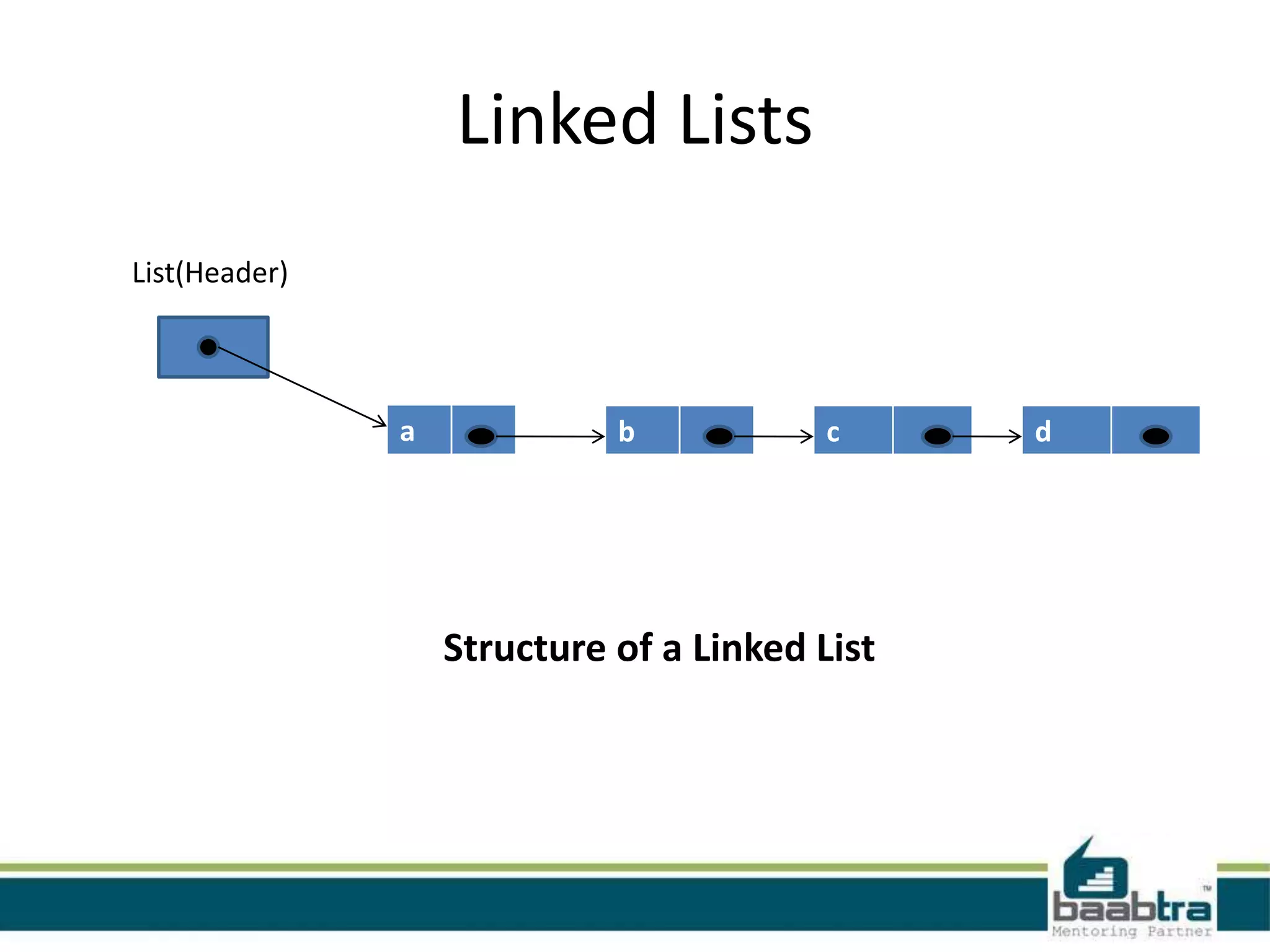
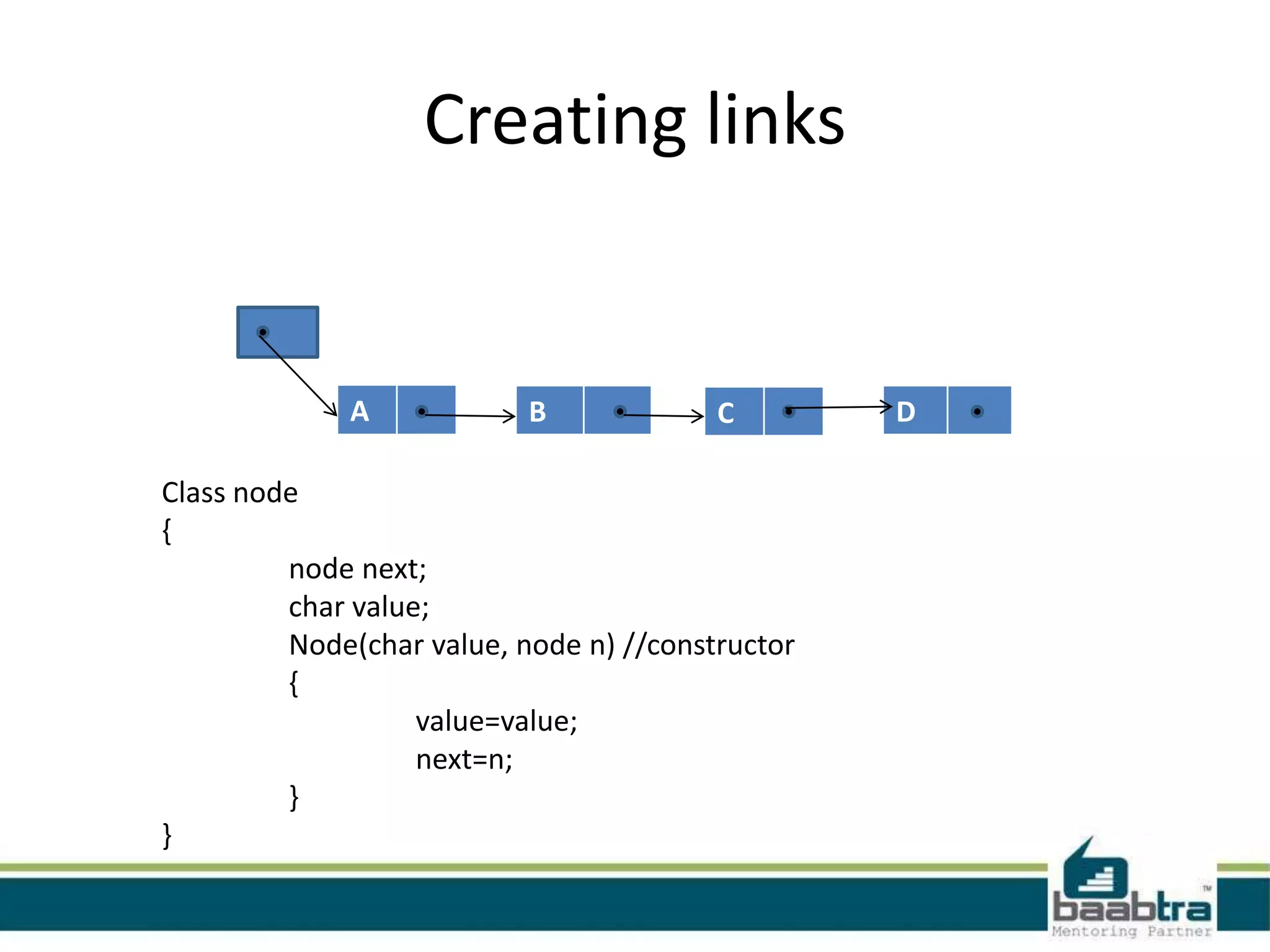
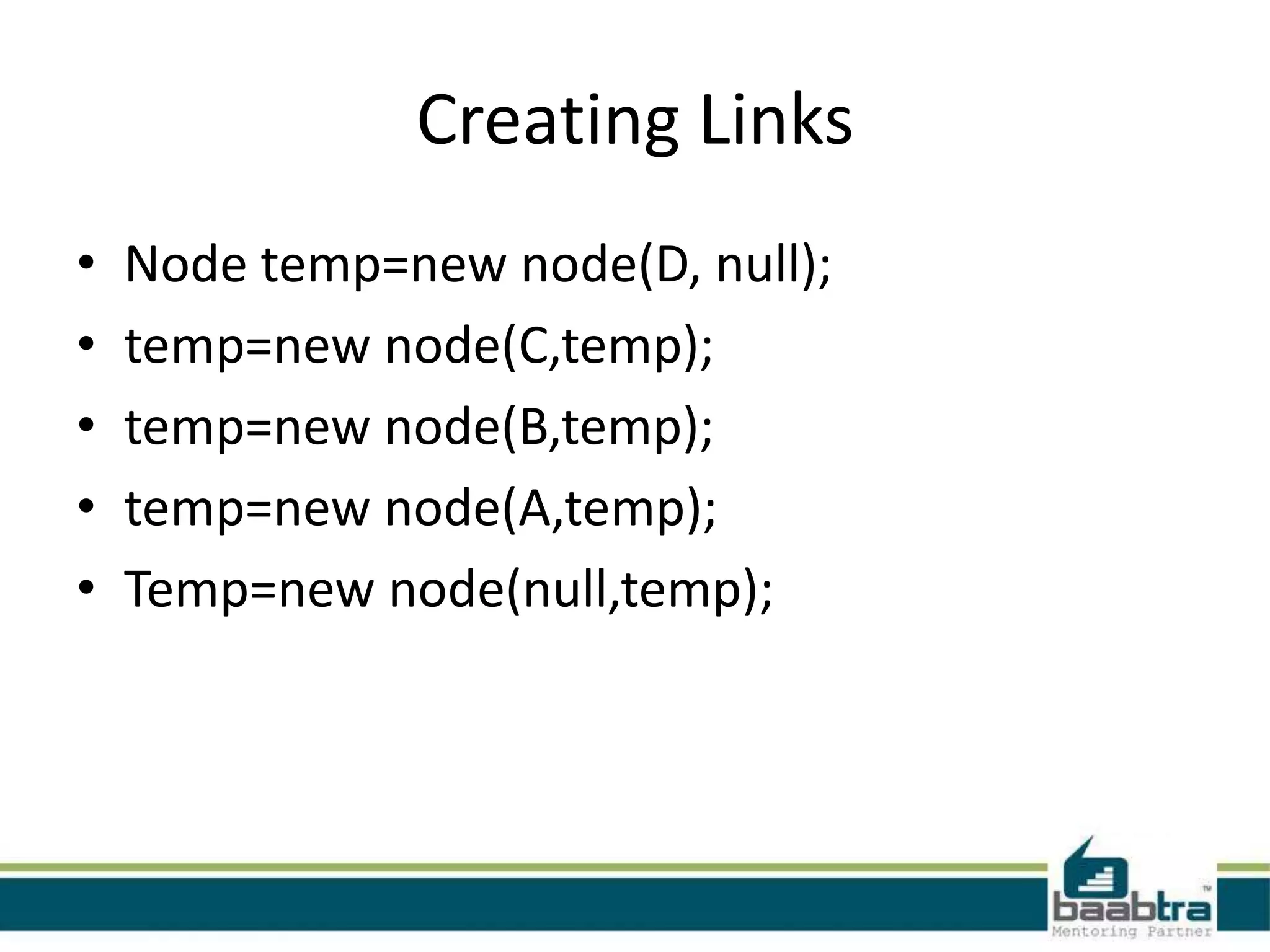
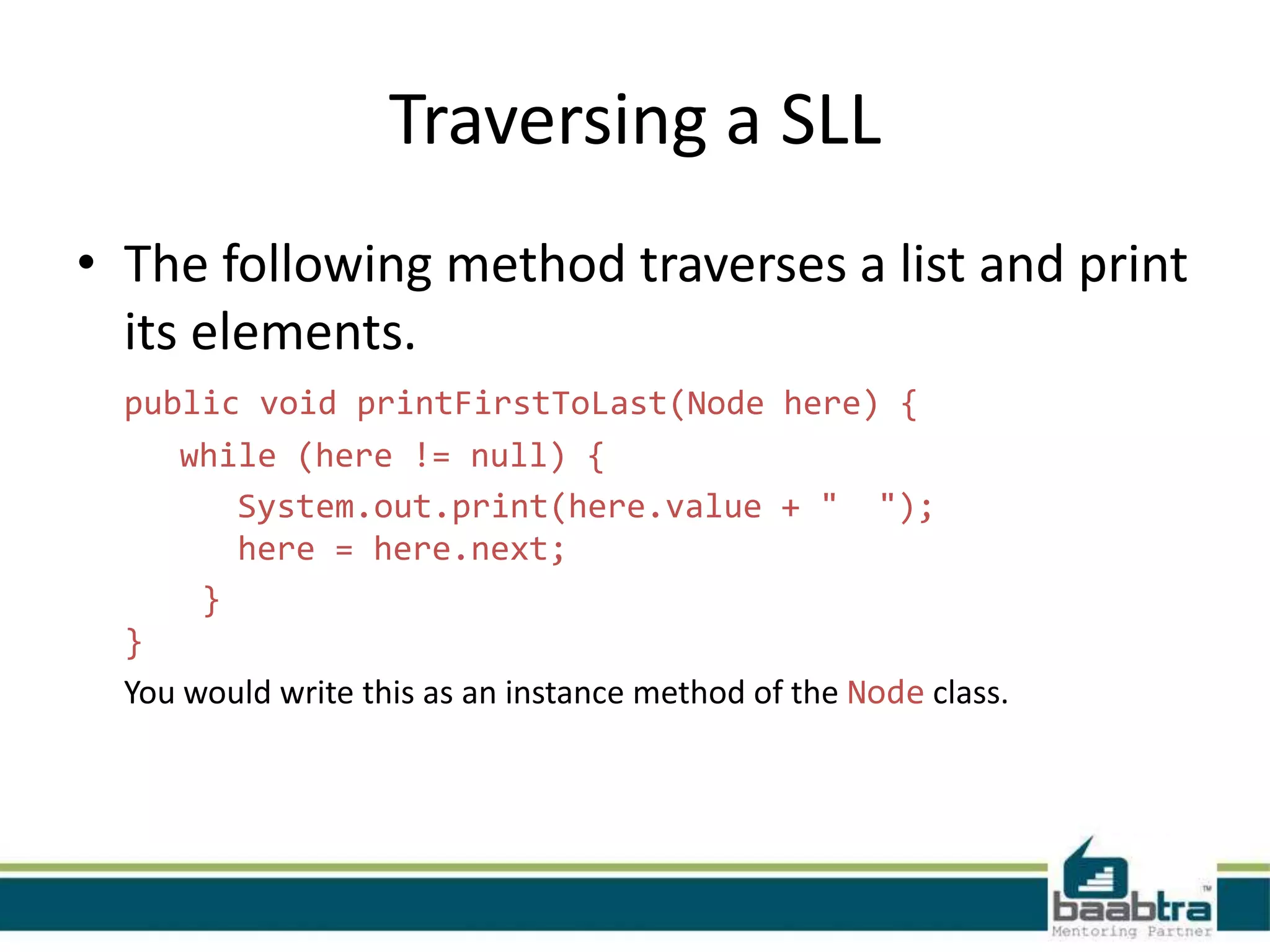
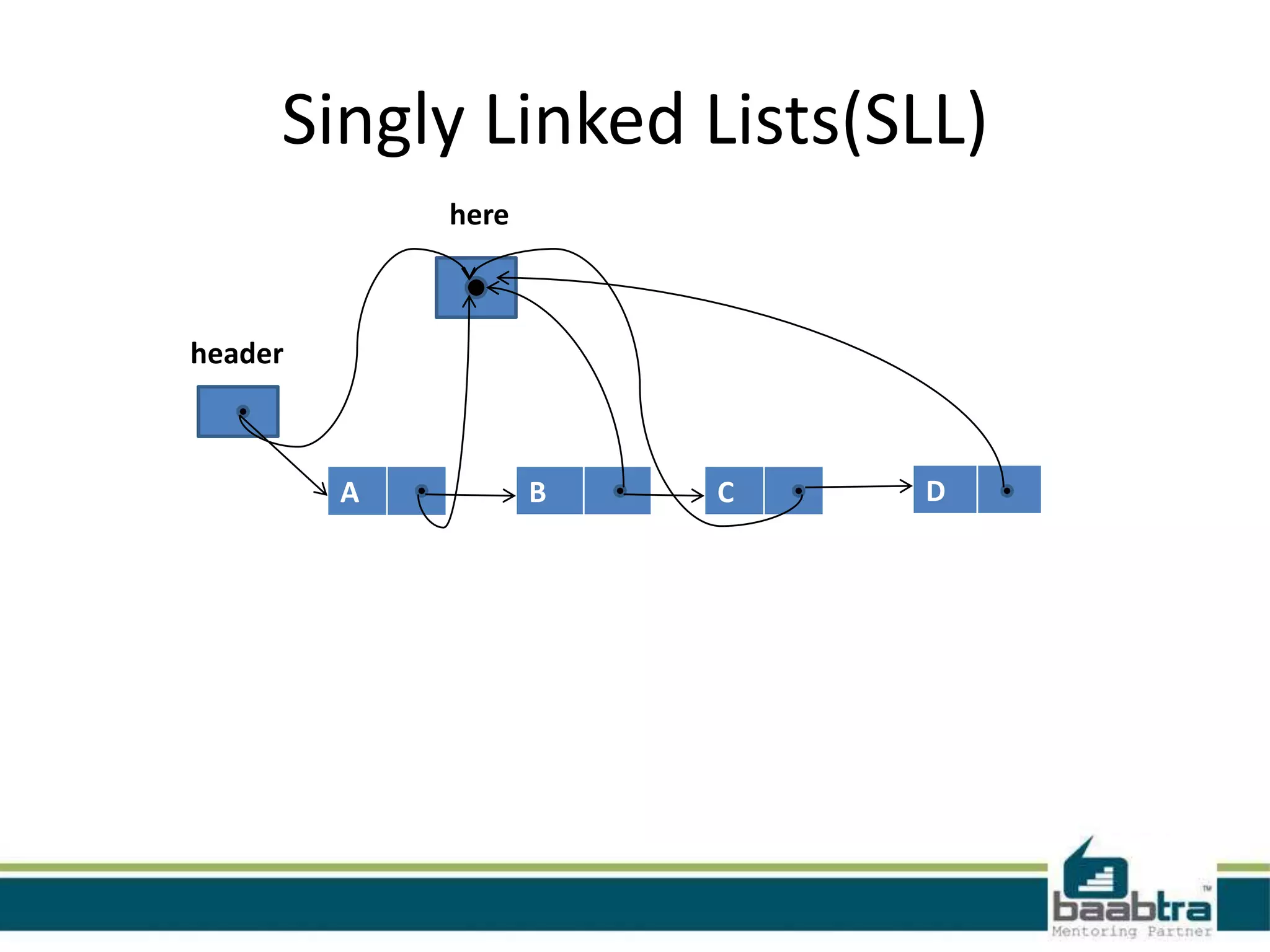
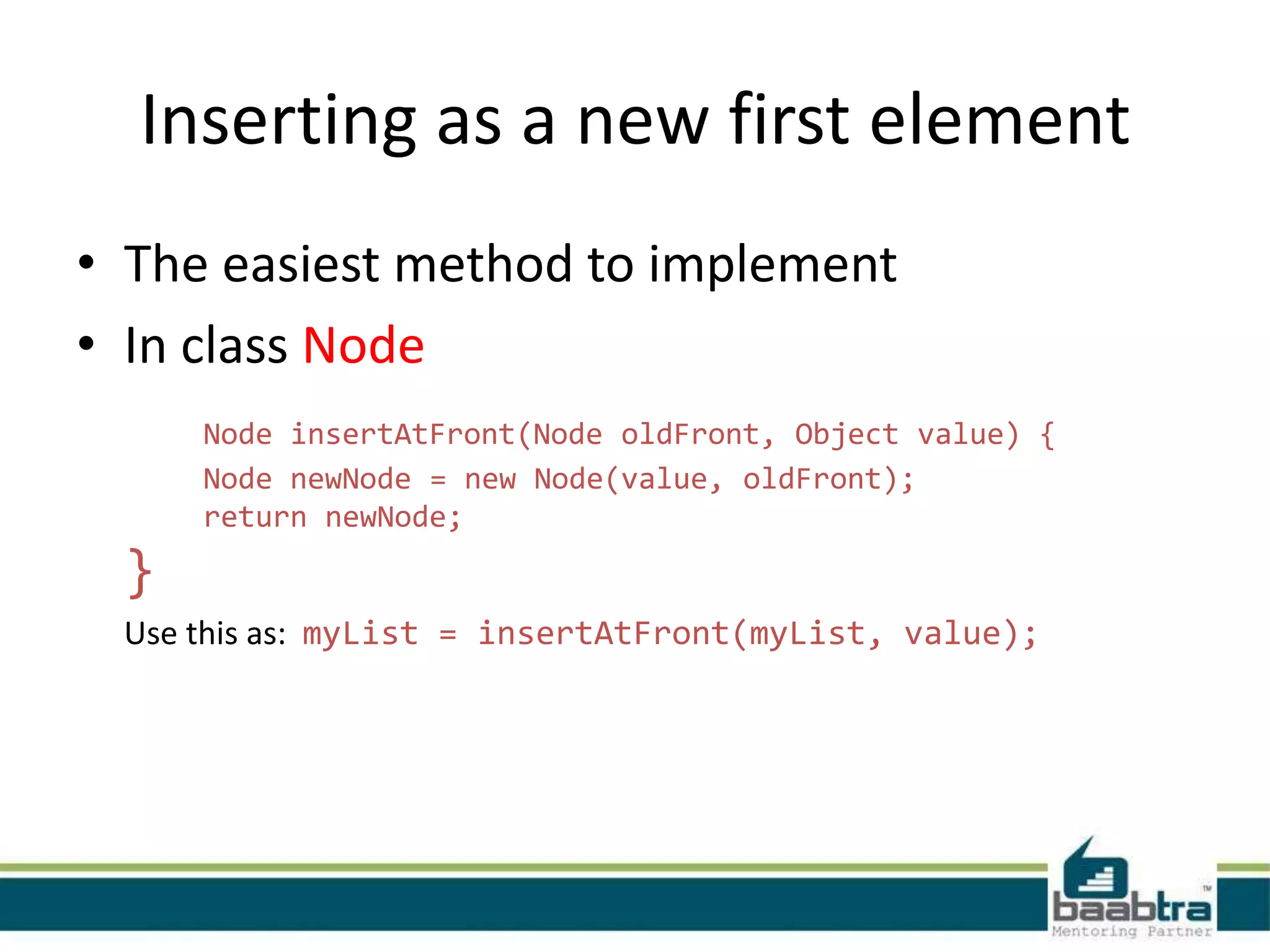
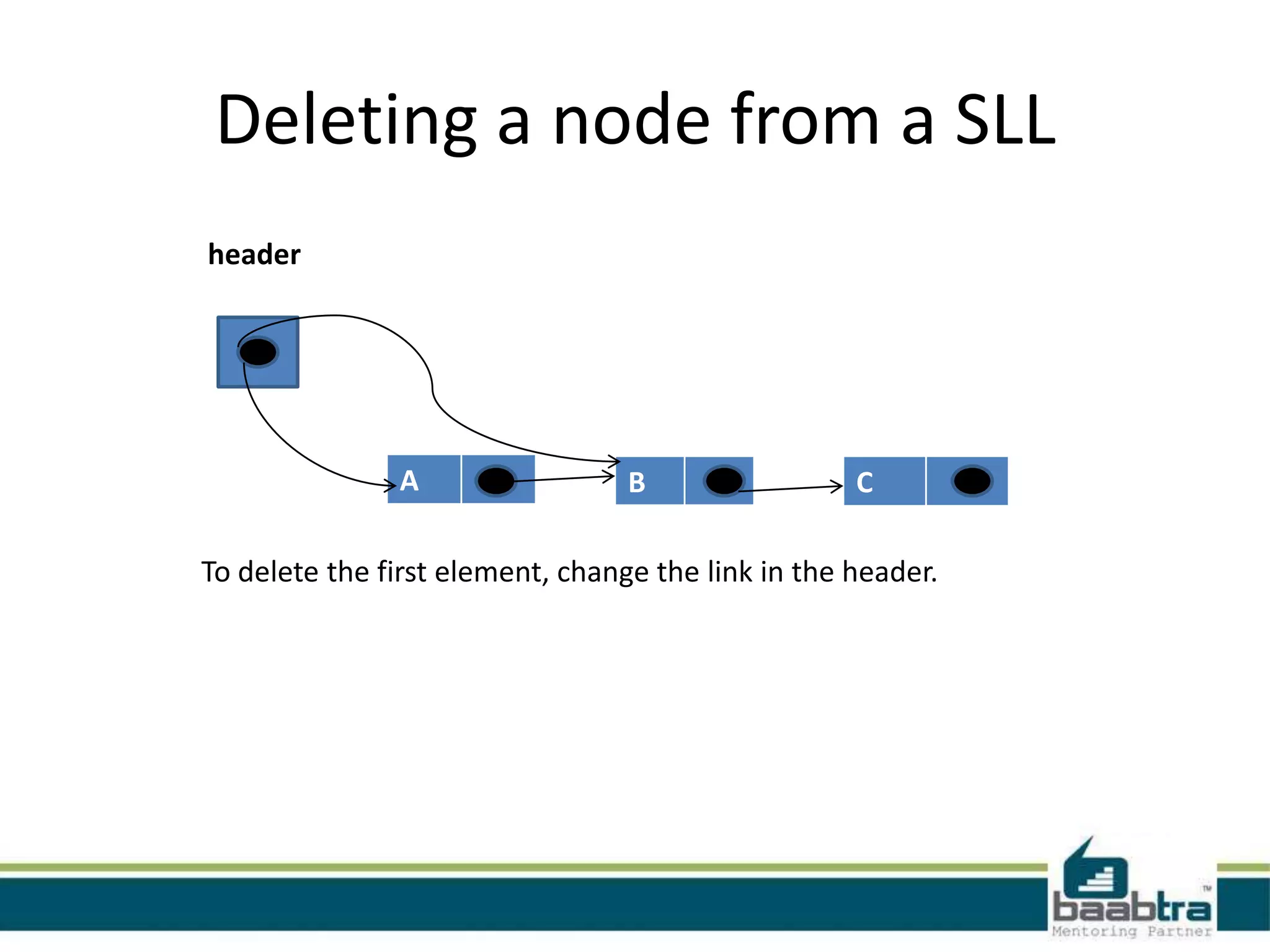
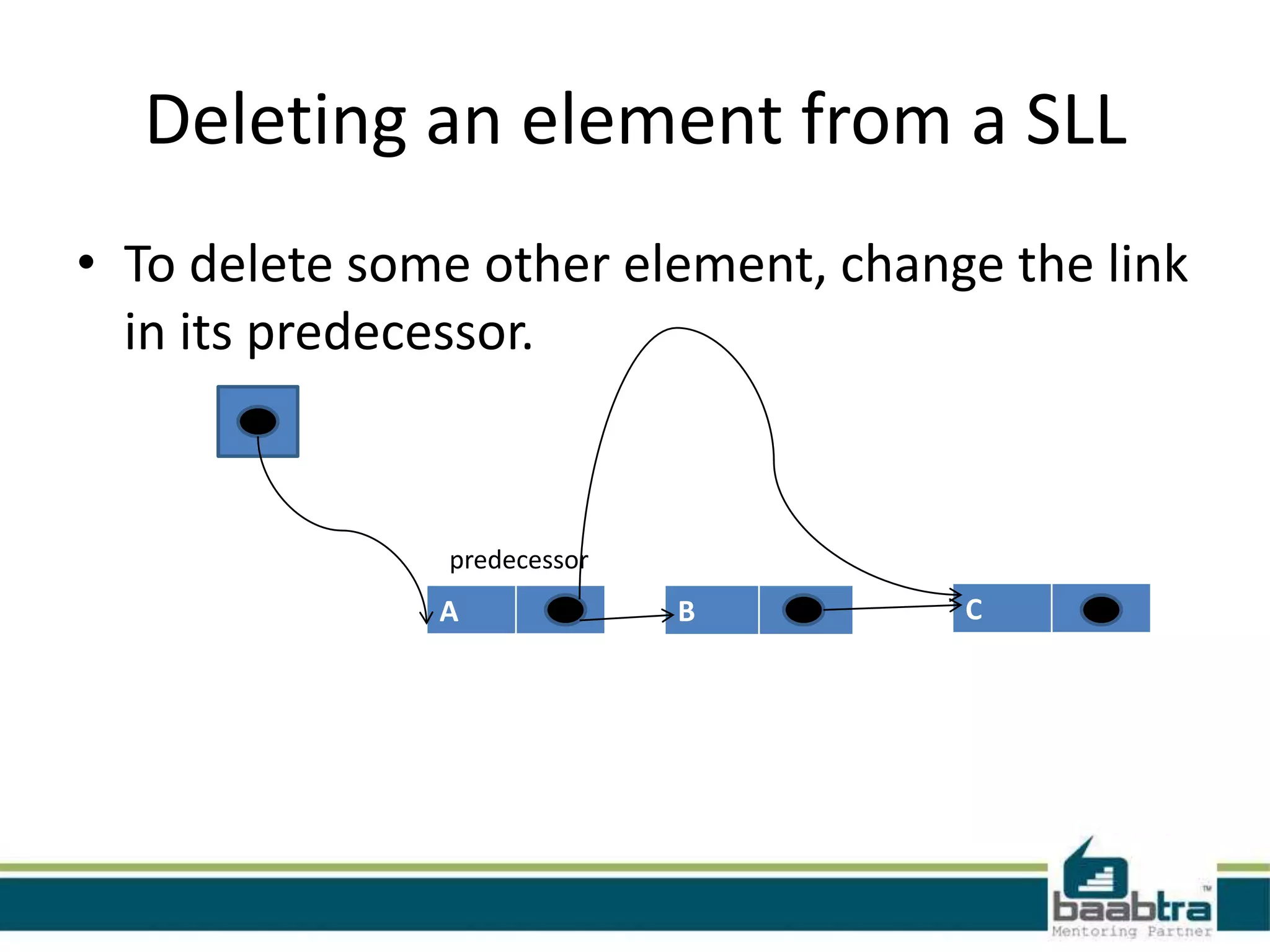
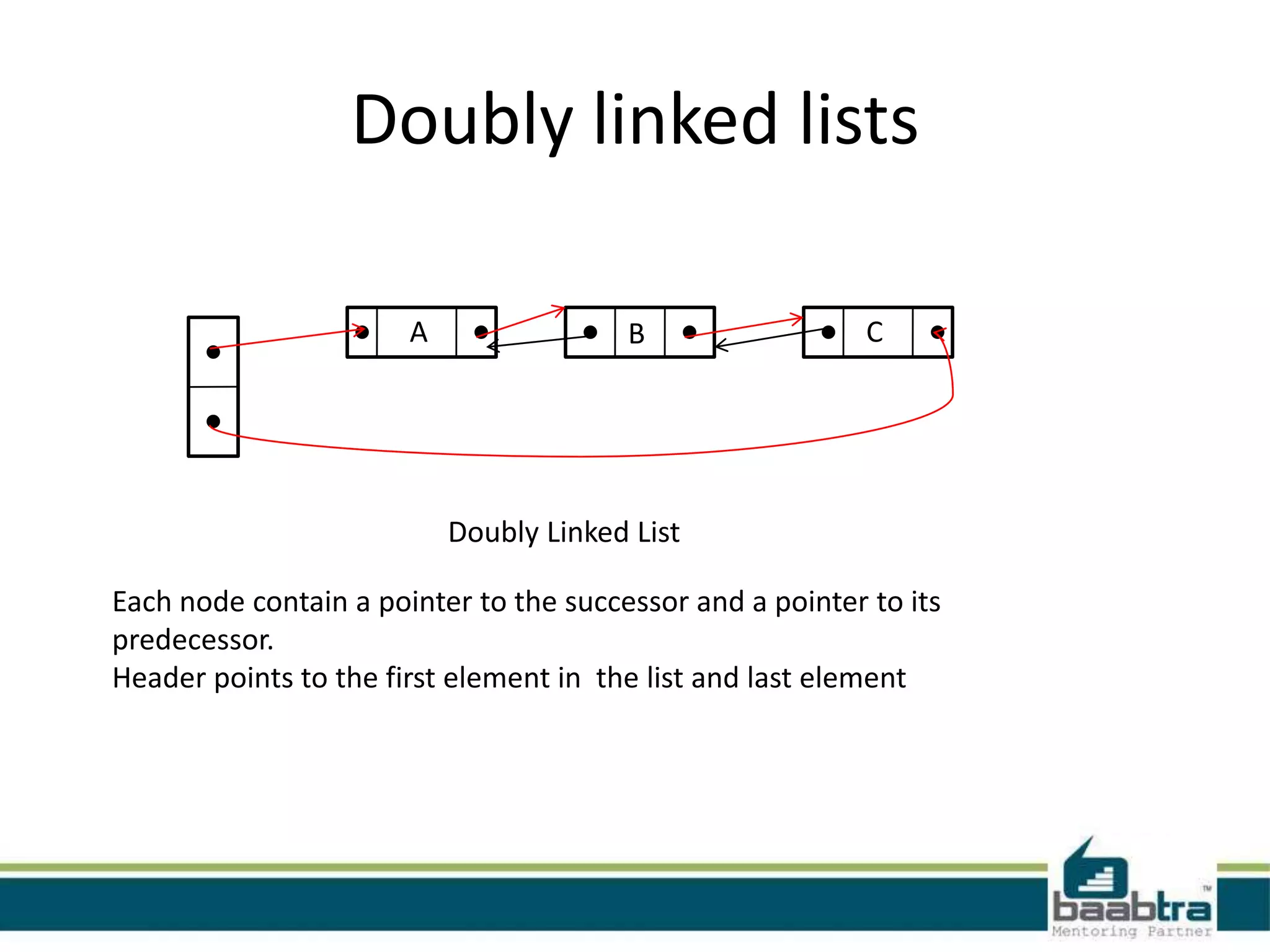
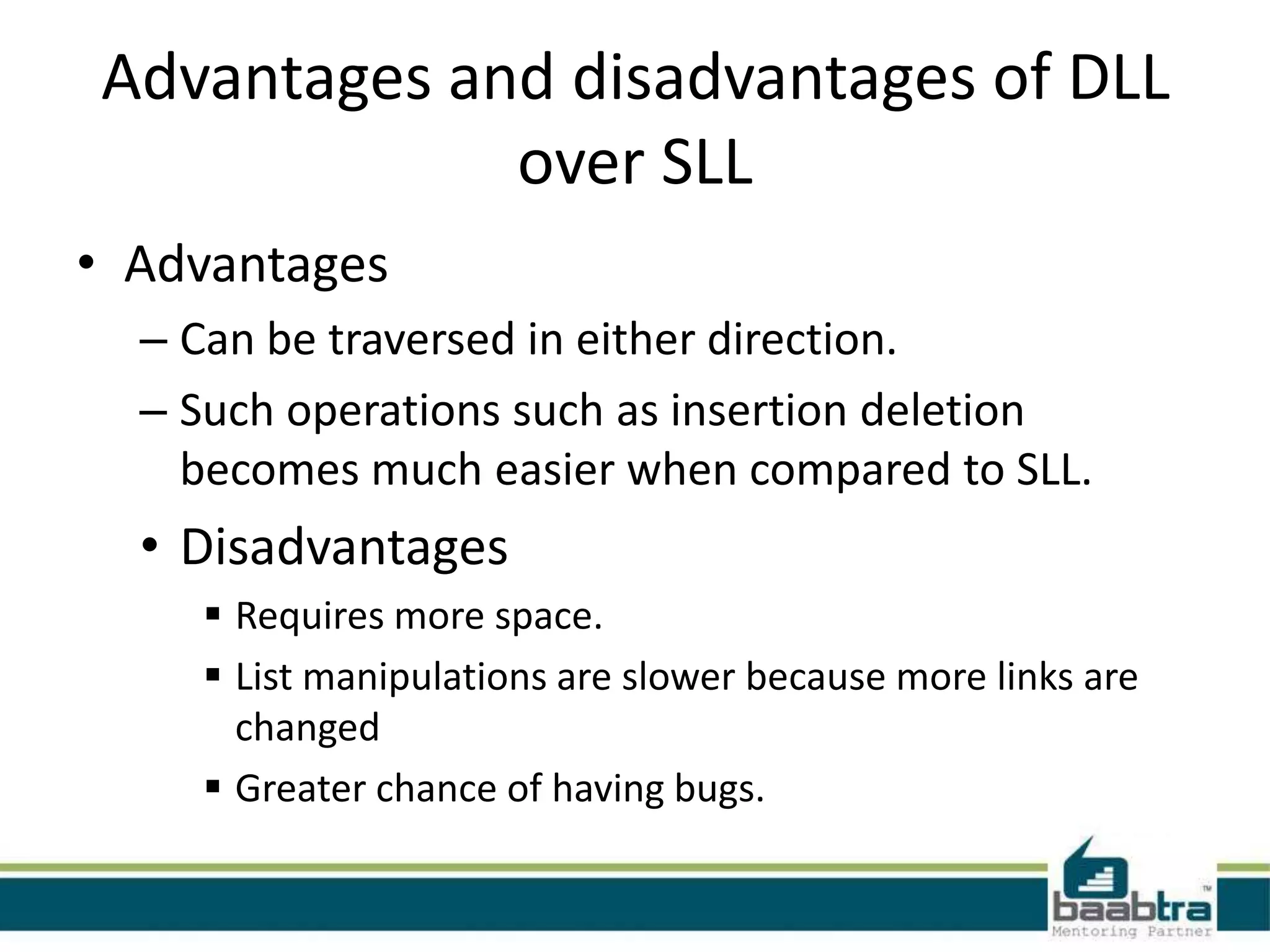
This document discusses linked lists and their implementation in programming languages. It begins by defining a linked list as a sequence of nodes where each node contains a value and a pointer to the next node. It describes the structure of singly linked lists and doubly linked lists. It then covers creating and traversing linked lists in Java using references rather than pointers. Finally, it discusses operations like inserting and deleting nodes from singly linked lists.