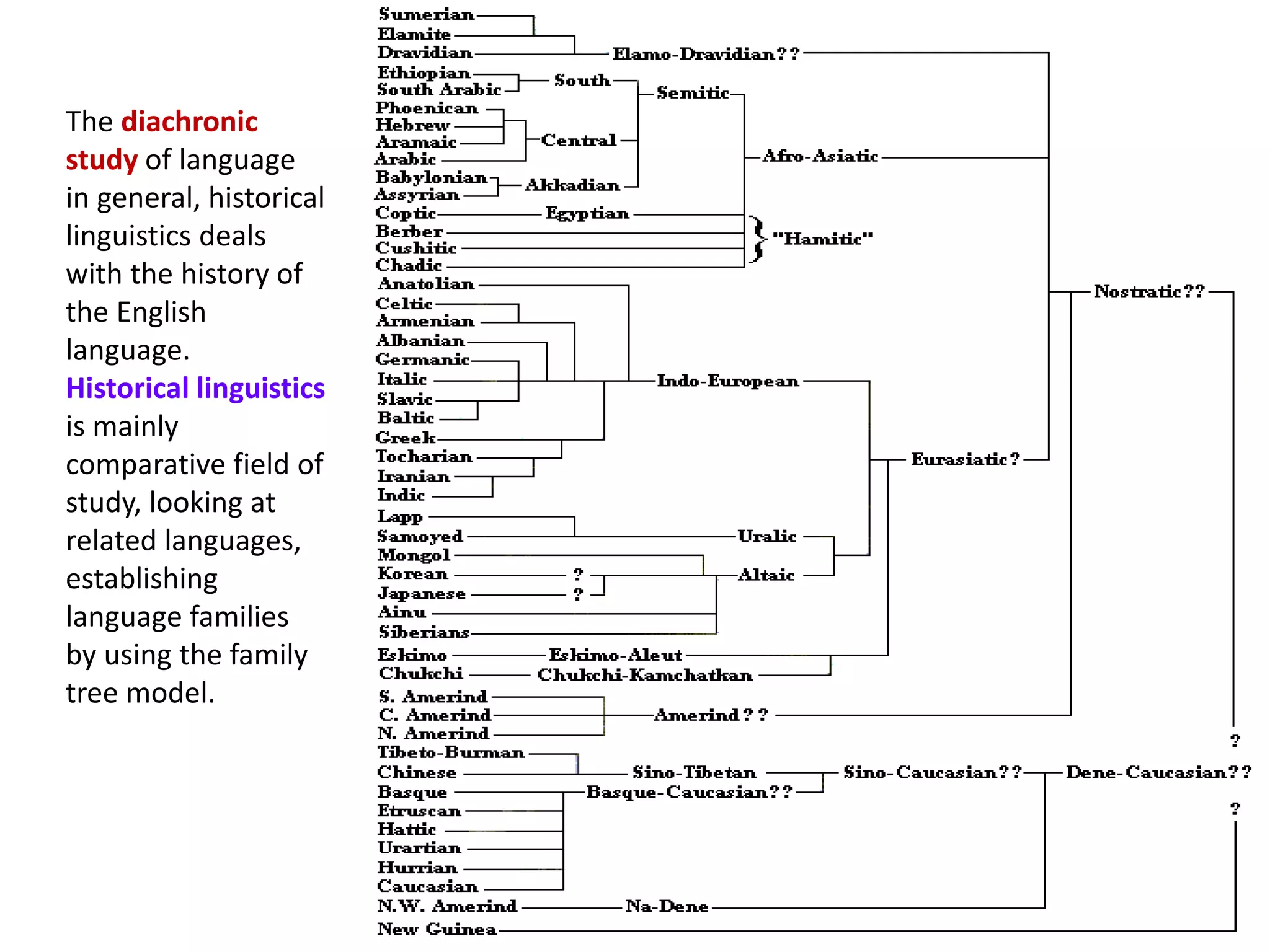
The document explores the origins and development of language, emphasizing its role as a human cognitive skill and a system of communication through sounds or gestures. It examines early theories of language origin, the evolution of writing systems, and the scientific study of linguistics, including its various branches and applications. The historical and comparative aspects of linguistics, as well as contributions by figures such as Noam Chomsky and Pāṇini, are also discussed.