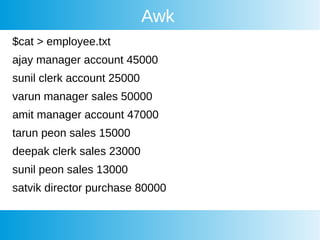
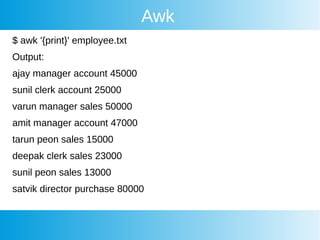
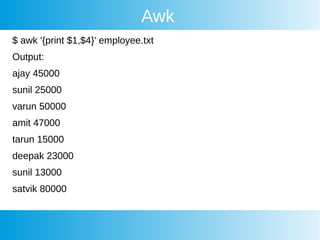
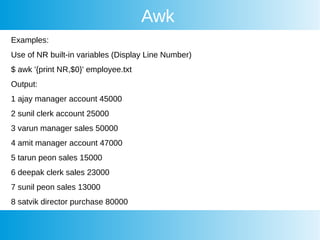
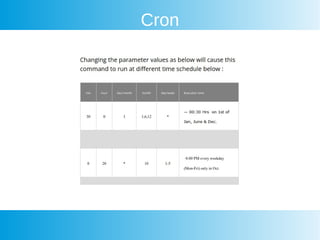
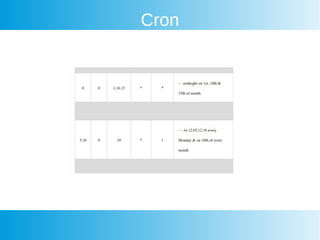
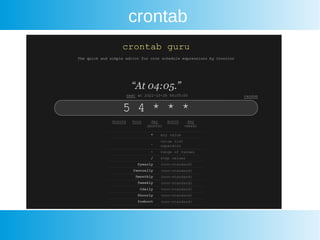
This document provides an overview of awk, cron, and shell scripting. It includes examples of using awk to parse text files and extract specific fields. Built-in awk variables like NR, NF, FS are described. Cron is introduced but not explained in detail. Links are provided for more information on awk, crontab, and shell scripting. Quizzes from an online course are listed.