Embed presentation
Download to read offline
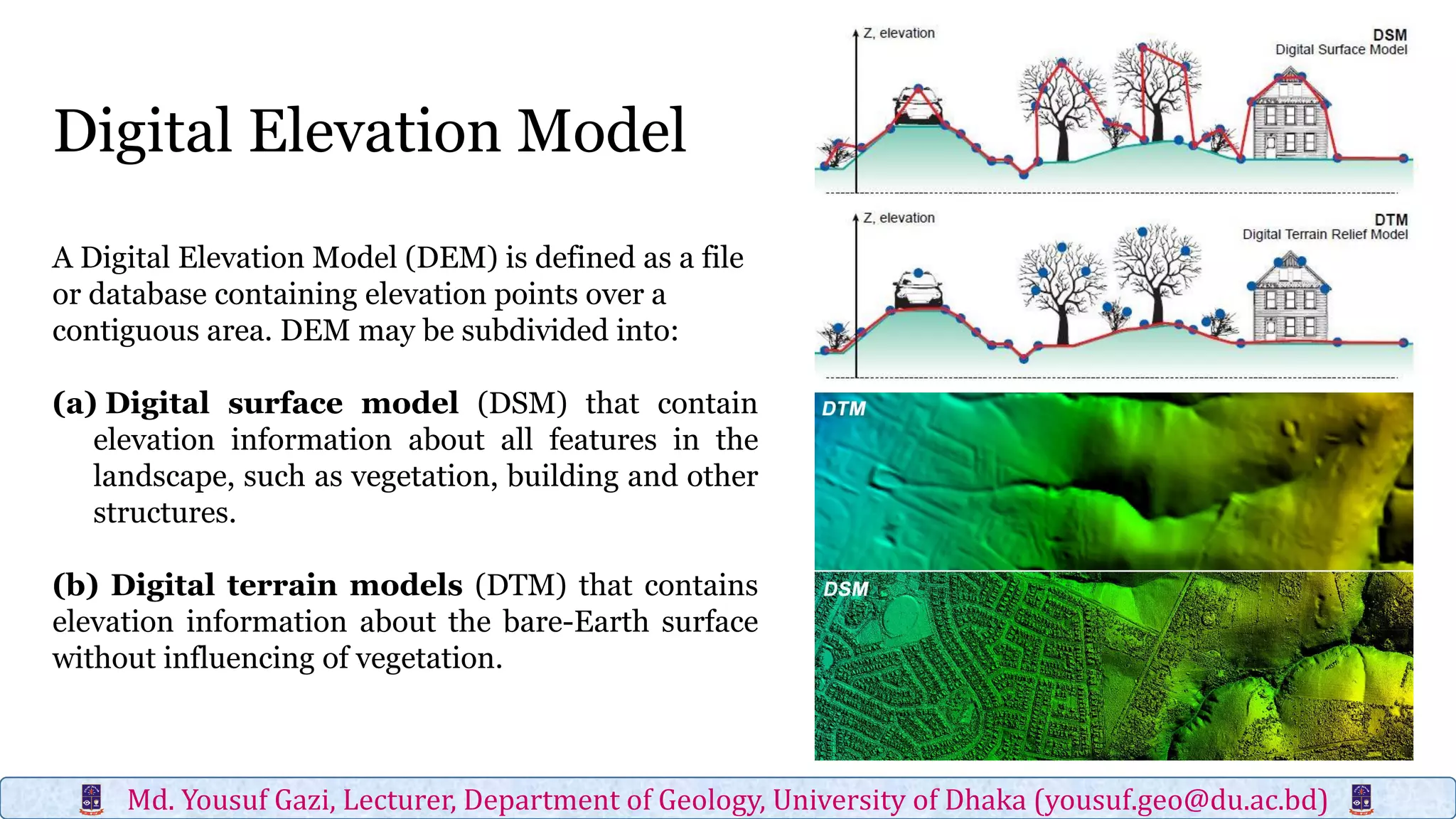

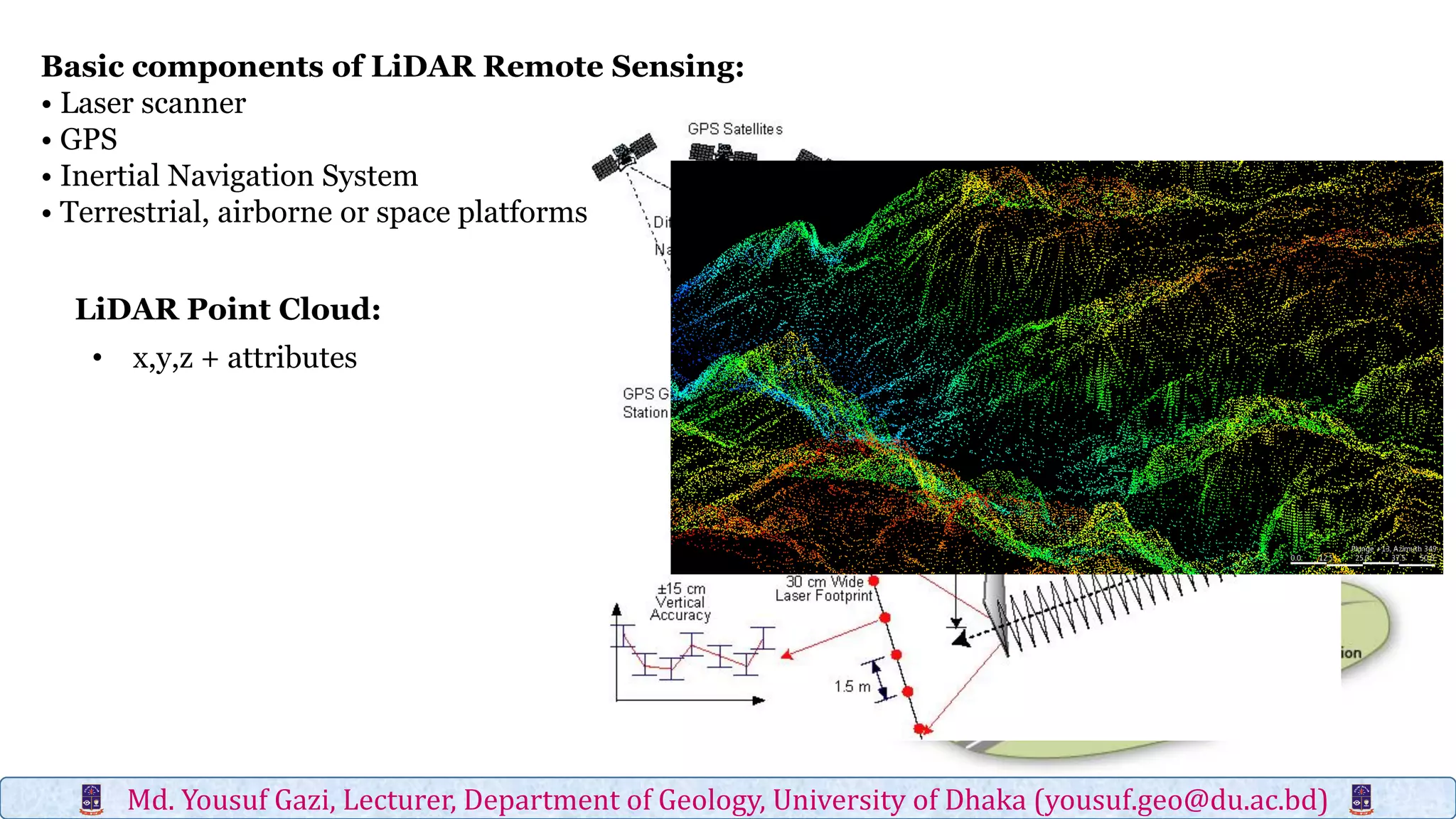
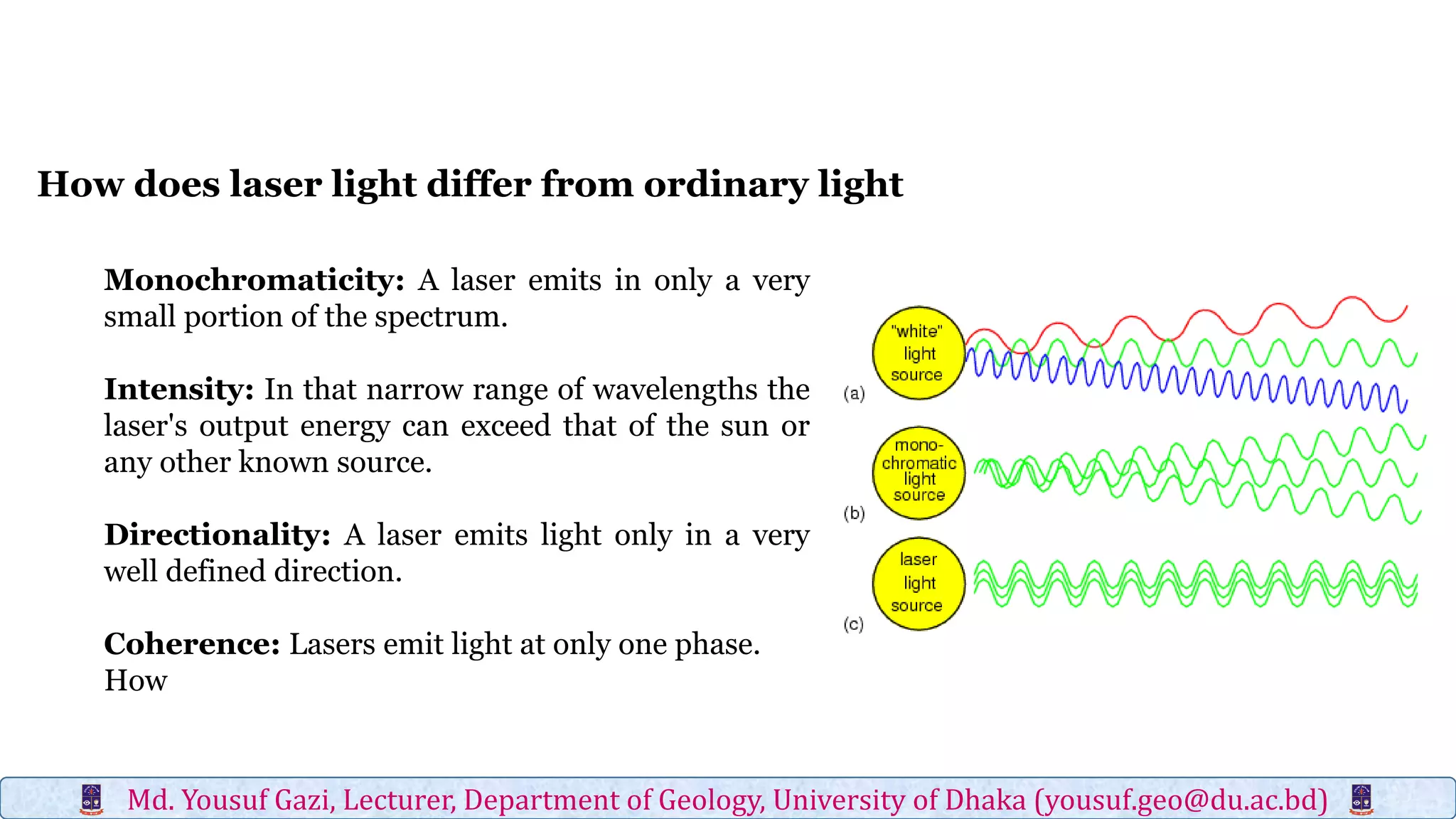

Digital elevation models (DEMs) contain elevation point data over a contiguous area and can represent bare earth surfaces (digital terrain models) or elevations of all landscape features, including vegetation and structures (digital surface models). Light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is one of four major technologies used to obtain high-resolution elevation data and create DEMs, along with in situ surveying, photogrammetry, and interferometric synthetic aperture radar. LiDAR uses laser scanners mounted to terrestrial, airborne, or spaceborne platforms to measure elevations of the terrain and return precise three-dimensional location data.





