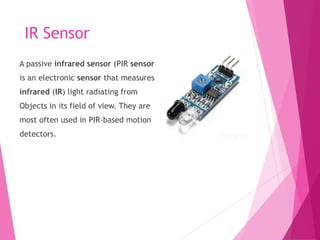
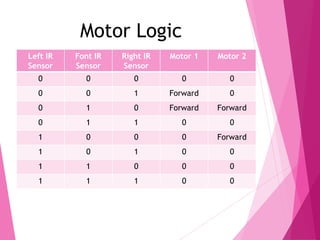
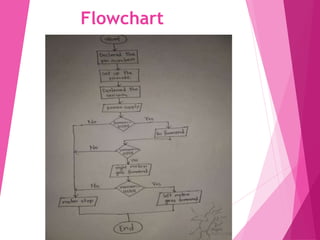
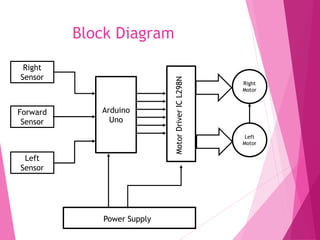
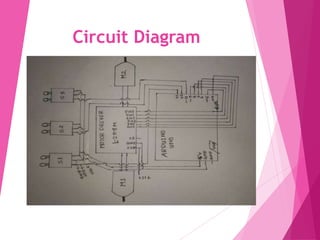
This document describes a line following robot project built using an Arduino microcontroller. It lists the components used, which include the Arduino UNO, IR sensors, an L298N motor driver, DC motors, and a chassis. It explains the working principle of how the IR sensors detect a line and the motor driver is used to control the DC motors to follow the line. Diagrams of the circuit, programming code, potential applications, and advantages/disadvantages of the line following robot are also provided.