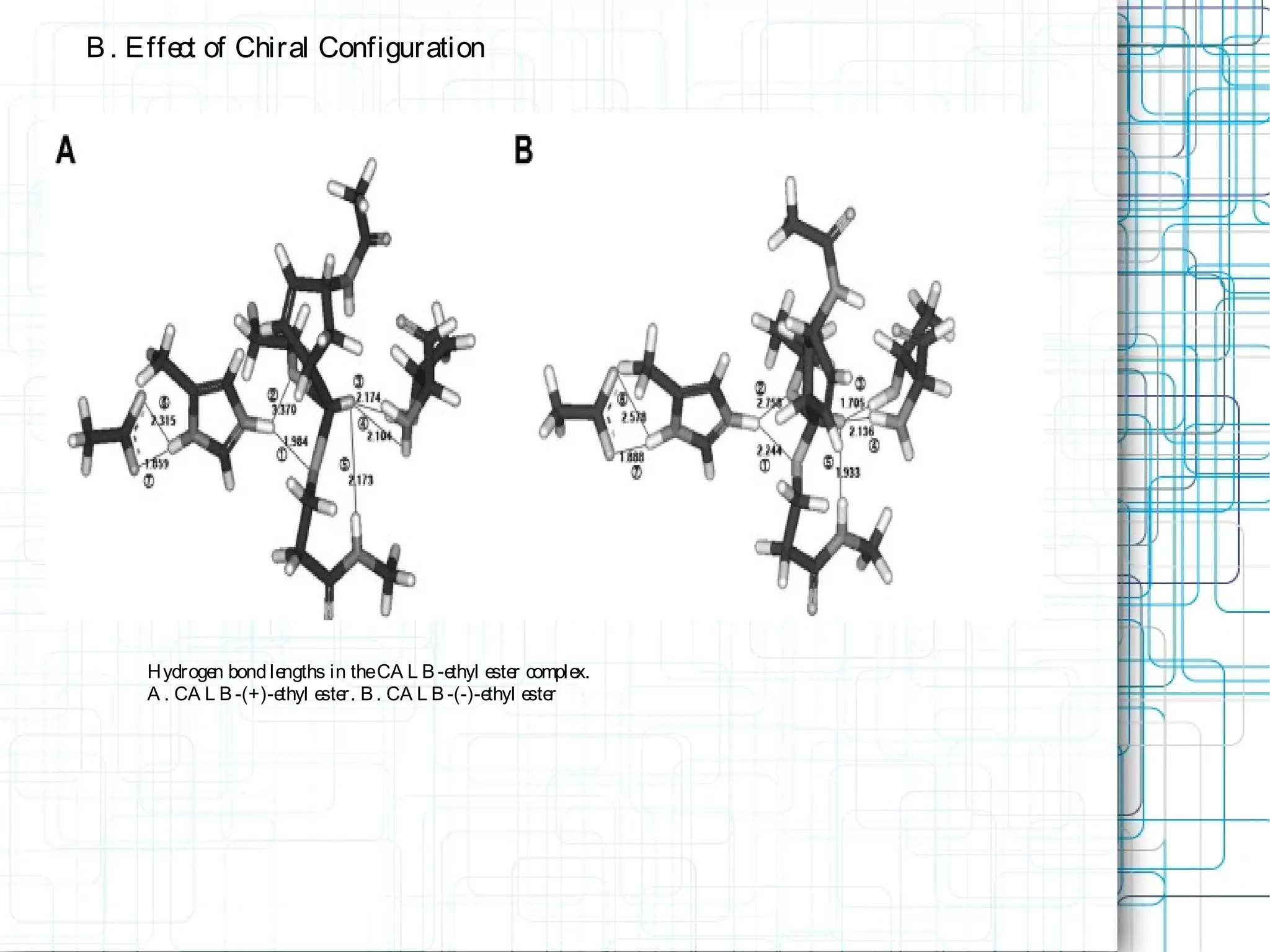
3) Molecular modeling was used to study the reaction mechanism and conformational preferences of Candida antarctica lipase B. The results supported a