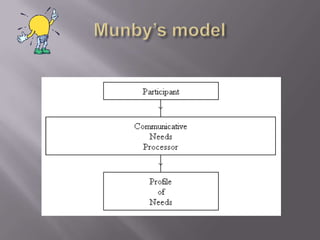
This document outlines a framework for analyzing English for specific purposes (ESP) with 7 categories: 1) purpose, 2) setting, 3) interaction, 4) instrumentality, 5) dialect, 6) target level, and 7) communicative event. It then applies this framework to analyze ESP for social science students, identifying key communicative events like lectures, seminars, and exams. It also discusses specifying an ESP syllabus by focusing on micro-skills, micro-functions, and linguistic forms. Finally, it summarizes criticisms of ESP models for lacking consistency and a clear link to syllabus design.