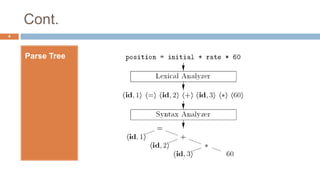
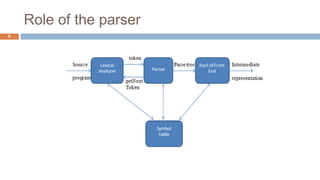
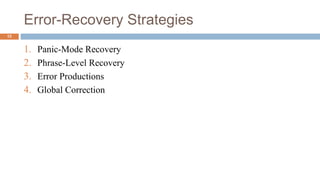
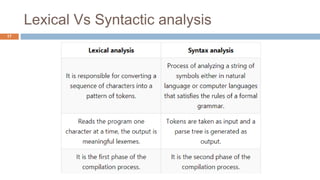
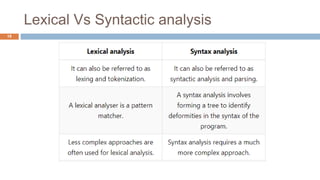
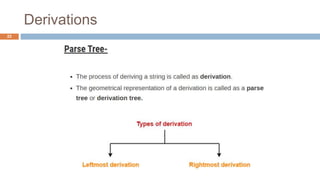
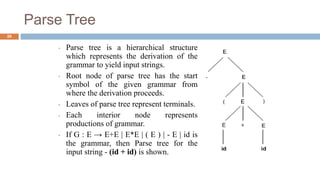
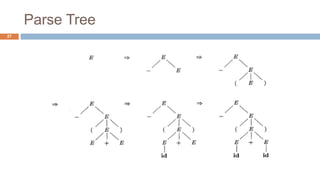
Syntax analysis is the second phase of compiler design after lexical analysis. The parser checks if the input string follows the rules and structure of the formal grammar. It builds a parse tree to represent the syntactic structure. If the input string can be derived from the parse tree using the grammar, it is syntactically correct. Otherwise, an error is reported. Parsers use various techniques like panic-mode, phrase-level, and global correction to handle syntax errors and attempt to continue parsing. Context-free grammars are commonly used with productions defining the syntax rules. Derivations show the step-by-step application of productions to generate the input string from the start symbol.