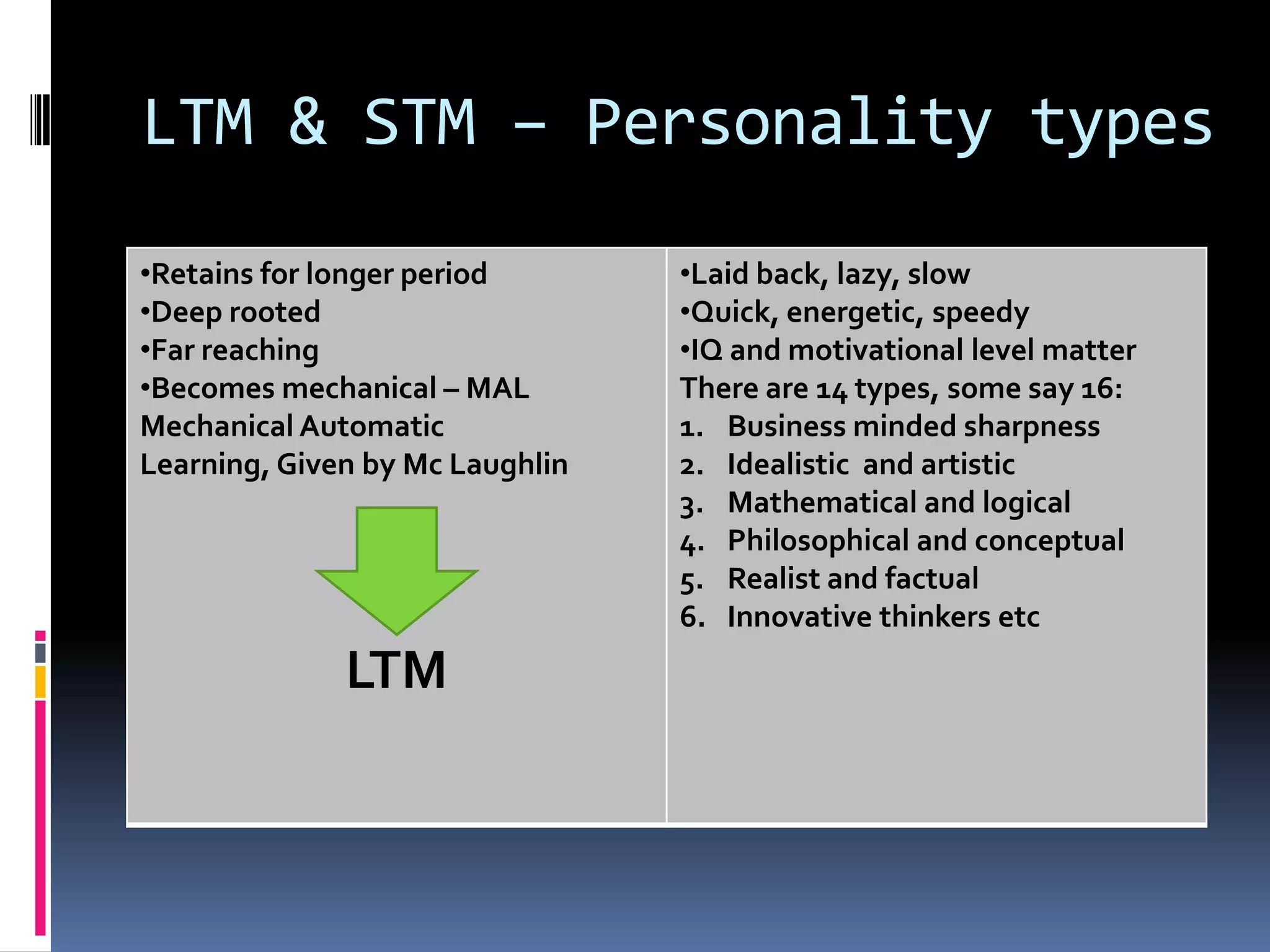
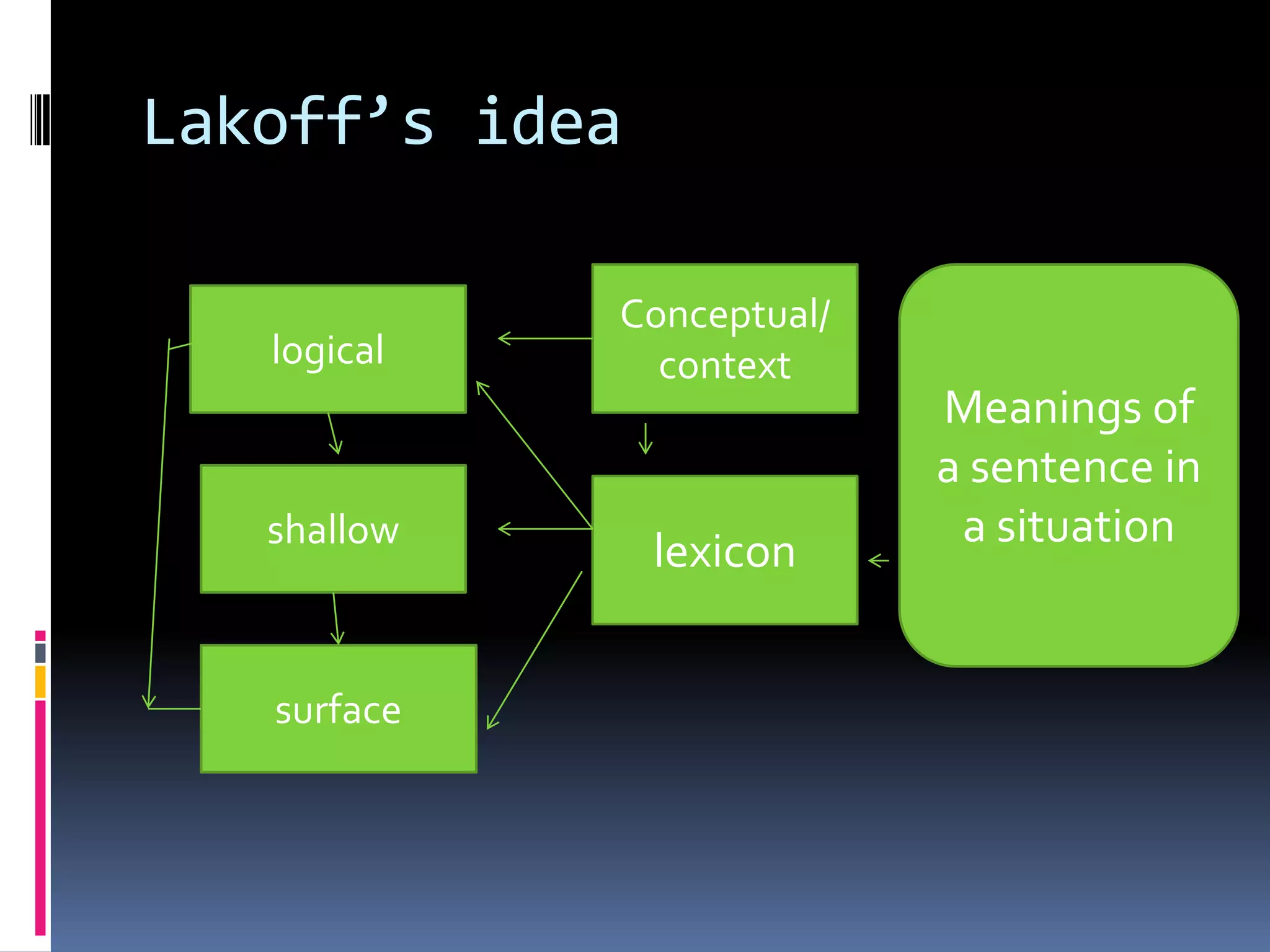
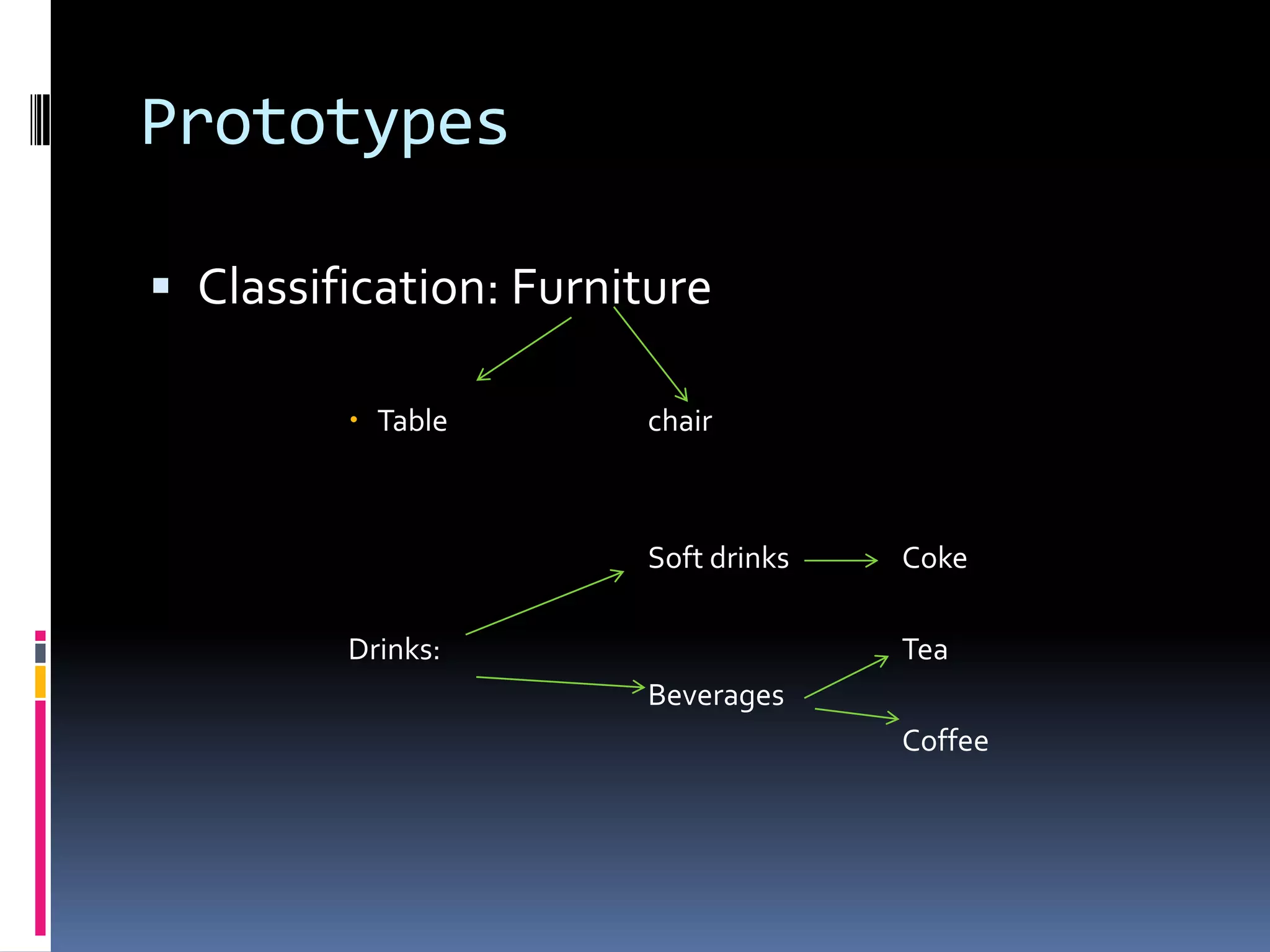
This document provides an introduction to applied linguistics and outlines several subfields. It discusses micro linguistics including phonetics, phonology, syntax, morphology, semantics. It then covers macro linguistics such as sociolinguistics, psycholinguistics, stylistics, anthropological linguistics, and philosophical linguistics. It provides definitions and examples of concepts within each subfield.