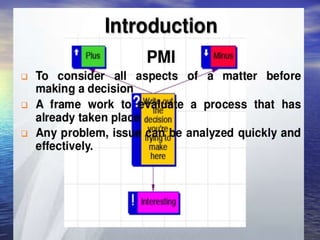
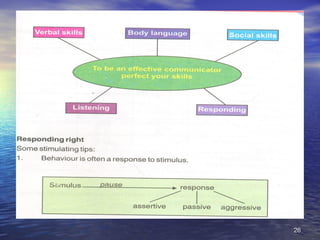
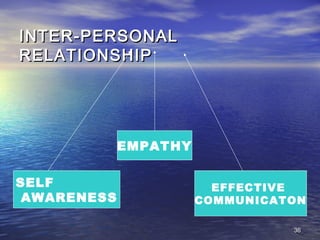
- Life skills are abilities that help individuals deal effectively with daily life demands and challenges. They include self-awareness, problem-solving, decision-making, critical thinking, creative thinking, interpersonal relationships, communication, empathy, coping with stress and emotions, and other skills.
- Major initiatives promoting life skills education began in the 1990s by WHO and UNICEF to support complete physical, mental and social well-being.
- Developing life skills can facilitate well-being by helping people effectively address problems, make decisions, and interact with others.