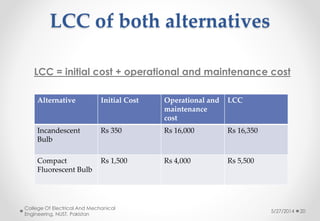
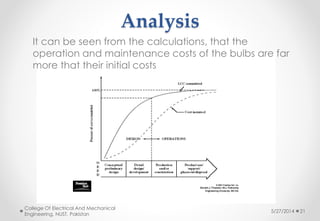
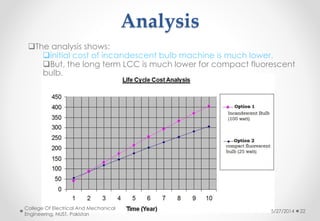
This document discusses life cycle cost analysis and presents a case study comparing the total costs of incandescent and compact fluorescent light bulbs over 10,000 hours of use. It finds that while the initial cost of incandescent bulbs is lower, the operational and maintenance costs over the bulbs' lifetimes are much higher. As a result, the total life cycle cost of incandescent bulbs is about $16,350 compared to around $5,500 for compact fluorescent bulbs, making compact fluorescent bulbs the more economical choice over the long run.