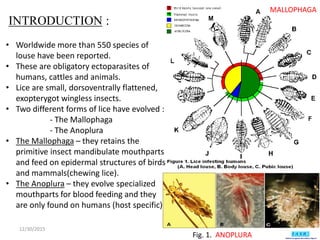
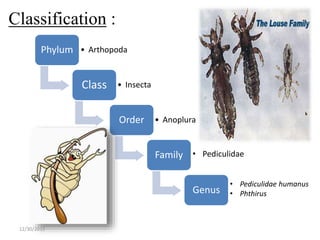
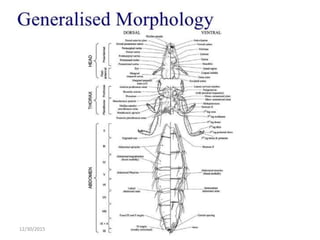
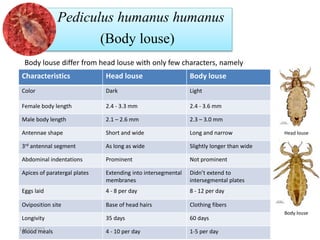
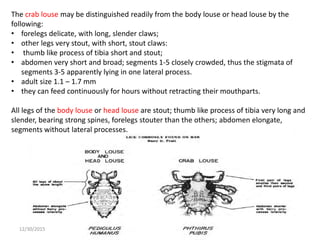
The document discusses lice, specifically focusing on the three types of human lice: head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis), body lice (Pediculus humanus corporis), and pubic lice (Pthirus pubis), detailing their characteristics, life cycles, and modes of transmission. It highlights the medical importance of lice due to their ability to spread diseases, especially through body lice. The document also outlines collection and preservation techniques for lice specimens.