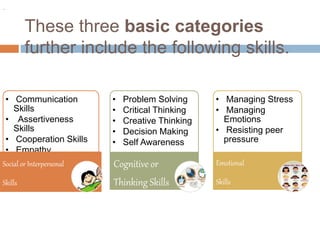
The document outlines life skills education defined by various organizations, emphasizing that these skills involve a balance of knowledge, attitudes, and abilities essential for dealing with everyday challenges. It categorizes life skills into three basic areas: social, cognitive, and emotional skills, detailing specific competencies such as communication, problem-solving, and empathy. The aim is to equip individuals with the necessary abilities to lead productive and satisfying lives while fostering positive interpersonal relationships.