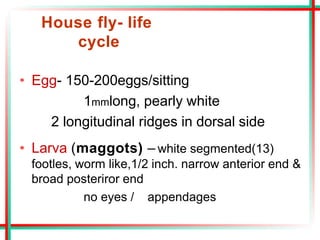
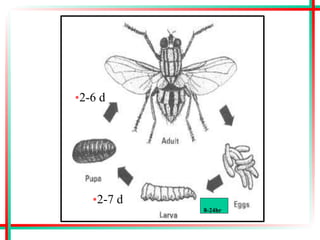
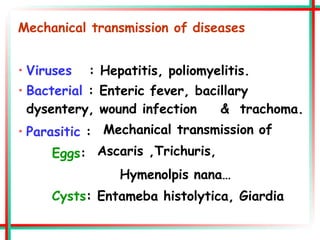
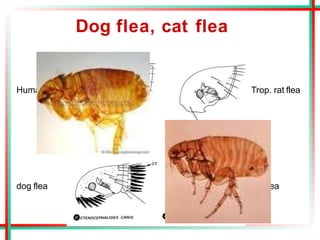
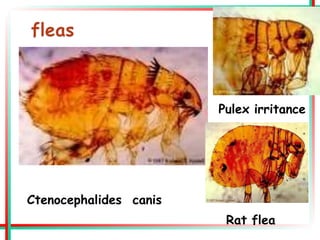
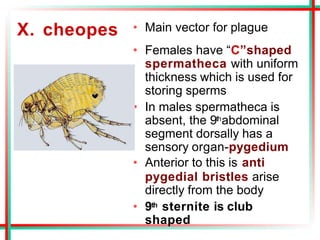
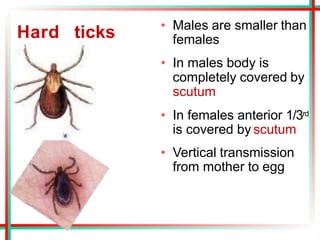
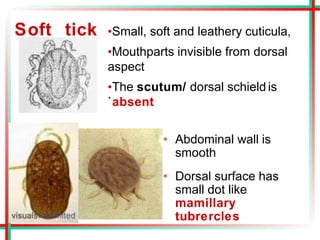
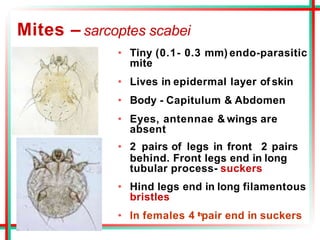
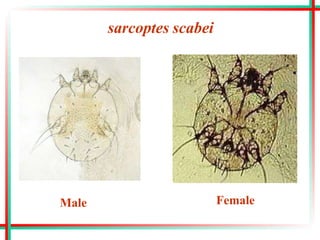
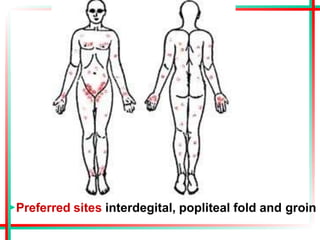
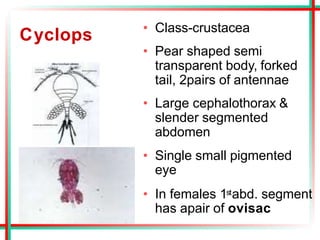
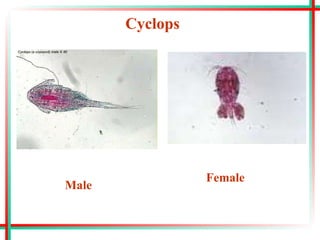
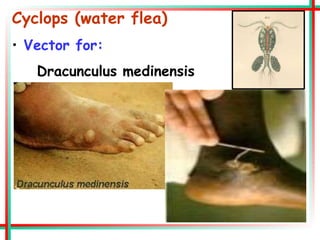
This document summarizes various insects of public health importance including mosquitoes, flies, lice, fleas, ticks, mites, and water fleas. It describes the key physical features and life cycles of insects like house flies, sand flies, dog and rat fleas, head and body lice, hard and soft ticks, scabies mites, and water fleas. It also discusses diseases transmitted by these insects including malaria, leishmaniasis, plague, typhus, and guinea worm and methods of control like insecticides, sanitation, and biological controls.