[DOCUMENT]: Universidad central del ecuador Facultad de filosofía letras y ciencia de la educación Carrera de idiomas Viviana Socasi 5to Semestre Francés
The document is from a university in Ecuador and discusses linguistics topics in 3 sentences or less:
1) It discusses the Carrera de idiomas (language career) at the Universidad Central del Ecuador's Faculty of Philosophy, Letters and Science Education.
2) It mentions Viviana Socasi and notes she is in her 5th semester studying French.
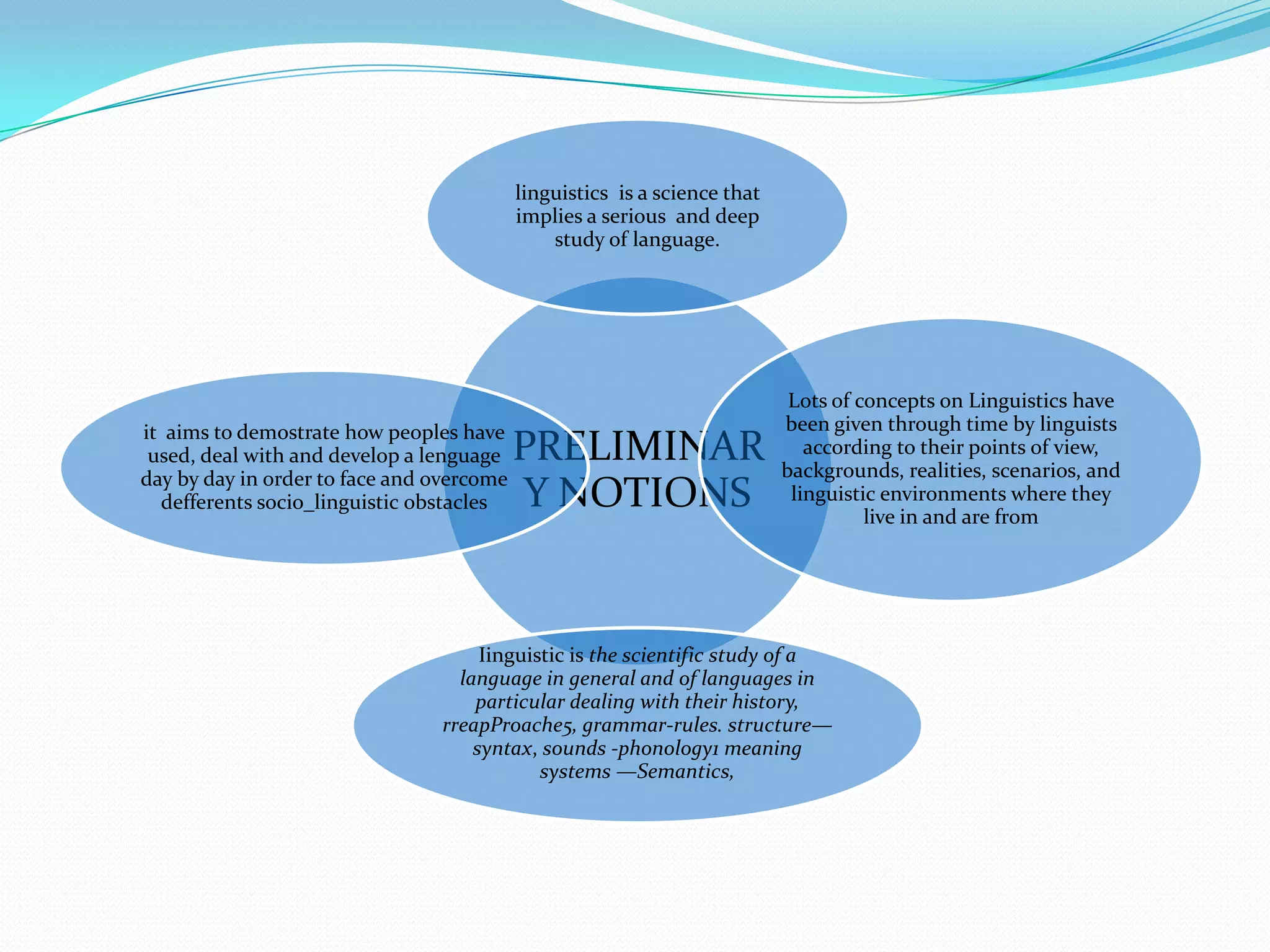
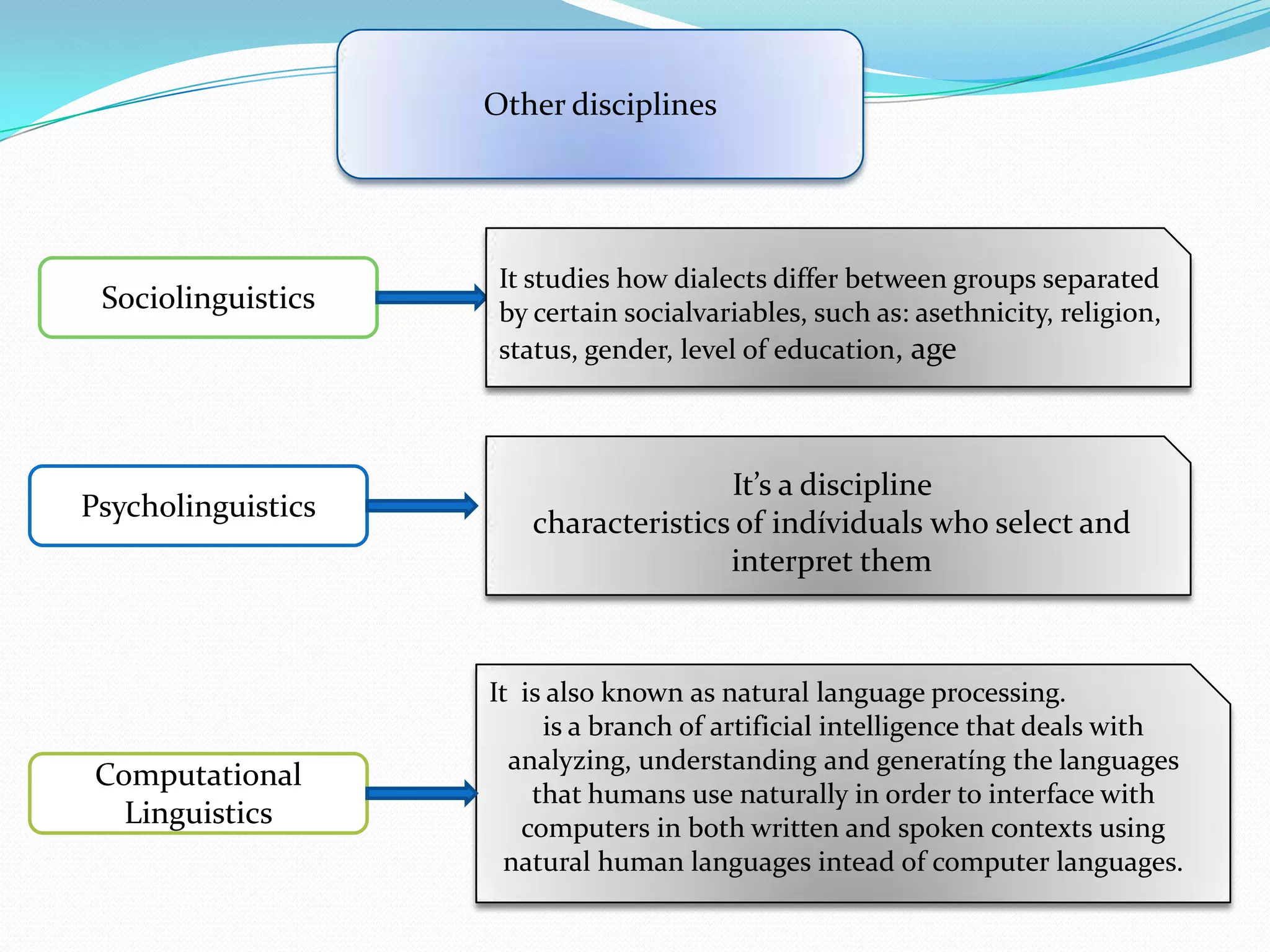
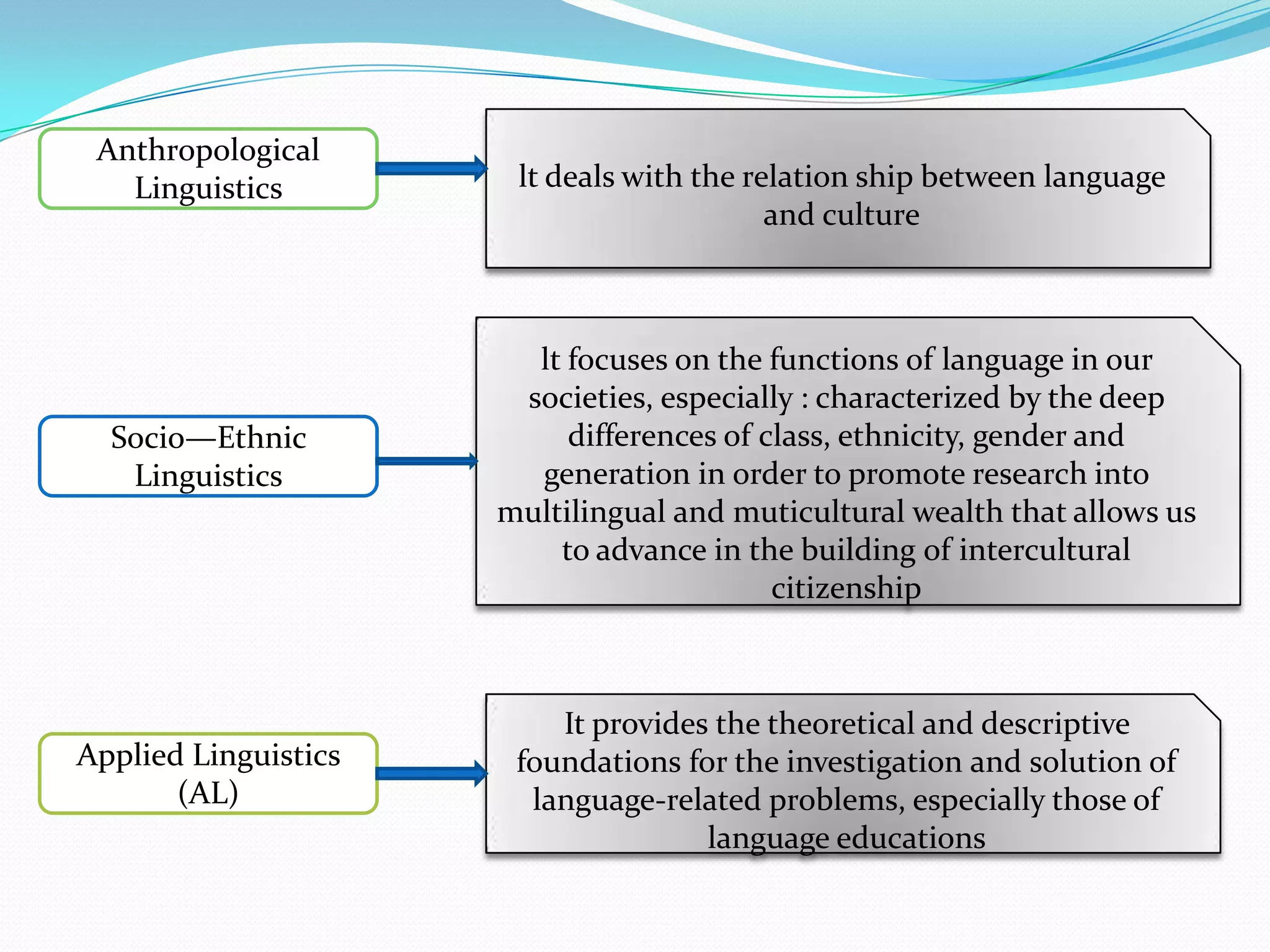
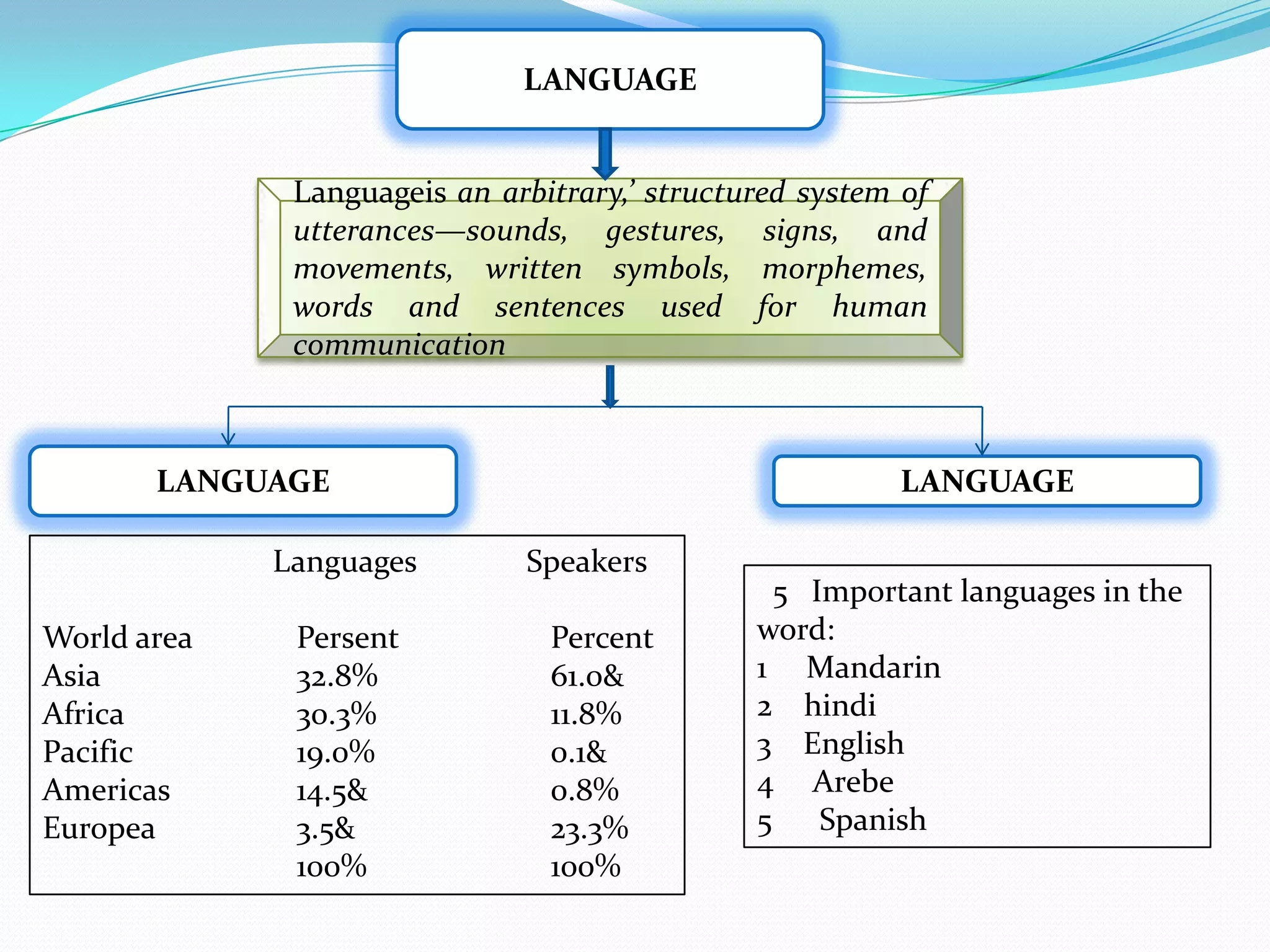
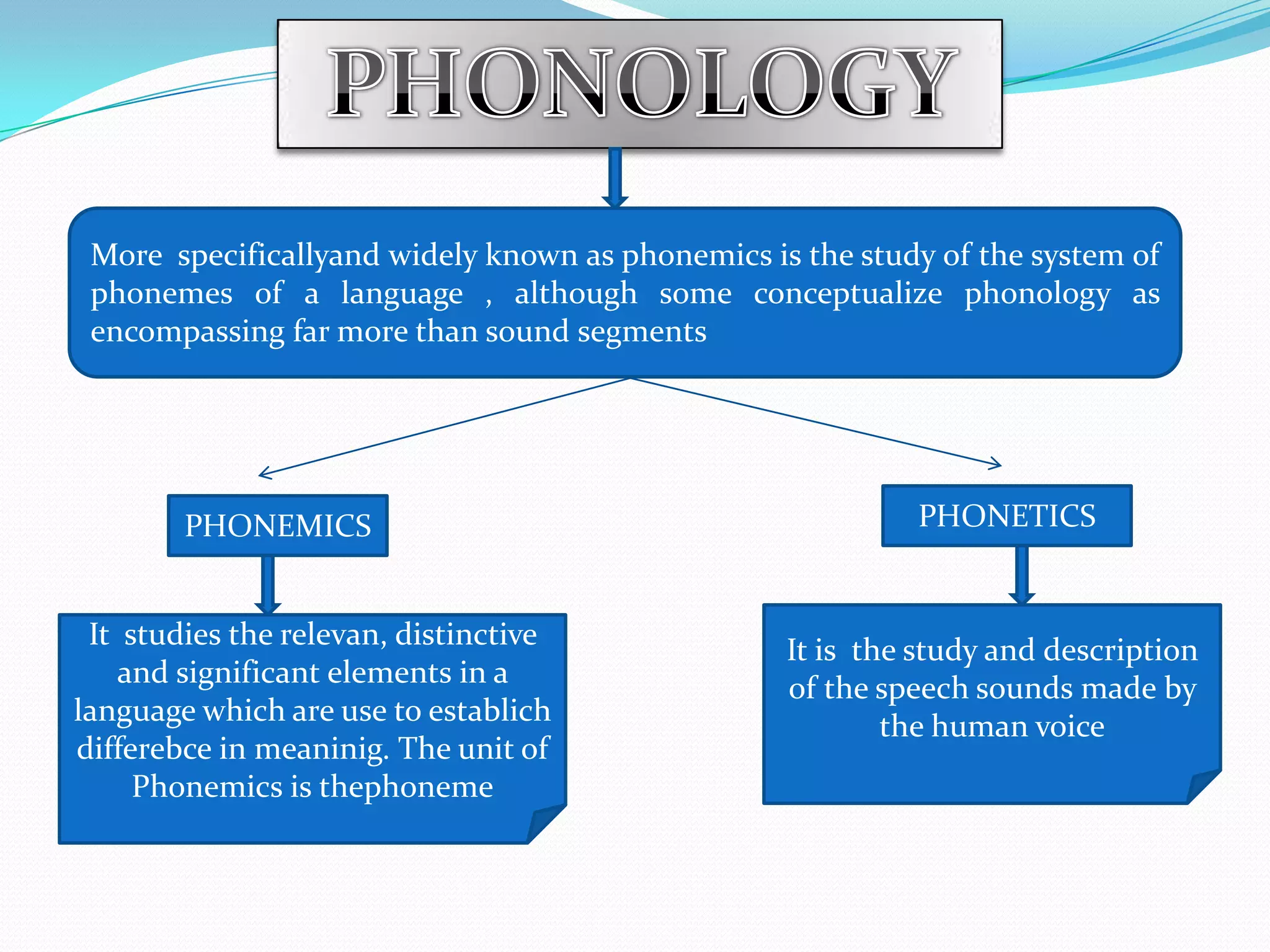
3) The document provides background information on linguistic topics like phonology, morphology, syntax and related disciplines in a introductory










![LANGUAGE INCONSISTENCIES
It is hte incompatibility, it is the quelity or state of being inconsistent lack of
concordance with a structural patten, these inconsistences happen due to 1,2,3,.
1 The same letter or letter combination can refer to different sounds
Spanish English Françe
Cine [ sine ] Gymnasium
Cama [ káma ] [dʒɪmneɪzɪəm]
Gynecology
[gainəkalədʒɪ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuadros-con-fonologia-120506195642-phpapp02/75/CONTRASTIVE-LINGUISTIC-por-VIVIANA-SOCASI-15-2048.jpg)
![The same sounds can be written with diffrent
2 letters or letters combinations
SPANISH ENGLISH FRANÇE
Bonito Gypsy [ dʒɪpsɪ] Risquer [riske]
[ bo 'ni to ] Canjugate [ kandʒ ə get ] Kenya [kenja]
Vacaciones
[ ba ka 'θjo nes ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuadros-con-fonologia-120506195642-phpapp02/75/CONTRASTIVE-LINGUISTIC-por-VIVIANA-SOCASI-16-2048.jpg)
![Diffrent dialects pronounce the same worl
3 differently
SPANISH ENGLISH FRANÇE
Mismo [mísmo] s.e- Milk [mɪlk ] britanico Crime [kRim]
Mismo [míhmo] c.e Mik [məlk] ingles Crime [krim]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuadros-con-fonologia-120506195642-phpapp02/75/CONTRASTIVE-LINGUISTIC-por-VIVIANA-SOCASI-17-2048.jpg)






![TRANSCRIPTION:
It is a systems of notation that represents utterances or partial
utterrances of a language pronounced by people in general
BROAD TRANSCRIPTION: Also PE DAGOGICAL HINTS: Marking stress in booth
identified as Phonemic Trascription, its monosyllabic and multisyllabic words issome
the notation that represent utterances of didactic advice for students to be able to use and
language by indicating only the significat pronounce properly thestressed syllables in words.
and underlying sounds (phonemes) that
make up a word
NARROW TRANSCRIPTION: It is written
between square brackets (phonetic bracket): []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuadros-con-fonologia-120506195642-phpapp02/75/CONTRASTIVE-LINGUISTIC-por-VIVIANA-SOCASI-26-2048.jpg)
![SYMBOLS USED FOR TRASCRIPTION
Stress mark It shows the following syllable is
stressed.
´
Angle brackets They are used to enclose the
spelling of the orthographic
< > notation.
Slant brackets Phonemic trascriptionuses
them.
//
Square brackets They are used arounddetailed
phonetic trascription.
[]
Vertical line It shows a pause in phonetic
trascription.
Division marker . It shows the boundaries
between syllables.
Diacritics It shows the variation in the
vowel or consonant quality.
Nasal or dark quality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuadros-con-fonologia-120506195642-phpapp02/75/CONTRASTIVE-LINGUISTIC-por-VIVIANA-SOCASI-27-2048.jpg)