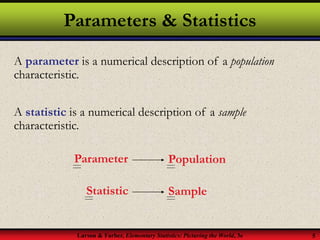
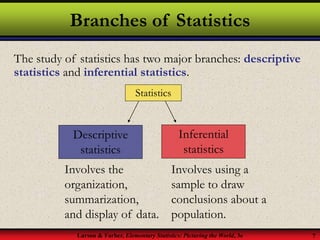
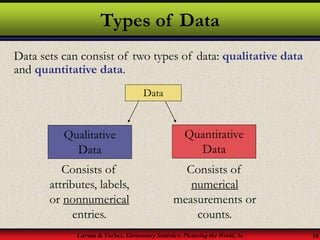
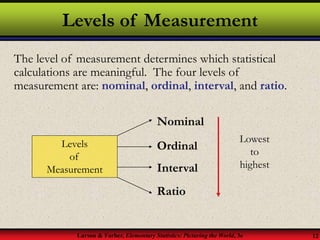
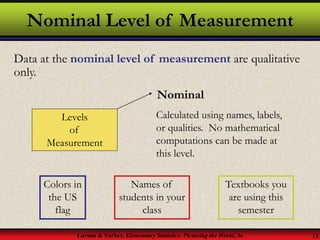
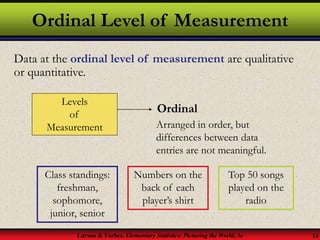
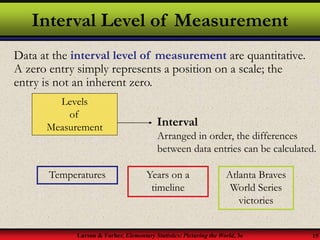
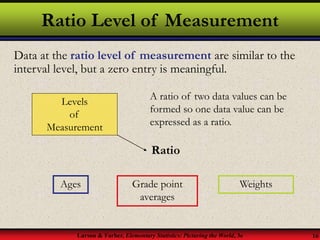
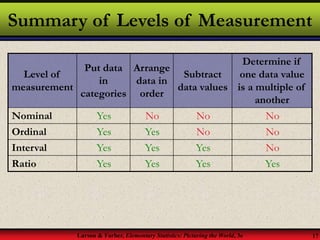
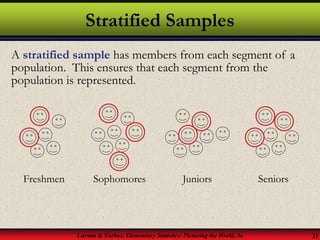
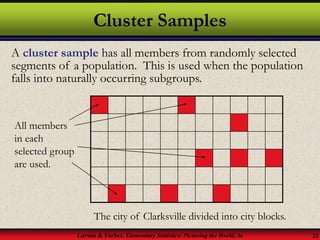
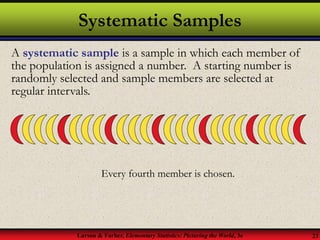
This document provides an introduction to statistics, including definitions of key terms. It discusses how statistics involves collecting, organizing, analyzing and interpreting data. A population is the entire set of data, while a sample is a subset of a population. Parameters describe populations and statistics describe samples. There are two main branches of statistics - descriptive statistics which organizes and summarizes data, and inferential statistics which uses samples to draw conclusions about populations. Data can be qualitative like names or quantitative with numerical values, and have different levels of measurement from nominal to ratio. Experimental design involves identifying variables of interest and collecting representative data using methods like surveys, experiments or sampling techniques.