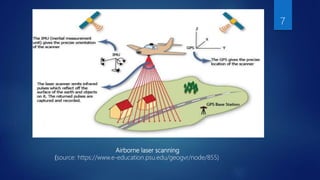
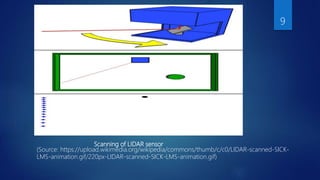
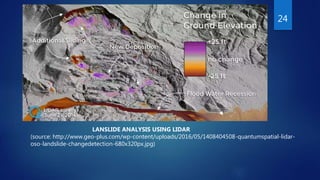
The document discusses the use of LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology in civil engineering applications. It describes LIDAR's components, principles of operation, and its advantages over other remote sensing methods. Key applications mentioned include topographic and hydrographic surveying to generate digital terrain models, bridge clearance measurement, and sewer inspection. The document concludes that LIDAR offers highly accurate data collection with minimal human involvement.