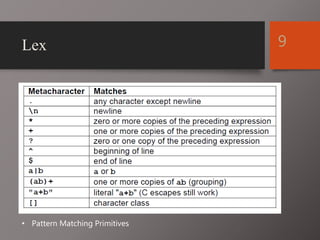
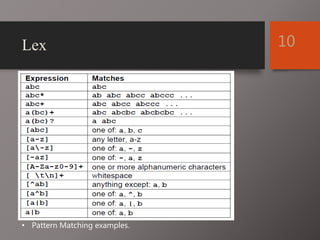
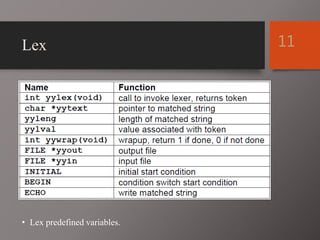
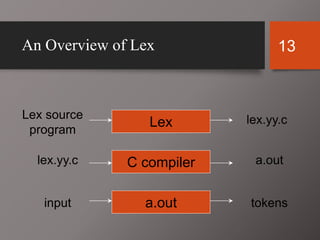
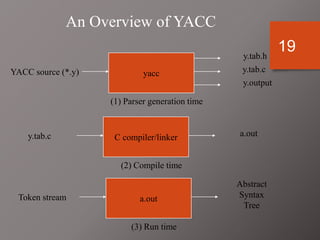
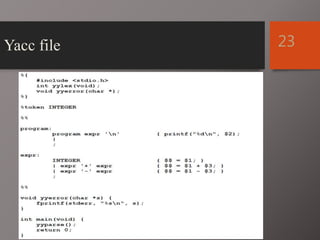
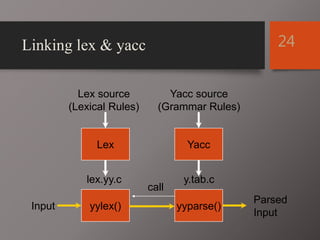
The document discusses Lex and Yacc, which are programs that generate lexical analyzers and parsers. Lex uses regular expressions to generate a scanner that tokenizes input into tokens, while Yacc uses context-free grammars to generate a parser that analyzes tokens based on syntax rules. The document provides examples of how Lex and Yacc can be used together, with Lex generating tokens from input that are then passed to a Yacc-generated parser to build a syntax tree based on the grammar.



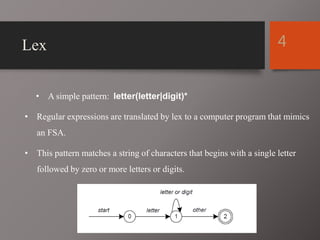


![7Operators
“ [ ] ^ - ? . * + | ( ) $ / { } % < >
• If they are to be used as text characters, an escape
should be used
$ = “$”
= “”
• Every character but blank, tab (t), newline (n) and
the list above is always a text character](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lexyacc-copy-170713202901/85/Lex-yacc-7-320.jpg)