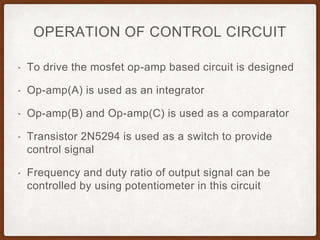
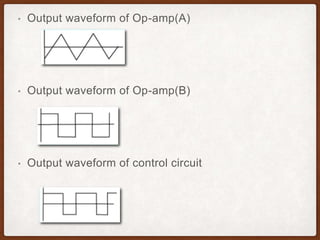
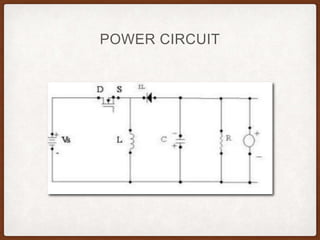
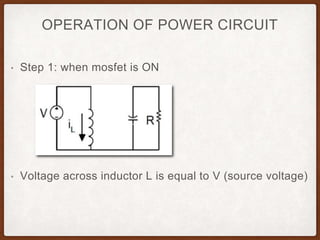
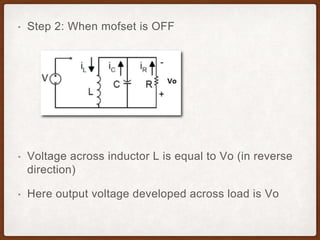
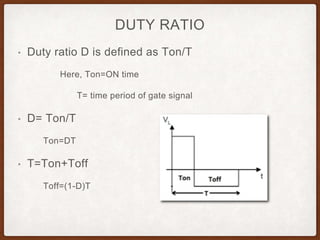
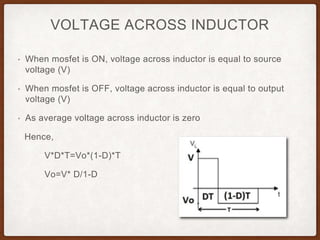
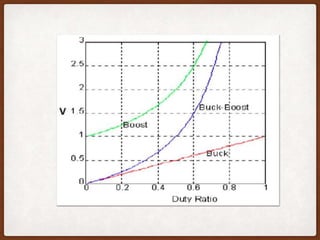
The document describes the operation of a buck-boost converter. It discusses how the buck-boost converter can operate in both buck and boost modes depending on the duty ratio of the control signal. It also explains the control circuit design using op-amps, the transistor switch, and how the frequency and duty ratio can be controlled. Finally, it discusses the power circuit operation in three steps and how the output voltage is determined based on the duty ratio and input voltage.